Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture▼ | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Yesterday
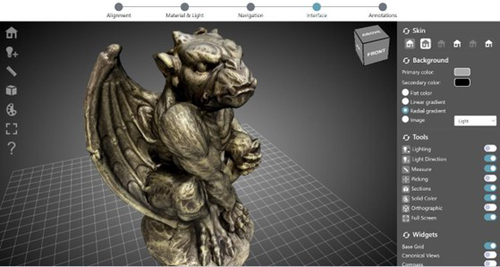
ARIADNEplus Visual Media Service 3D configurator: toward full guided publication of high-resolution 3D dataPotenziani, Marco; Ponchio, Federico; Callieri, Marco; Cignoni, Paolo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8075050ARIADNEplus Visual Media Service 3D configurator: a new tool for the visual organisation of 3D datasetsRecommended by Ian Moffat based on reviews by Sebastian Hageneuer, Vayia Panagiotidis, Erik Champion and Martina Trognitz based on reviews by Sebastian Hageneuer, Vayia Panagiotidis, Erik Champion and Martina Trognitz
The manuscript "ARIADNEplus Visual Media Service 3D configurator: toward full guided publication of high-resolution 3D data" by Potenziani et al. [1] provides an excellent introduction to the Visual Media Service 3D Configurator. This is an exciting tool, focused on cultural heritage, that forms part of the Visual Media Service, a web-based platform for uploading a range of complex data sets, including high-resolution images, Reflectance Transformation Imaging images and 3D models and transforming them into an appropriate format for interation and visualisation on the web. The 3D Configurator Tool provides researchers with a wizard which assist with the presentation of 3D models. This manuscript provides a history and context for the development of the Visual Media Service and previous related tools such as 3DHOP, Nexus and Relight/OpenLIME. It also provides detailed information about the functionality of the 3D Configurator, including the Alignment, Material & Light, Navigation, Interface and Annotation steps. The Discussion section provides information about applications and users of the Visual Media Service, current limitations and planned future developments. Reviewers Hageneuer, Champion, Trognitz and Panagiotidis all provided important suggestions to the authors which have improved the clarity and scope of this manuscript. While this manscript does not present a case study using this tool, I recommend it to readers as a detailed and clear introduction to the Visual Media Service 3D configurator which may inspire them to use this for their own research. [1] Potenziani, M., Ponchio, F., Callieri, M., and Cignoni, P. (2024). ARIADNEplus Visual Media Service 3D configurator: toward full guided publication of high-resolution 3D data. Zenodo, 8075050, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10894515 | ARIADNEplus Visual Media Service 3D configurator: toward full guided publication of high-resolution 3D data | Potenziani, Marco; Ponchio, Federico; Callieri, Marco; Cignoni, Paolo | <p>The use of digital visual media in everyday work is nowadays a common practice in many different domains, including Cultural Heritage (CH). Because of that, the presence of digital datasets in CH archives and repositories is becoming more and m... |  | Computational archaeology | Ian Moffat | 2023-06-23 17:37:47 | View | |
11 Dec 2023
A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in EuropeFelix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus, Damian Stefański, Hans Vandendriessche, Shumon T. Hussain https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587Questioning Final Palaeolithic and early Mesolithic cultural taxonomy with a data-driven statistical approachRecommended by Anaïs Vignoles based on reviews by Dirk Leder and 2 anonymous reviewersCultural taxonomies are an essential tool for archaeologists working with prehistoric material cultures as they have historically been used to create the basic analytical units for studying cultural evolution through time (de Mortillet, 1883 ; Breuil, 1913). This approach has its limits as the taxonomic units are essentially etic constructions, i.e., they are defined in a cultural context exterior to the one that produced the material culture on which they are based (e.g., Pesesse, 2019). But to approach questions related to cultural evolution, one has to define archaeological units with clear geographic and chronological delineations in order to be compared synchronically and diachronically (e.g., Willey and Philips, 1958). In « A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolitic/Earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe », F. Riede and colleagues propose a novel and interesting approach to question the end of the Palaeolithic and beginning of the Mesolithic’s « named archaeological cultures » (NACs) analytical pertinence (Riede et al., 2023). In this particular context, NACs are indeed very numerous (n = 86) and result from complex and regional research histories. It seems thus pertinent to question the extent to which the said NACs chronological and geographic patterns result from past cultural diversity and evolution, and are not artefacts of research. To do so, the authors adopted a data-driven approach that they describe in detail in the paper. First, they gathered an European data base of lithic tool-kit composition, blade and bladelet technology and armature morphology at 350 key sites considered representative of NACs, dated between 15 and 11 ka (Hussain et al., 2023). These data were then analyzed using geometric morphometrics and a set of statisticaal tests in order to 1) test the coherence of these taxonomic units, and 2) test the chronological change in artefact shape variation. The authors conclude that the data set is partially biased by reasearch practices and histories, as their data-driven approach has only partially replicated traditional NACs for the european Late Palaeolithic/Early Mesolithic. However, their analysis of armature shape evolution has shown a tendency to