Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * ▲ | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
02 Apr 2024
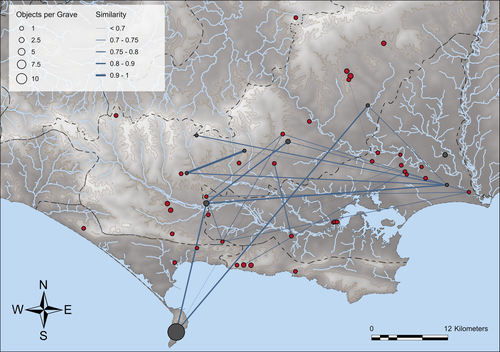
Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological DatasetsTimo Geitlinger https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239A different approach to similarity networks in Archaeology - Similarity Network FusionRecommended by Joel Santos based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewerThis is a fascinating paper for anyone interested in network analysis or the chronology and cultures of the case study, namely the Late prehistoric burial sites in Dorset, for which the author’s approach allowed a new perspective over an already deeply studied area [1]. This paper's implementation of Similarity Network Fusion (SNF) is noteworthy. This method is typically utilized within genetic research but has yet to be employed in Archaeology. SNF has the potential to benefit Archaeology due to its unique capabilities and approach significantly. The author exhibits a deep and thorough understanding of previous investigations concerning material and similarity networks while emphasizing the innovative nature of this particular study. The SNF approach intends to improve a lack of the most used (in Archaeology) similarity coefficient, the Brainerd-Robinson, in certain situations, mainly in heterogenous and noisy datasets containing a small number of samples but a large number of measurements, scale differences, and collection biases, among other things. The SNF technique, demonstrated in the case study, effectively incorporates various similarity networks derived from different datatypes into one network. As shown during the Dorset case study, the SNF application has a great application in archaeology, even in already available data, allowing us to go further and bring new visions to the existing interpretations. As stated by the author, SNF shows its potential for other applications and fields in archaeology coping with similar datasets, such as archaeobotany or archaeozoology, and seems to complement different multivariate statistical approaches, such as correspondence or cluster analysis. This paper has been subject to two excellent revisions, which the author mostly accepted. One of the revisions was more technical, improving the article in the metadata part, data availability and clarification, etc. Although the second revision was more conceptual and gave some excellent technical inputs, it focused more on complementary aspects that will allow the