diversification overtime, a pattern that was already observed in more « traditional » approaches. This study is, in my opinion, an excellent contribution for a significant step in macro-regional approaches to the archaeological record: defining discrete archaeological units that serve as a basis for subsequent analyses aimed at delineating cultural evolutionary processes. The authors propose a carefully designed and statistically grounded procedure in order to achieve these definitions in the most replicable and explicit possible manner. Taking advantage of drawings as a primary source of information is also very original despite several limitations of this approach (such as the necessary selection of most typical artefacts to be represented, the incompleteness of data publication or the difficulty to access all published work across such a large geographic area). The results of the study are convincing enough to allow the authors to discuss the pertinence of European Late Paleo/Early Mesolithic NACs, the potential epistemological and historical factors that could affect this taxonomic framework, as well as to give more weight to the traditional hypothesis of lithic cultural diversification towards the end of the Pleistocene/beginning of the Holocene in Europe. I would also like to underline the authors’ important efforts to ensure transparence and replicability of their study, as well as the accessibility of the data, thanks to extensive supplementary data and a data paper describing their data set in detail. Anaïs L. Vignoles References Breuil, H. (1913). Les subdivisions du paléolithique supérieur et leur signification. In Congrès international d’anthropologie et d’archéologie préhistoriques - compte-rendu de la XIVème session, tome 1:165‑238. Genève: Imprimerie Albert Kündig. Hussain, S. T., Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D. and Vandendriessche, H. (2023). A Pan-European Dataset Revealing Variability in Lithic Technology, Toolkits, and Artefact Shapes ~15-11 Kya. Scientific Data 10 (1): 593. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02500-9. Mortillet, G. (1883). Le Préhistorique, antiquité de l’homme. Reinwald. Paris. Pesesse, D. (2019). Analyser un silex, le façonner à nouveau ? Sur certains usages de la chaîne opératoire au Paléolithique supérieur. Techniques & culture, no 71: 74‑77. https://doi.org/10.4000/tc.11321. Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D., Vandendriessche, H. and Hussain, S. T. (2023). A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe, Zenodo, 8195587., ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587 Willey, G. R. and Phillips, P. (1958). Method and Theory in American Archaeology. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press. | A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe | Felix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus,... | <p>Archaeological systematics, together with spatial and chronological information, are commonly used to infer cultural evolutionary dynamics in the past. For the study of the Palaeolithic, and particularly the European Final Palaeolithic and earl... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Lithic technology, Mesolithic, Upper Palaeolithic | Anaïs Vignoles | 2023-07-29 16:06:17 | View | |
17 Dec 2020

Experimentation preceding innovation in a MIS5 Pre-Still Bay layer from Diepkloof Rock Shelter (South Africa): emerging technologies and symbolsGuillaume Porraz, John E. Parkington, Patrick Schmidt, Gérald Bereiziat, Jean-Philip Brugal, Laure Dayet, Marina Igreja, Christopher E. Miller, Viola C. Schmid, Chantal Tribolo, Aurore Val, Christine Verna, Pierre-Jean Texier https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/ch53rExperimentation as a driving force for innovation in the Pre-Still Bay from Southern AfricaRecommended by Anne Delagnes based on reviews by Francesco d'Errico, Enza Elena Spinapolice and Kathryn RanhornThe article submitted by Guillaume Porraz et al. [1] shed light on the evolutionary changes recorded during the Pre-Still Bay Lynn stratigraphic unit (SU) from Diepkloof (Southern Africa). It promotes a multi-proxy and integrative approach based on a set of innovative behaviors, such as the engraving of geometric forms, silcrete heat- treatment, the use of adhesive, bladelet and bifacial tools production. This approach is not so common in Middle Stone Age (MSA) studies and makes a lot of sense for discussing the mechanisms that have fostered later innovations during the Still Bay and Howiesons Poort periods. The various innovations that emerge synchronously in this layer contrast with earlier innovations which appear as isolated phenomena in the MSA archaeological record. The strong inventiveness documented in Lynn SU is reported to a phase of experimentation for testing new ideas, new behaviors that would have played a crucial role for the emergence of the Still Bay in a context of socio-economic transformation. The data presented in this article broadens the scope of two previous articles [2-3] based on a more representative record, collected on an area of 3,5 m² opposed to 2 m² previously, and on the first presentation and description of an engraved bone with a rhomboid pattern. Macro- and microscopic analyses together with the analysis of the distribution of the engraved lines argue convincingly for an intentional engraving. This article constitutes a key contribution to the question of HOW emerged modern cultures in Southern Africa, while calling for further research related to sites’ function, environment and local resources to address the ever-debated question of WHY the MSA groups from Southern Africa developed such unprecedented inventiveness. It makes no doubt that this article deserves recommendation by PCI Archaeology. [1] Porraz, G., Schmidt, P., Bereiziat, G., Brugal, J.Ph., Dayet, L., Igreja, M., Miller, C.E., Viola, C., Tribolo, C., Val, A., Verna, C., Texier, P.J. 2020. Experimentation preceding innovation in a MIS5 Pre-Still Bay layer from Diepkloof Rock Shelter (South Africa): emerging technologies and symbols. 10.32942/osf.io/ch53r [2] Porraz, G., Texier, P.J., Archer, W., Piboule, M., Rigaud, J.P, Tribolo, C. 2013. Technological successions in the Middle Stone Age sequence of Diepkloof Rock Shelter, Western Cape, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science 40, 3376–3400. 10.1016/j.jas.2013.02.012 [3] Porraz, G., Texier, J.P. Miller, C.E., 2014. Le complexe bifacial Still Bay et ses modalités d’émergence à l’abri Diepkloof (Middle Stone Age, Afrique du Sud). In: XXVIIème Congrès Préhistorique de France, Transitions, Ruptures et Continuité en Préhistoire. Mémoires de la Société Préhistorique Française, 155–175. | Experimentation preceding innovation in a MIS5 Pre-Still Bay layer from Diepkloof Rock Shelter (South Africa): emerging technologies and symbols | Guillaume Porraz, John E. Parkington, Patrick Schmidt, Gérald Bereiziat, Jean-Philip Brugal, Laure Dayet, Marina Igreja, Christopher E. Miller, Viola C. Schmid, Chantal Tribolo, Aurore Val, Christine Verna, Pierre-Jean Texier | <p>In South Africa, key technologies and symbolic behaviors develop as early as the later Middle Stone Age in MIS5. These innovations arise independently in various places, contexts and forms, until their full expression during the Still Bay and t... |  | Africa, Lithic technology, Middle Palaeolithic, Symbolic behaviours | Anne Delagnes | 2020-08-04 09:13:27 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information SystemsEric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732Exploring The Role of Archaeological Information Systems in Improving Data Management and InteroperabilityRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In response to the feedback provided by the reviewers, the authors have undertaken a comprehensive revision of the manuscript [1]. These revisions have specifically targeted the primary concerns raised regarding the clarity and structure of the argument concerning the transformative impact of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) on archaeological practices. In my view the revised manuscript now more clearly articulates the distinction between internal and external interoperability and emphasizes the critical importance of integrating contextual information with archaeological data. This approach directly addresses the previously identified need for enhanced traceability and usability of archaeological data, ensuring that the manuscript's contributions to the field are both clear and impactful. Moreover, the application of the proposed model at the Bibracte site is illustrated with greater clarity, serving as a concrete example of how the challenges associated with documentation and data management can be effectively addressed through the methodologies proposed in the paper. This practical demonstration enriches the manuscript, providing readers with a much clearer understanding of the model's applicability and benefits in real-world archaeological practice. The authors have also made significant efforts to refine the overall structure and coherence of the manuscript. By making complex concepts more accessible and ensuring a cohesive narrative flow throughout, the manuscript now offers a more engaging and comprehensible read. This has been achieved through careful rephrasing and restructuring of sections, particularly those relating to the T!O model's application and the conclusion, thereby enhancing reader engagement and comprehension. Alongside these structural and conceptual clarifications, explicit discussion of potential areas for future research, not only acknowledges the limitations of the current study but also highlights the significant potential for digital technologies to contribute to archaeological methodology and knowledge production. As such, the manuscript opens up new avenues for exploration and invites further scholarly engagement with the topics it addresses. I believe, these revisions address the earlier feedback quite comprehensively, presenting a robust and compelling argument for the adoption of collaborative and technologically informed approaches in the field of archaeology. The manuscript now stands as a strong example of the critical role AIS could/should play in transforming archaeological practices, offering valuable insights into how these kinds of systems might enhance the management, accessibility, and understanding of archaeological data. Through this revised submission, the authors have significantly strengthened their contribution to the ongoing discourse on digital archaeology, demonstrating the practical and theoretical implications of their work for the broader archaeological community. I am happy, therefore to recommend this paper for acceptence. Reference [1] Lacombe, E., Lukas, D. and Durost, S. (2024). The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems. Zenodo, 8309732, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732
| The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems | Eric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost | <p>The adoption of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) evolves according to multiple factors, both human and technical, as well as endogenous and exogenous. In consequence the ever increasing scope of digital tools, which allow for the organi... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Protohistory, Theoretical archaeology | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 18:58:26 | View | |
23 Nov 2023
Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publicationSophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497Sharing Research Code in ArchaeologyRecommended by James Allison based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper “Percolation Package – From Script Sharing to Package Publication” by Sophie C. Schmidt and Simon Maddison (2023) describes the development of an R package designed to apply Percolation Analysis to archaeological spatial data. In an earlier publication, Maddison and Schmidt (2020) describe Percolation Analysis and provide case studies that demonstrate its usefulness at different spatial scales. In the current paper, the authors use their experience collaborating to develop the R package as part of a broader argument for the importance of code sharing to the research process. The paper begins by describing the development process of the R package, beginning with borrowing code from a geographer, refining it to fit archaeological case studies, and then collaborating to further refine and systematize the code into an R package that is more easily reusable by other researchers. As the review by Joe Roe noted, a strength of the paper is “presenting the development process as it actually happens rather than in an idealized form.” The authors also include a section about the lessons learned from their experience. Moving on from the anecdotal data of their own experience, the authors also explore code sharing practices in archaeology by briefly examining two datasets. One dataset comes from “open-archaeo” (https://open-archaeo.info/), an on-line list of open-source archaeological software maintained by Zack Batist. The other dataset includes articles published between 2018 and 2023 in the Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology. Schmidt and Maddison find that these two datasets provide contrasting views of code sharing in archaeology: many of the resources in the open-archaeo list are housed on Github, lack persistent object identifiers, and many are not easily findable (other than through the open-archaeo list). Research software attached to the published articles, on the other hand, is more easily findable either as a supplement to the published article, or in a repository with a DOI. The examination of code sharing in archaeology through these two datasets is preliminary and incomplete, but it does show that further research into archaeologists’ code-writing and code-sharing practices could be useful. Archaeologists often create software tools to facilitate their research, but how often? How often is research software shared with published articles? How much attention is given to documentation or making the software usable for other researchers? What are best (or good) practices for sharing code to make it findable and usable? Schmidt and Maddison’s paper provides partial answers to these questions, but a more thorough study of code sharing in archaeology would be useful. Differences among journals in how often they publish articles with shared code, or the effects of age, gender, nationality, or context of employment on attitudes toward code sharing seem like obvious factors for a future study to consider. Shared code that is easy to find and easy to use benefits the researchers who adopt code written by others, but code authors also have much to gain by sharing. Properly shared code becomes a citable research product, and the act of code sharing can lead to productive research collaborations, as Schmidt and Maddison describe from their own experience. The strength of this paper is the attention it brings to current code-sharing practices in archaeology. I hope the paper will also help improve code sharing in archaeology by inspiring more archaeologists to share their research code so other researchers can find and use (and cite) it. References Maddison, M.S. and Schmidt, S.C. (2020). Percolation Analysis – Archaeological Applications at Widely Different Spatial Scales. Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology, 3(1), p.269–287. https://doi.org/10.5334/jcaa.54 Schmidt, S. C., and Maddison, M. S. (2023). Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication, Zenodo, 7966497, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497 | Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication | Sophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison | <p>In this paper we trace the development of an R-package starting with the adaptation of code from a different field, via scripts shared between colleagues, to a published package that is being successfully used by researchers world-wide. Our aim... |  | Computational archaeology | James Allison | 2023-05-24 15:40:15 | View | |
20 Dec 2020

For our world without sound. The opportunistic debitage in the Italian context: a methodological evaluation of the lithic assemblages of Pirro Nord, Cà Belvedere di Montepoggiolo, Ciota Ciara cave and Riparo Tagliente.Marco Carpentieri, Marta Arzarello https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/2ptjbInvestigating the opportunistic debitage – an experimental approachRecommended by Alice Leplongeon based on reviews by David Hérisson and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper “For our world without sound. The opportunistic debitage in the Italian context: a methodological evaluation of the lithic assemblages of Pirro Nord, Cà Belvedere di Montepoggiolo, Ciota Ciara cave and Riparo Tagliente” [1] submitted by M. Carpentieri and M. Arzarello is a welcome addition to a growing number of studies focusing on flaking methods showing little to no core preparation, e.g., [2–4]. These flaking methods are often overlooked or seen as ‘simple’, which, in a Middle Palaeolithic context, sometimes leads to a dichotomy of Levallois vs. non-Levallois debitage (e.g., see discussion in [2]). The authors address this topic by first providing a definition for ‘opportunistic debitage’, derived from the definition of the ‘Alternating Surfaces Debitage System’ (SSDA, [5]). At the core of the definition is the adaptation to the characteristics (e.g., natural convexities and quality) of the raw material. This is one main challenge in studying this type of debitage in a consistent way, as the opportunistic debitage leads to a wide range of core and flake morphologies, which have sometimes been interpreted as resulting from different technical behaviours, but which the authors argue are part of a same ‘methodological substratum’ [1]. This article aims to further characterise the ‘opportunistic debitage’. The study relies on four archaeological assemblages from Italy, ranging from the Lower to the Upper Pleistocene, in which the opportunistic debitage has been recognised. Based on the characteristics associated with the occurrence of the opportunistic debitage in these assemblages, an experimental replication of the opportunistic debitage using the same raw materials found at these sites was conducted, with the aim to gain new insights into the method. Results show that experimental flakes and cores are comparable to the ones identified as resulting from the opportunistic debitage in the archaeological assemblage, and further highlight the high versatility of the opportunistic method. One outcome of the experimental replication is that a higher flake productivity is noted in the opportunistic centripetal debitage, along with the occurrence of 'predetermined-like' products (such as déjeté points). This brings the authors to formulate the hypothesis that the opportunistic debitage may have had a role in the process that will eventually lead to the development of Levallois and Discoid technologies. How this articulates with for example current discussions on the origins of Levallois technologies (e.g., [6–8]) is an interesting research avenue. This study also touches upon the question of how the implementation of one knapping method may be influenced by the broader technological knowledge of the knapper(s) (e.g., in a context where Levallois methods were common vs a context where they were not). It makes the case for a renewed attention in lithic studies for flaking methods usually considered as less behaviourally significant. [1] Carpentieri M, Arzarello M. 2020. For our world without sound. The opportunistic debitage in the Italian context: a methodological evaluation of the lithic assemblages of Pirro Nord, Cà Belvedere di Montepoggiolo, Ciota Ciara cave and Riparo Tagliente. OSF Preprints, doi:10.31219/osf.io/2ptjb [2] Bourguignon L, Delagnes A, Meignen L. 2005. Systèmes de production lithique, gestion des outillages et territoires au Paléolithique moyen : où se trouve la complexité ? Editions APDCA, Antibes, pp. 75–86. Available: https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs-00447352 [3] Arzarello M, De Weyer L, Peretto C. 2016. The first European peopling and the Italian case: Peculiarities and “opportunism.” Quaternary International, 393: 41–50. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2015.11.005 [4] Vaquero M, Romagnoli F. 2018. Searching for Lazy People: the Significance of Expedient Behavior in the Interpretation of Paleolithic Assemblages. J Archaeol Method Theory, 25: 334–367. doi:10.1007/s10816-017-9339-x [5] Forestier H. 1993. Le Clactonien : mise en application d’une nouvelle méthode de débitage s’inscrivant dans la variabilité des systèmes de production lithique du Paléolithique ancien. Paléo, 5: 53–82. doi:10.3406/pal.1993.1104 [6] Moncel M-H, Ashton N, Arzarello M, Fontana F, Lamotte A, Scott B, et al. 2020. Early Levallois core technology between Marine Isotope Stage 12 and 9 in Western Europe. Journal of Human Evolution, 139: 102735. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2019.102735 [7] White M, Ashton N, Scott B. 2010. The emergence, diversity and significance of the Mode 3 (prepared core) technologies. Elsevier. In: Ashton N, Lewis SG, Stringer CB, editors. The ancient human occupation of Britain. Elsevier. Amsterdam, pp. 53–66. [8] White M, Ashton N. 2003. Lower Palaeolithic Core Technology and the Origins of the Levallois Method in North‐Western Europe. Current Anthropology, 44: 598–609. doi:10.1086/377653 | For our world without sound. The opportunistic debitage in the Italian context: a methodological evaluation of the lithic assemblages of Pirro Nord, Cà Belvedere di Montepoggiolo, Ciota Ciara cave and Riparo Tagliente. | Marco Carpentieri, Marta Arzarello | <p>The opportunistic debitage, originally adapted from Forestier’s S.S.D.A. definition, is characterized by a strong adaptability to local raw material morphology and its physical characteristics and it is oriented towards flake production. Its mo... |  | Ancient Palaeolithic, Lithic technology, Middle Palaeolithic | Alice Leplongeon | 2020-07-23 14:26:04 | View | |
26 Apr 2022
Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a reviewAllowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/skeu5Archaeophenomics: an up-and-coming field in bioarchaeologyRecommended by Anneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewerAnneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewer Phenomics is the analysis of high-dimensional phenotypic data [1]. Phenomics research strategies are capable of linking genetic variation to phenotypic variation [2], but a genetic component is not absolutely necessary. The paper “Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics: a review” by Evin and colleagues [3] examines the use of geometric morphometrics in bioarchaeology and coins the term archaeophenomics. Archaeophenomics can be described as the large-scale phenotyping of ancient remains, and both addresses taxonomic identification, as well as infers spatio-temporal agrobiodiversity dynamics. It is a relatively new field in bioarchaeology with the first paper using this approach stemming from 2004. This study by Evin et al. [3] presents an excellent review and unquestionably demonstrates the potential of archaeophenomics. The authors provide an exhaustive review specifically of bioarchaeological studies in international journals using geometric morphometrics to study archaeological remains of domestic species. Although geometric morphometrics lends itself well for archaeophenomics, readers should keep in mind that this is not the only method and other approaches might equally fall under archaeophenomics as long as high-dimensional phenotypic archaeological data are involved. Distinguishing archaeophenomics from phenomics is important because of a critical difference. Archaeological remains are often altered by taphonomical processes. As such data may not be as complete as when working with modern specimens. Although this poses difficulties, morphometric analyses can usually still be performed as long as the structures presenting the relevant geometrical features are present. Even fragmented remains can be studied with a restricted version of the original landmarking/measurement protocol. Evin et al. [3] define archaeophenomics as “phenomics of the past”. This is only partly correct. It can be deduced from their review that they really mean phenomics of our (human) past. This leaves a gap for phenomics of the non-human past, for which I suggest the term palaeophenomics. [1] Jin, L. (2021). Welcome to the Phenomics Journal. Phenomics, 1, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-020-00009-4.
| Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a review | Allowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral | <p>Geometric morphometrics revolutionized domestication studies through the precise quantification of the phenotype of ancient plant and animal remains. Geometric morphometrics allow for an increasingly detailed understanding of the past agrobiodi... |  | Archaeobotany, Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Zooarchaeology | Anneke H. van Heteren | 2022-02-17 09:50:39 | View | |
26 Mar 2024
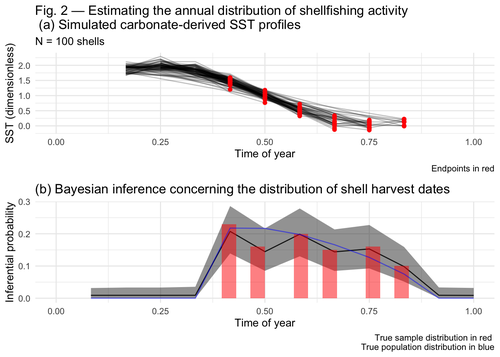
Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approachJordan Brown and Gabriel Lewis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7949547Mixture models and seasonal mobilityRecommended by Alfredo Cortell-Nicolau and Simon Carrignon based on reviews by Iza Romanowska and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper by Brown & Lewis [1] presents an approach to measure seasonal mobility and subsistence practices. In order to do so, the paper proposes a Bayesian mixture model to estimate the annual distribution of shellfish harvesting activity. Following the recommendations of the two reviewers, the paper presents a clear and innovative method to assess seasonal mobility for prehistoric groups, although it could benefit from additional references regarding isotopic literature. While the adequacy of isotope analysis for estimating mobility patterns in Archaeology has been extensively proven by now, work on specific seasonal mobility is not that much abundant. However, this is a key issue, since seasonal mobility is one of the main social components defining the differences between groups both considering farming vs hunting and gathering or even among hunter-gatherer groups themselves. In this regard, the paper brings a valuable methodological resources that can be used for further research in this issue. One of its greatest values is the fact that it can quantify the uncertainty present in previous isotope studies in seasonal mobility. As stated by the authors, the model can still undergo several optimisation aspects, but as it stands, it is already providing a valuable asset regarding the quantification of uncertainy in the isotopic studies of seasonal mobility. Reference [1] Brown, J. and Lewis, G. (2024). Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approach. Zenodo, 7949547, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7949547 | Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approach | Jordan Brown and Gabriel Lewis | <p>The problem of accurately and reliably estimating the annual distribution of seasonally-varying human settlement and subsistence practices is a classic concern among archaeologists, which has only become more relevant with the increasing import... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Environmental archaeology, North America, Palaeontology, Paleoenvironment, Zooarchaeology | Alfredo Cortell-Nicolau | Iza Romanowska, Eduardo Herrera Malatesta, Alejandro Sierra Sainz-Aja, Sam Leggett, Christianne Fernee, Anonymous, Asier García-Escárzaga , Paul Szpak , Maria Elena Castiello , Jasmine Lundy , Tansy Branscombe | 2023-10-03 04:45:54 | View |
21 Nov 2022

Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in ArchaeologyEmma Karoune and Esther Plomp https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029Three levels of reproducible workflow remove barriers for archaeologists and increase accessibilityRecommended by Ben Marwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick
Over the last decade, a small but growing community of archaeologists, from a diversity of intellectual and demographic backgrounds, have been striving for computational reproducibility in their published research. In their survey of the accomplishments of this thriving community, Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp (2022) analyzed the wide variety of approaches researchers have taken to enhance the reproducibility of their research. A key contribution of this paper is their excellent synthesis of diverse approaches into three levels of increasing complexity. This is helpful because it provides multiple entry points for researchers new to the challenge of fortifying their research. Many researchers assume that computational reproducibility is only achievable if they have a high degree of technical skill with computers, or is only necessary if their work is very computationally intensive. Karoune and Plomp give three compelling reasons why reproducibility is important for all archaeological research, and through their three levels they demonstrate that how these levels can be accomplished with basic, non-specialized computer skills and widely used free software. They showcase exemplary work from a variety of archaeologists to show how practical and achievable reproducible research is for all archaeologists. They advocate for archaeologists to use the most widely used and supported tools and services to support their reproducible research, such as the R and Python programming languages for data analysis, and Git and GitHub for collaboration. This paper, with its extensive appendix including thoughtful responses to frequently asked questions about reproducible research in archaeology, is likely to have a wide reach and influence, beyond previous works on this topic that have largely focused on technical details. Karoune and Plomp have provided the on-ramp for a generation of archaeologists who will find their questions about reproducible research answered here. They will also find an agreeable entry point to reproducible research in one of the three levels described by the authors. Will every archaeologist embrace this way of working? Should they? The work of Leonelli (2018) can help us anticipate the answers to these questions. Leonelli asks where are the limits to reproducibility, and how do the characteristics of different ways of knowing affect the desirability of reproducibility? Leonelli's work invites us to consider that there will be archaeologists coming from different epistemic cultures for whom the motivations presented by Karoune and Plomp will not resonate. For example, archaeologists engaged in mostly hermeneutical social science and humanities research, who do little or no quantitative analysis and statistics, are unlikely to see reproducibility as meaningful or desirable for their work. We can describe these researchers as working in interpretative or constructivist epistemic cultures. In these cultures, the particulars of how an individual researcher engages with their subject are exclusive and unique, and they would argue it cannot be fully captured or shared in an meaningful way (Elman and Kapiszewski 2017). Here, knowledge is situational, emerging from a specific, once-off combination of people and circumstances. One example in archaeology is the chaîne opératoire approach of stone artefact analysis, which Monnier and Missal (2014:61) describe as "based upon the analyst's experience and intuition, and it is not replicable, nor quantifiable". To make sense of this example we can draw on Galison's (1997) concept of 'image traditions' and 'logic traditions'. An image tradition is a way of knowing that is qualitative, based on composing narratives from drawings and photographs. A logic tradition is based on the use of instruments and statistical methods to collect standardised quantitative data. Chaîne opératoire approaches fall into the image tradition, along with many other ways of working in archaeology that do not generate numbers or use them to support claims about the past. Archaeologists working in a logic tradition will find reproducible research to be more meaningful than those working in an image tradition. We should be mindful not to claim that one epistemic culture is superior to another because reproducibility is not meaningful or attainable for researchers in one culture. Such a claim would threaten the plurality that is essential for the reliability of scientific knowledge (Massimi 2022). Instead we should identify those communities in archaeology where reproducible research is both meaningful and attainable, but has not yet been widely embraced. That is the where the most beneficial effects can be expected. According to Leonelli's (2018) framework, we can recognise these communities by a few basic characteristics. For example: they are doing computationally intensive archaeology, such as using or writing software to collect, simulate, analyse or visualise data; they are doing experimental archaeology; or they are making knowledge claims that are supported by tables of numeric data and data visualisations. Archaeologists whose work shares one or more of these characteristics will find the guidance provided here by Karoune and Plomp to be highly instructive and relevant, and stand the most to benefit from it. But it is not only individual archaeological scientists that have potential to benefit from how Karoune and Plomp have lowered the barriers to reproducible research. An especially important implication of this paper is that by lowering the barriers to reproducible research, Karoune and Plomp help us all to lower barriers to participation in archaeology in general. Documenting our research transparently, and sharing our materials (such as data and code and so on) openly, can profoundly change how others can participate in archaeology. By doing this, we are enabling students and researchers elsewhere, for example in low and middle income locations, to use our materials in their teaching and learning. Other researchers and students can apply our methods to their data, and combine their data with ours to achieve syntheses beyond what a single project can do. Similarly, for archaeologists working with local, descendant or marginalized communities, the tools of reproducible research are vital for enabling community members to have full access to the archaeological process, and thus reproducibility may be considered a necessity for decolonising the discipline. Karoune and Plomp present the CARE principles (Carroll et al. 2020) to guide archaeologists in ensuring community control of data so that reproducibility can be ethically accomplished with community safety and well-being as a priority. This may have a profoundly positive impact on the demographics of archaeology, as it lowers the barriers of meaningful participation by people far beyond our immediate groups of collaborators. Making archaeology more accessible is of critical importance in stemming the negative social impacts of pseudoarchaeologists, who often claim that archaeologists actively suppress the truth of the archaeological record through secrecy, elitism, and exclusiveness. The harm in this is twofold. First, that pseudoarchaeology typically erases Indigenous heritage by claiming that their past achievements were due to an ancient, extinct advanced civilization, not Indigenous people. These claims are often adopted by white supremacists to support racist and antisemitic conspiracy theories (Turner and Turner 2021), which sometimes leads to prejudice, physical violence, radicalization and extremism. A second type of harm that can come from claims of secrecy and elitism is it drains public trust in experts, leading to science denial. Not only trust in archaeologists, but trust in many kinds of experts, including those working on urgent contemporary issues such as public health and climate change. Karoune and Plomp's work is important here because it provides a practical and affordable pathway for archaeologists to fight claims of secrecy and elitism by sharing their work in ways that make it possible for non-academics to inspect the analyses and logic in detail. Claims of secrecy and elitism can be easily countered by openness, transparently and reproducibility by archaeologists. This is not only useful for tackling pseudoarchaeologists, but also in enacting an ethic of care, framing members of the public as people that not only care about archaeology as part of humanity's shared heritage, but also care for the construction of reliable interpretations of the archaeological record to provide secure and authentic foundations for their social identities and relationships (Wylie et al 2018; de la Bellacasa 2011). By striving for reproducible research in the way described by Karoune and Plomp, we are practicing a kind of reciprocal care among ourselves as archaeologists, and between archaeologists and members of the public as two communities who care about the human past.
References Karoune, E., and Plomp, E. (2022). Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology. Zenodo, 7320029, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029 de la Bellacasa, M. P. (2011). Matters of care in technoscience: Assembling neglected things. Social Studies of Science, 41(1), 85–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312710380301 Carroll, S. R., Garba, I., Figueroa-Rodríguez, O. L., Holbrook, J., Lovett, R., Materechera, S., Parsons, M., Raseroka, K., Rodriguez-Lonebear, D., Rowe, R., Sara, R., Walker, J. D., Anderson, J., and Hudson, M. (2020). The CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance. Data Science Journal, 19(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.5334/dsj-2020-043 Elman, C., and Kapiszewski, D. (2017). Benefits and Challenges of Making Qualitative Research More Transparent. Inside Higher Ed 2017, http://web.archive.org/web/20220407064134/https://www.insidehighered.com/blogs/rethinking-research/benefits-and-challenges-making-qualitative-research-more-transparent (accessed 21 Oct, 2022). Galison, P. (1997). Image and logic: a material culture of microphysics. Chicago (IL): University of Chicago Press. Leonelli, S. (2018). Re-Thinking Reproducibility as a Criterion for Research Quality [preprint]. Available online: http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/id/eprint/14352 (Accessed 21 Oct 2022). Massimi, M. (2022). Perspectival realism. Oxford University Press. Monnier, G. F., and Kele M.. "Another Mousterian debate? Bordian facies, chaîne opératoire technocomplexes, and patterns of lithic variability in the western European Middle and Upper Pleistocene." Quaternary International 350 (2014): 59-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.053 Turner, D. D., and Turner, M. I. (2021). “I’m Not Saying It Was Aliens”: An Archaeological and Philosophical Analysis of a Conspiracy Theory. In A. Killin and S. Allen-Hermanson (Eds.), Explorations in Archaeology and Philosophy (pp. 7–24). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61052-4_2 Wylie, C., Neeley, K., and Ferguson, S. (2018). Beyond Technological Literacy: Open Data as Active Democratic Engagement? Digital Culture & Society, 4(2), 157–182. https://doi.org/10.14361/dcs-2018-0209
| Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology | Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp | <p>Reproducible research is being implemented at different speeds in different disciplines, and Archaeology is at the start of this journey. Reproducibility is the practice of reanalysing data by taking the same steps and producing the same or sim... |  | Computational archaeology | Ben Marwick | 2022-06-07 10:02:46 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










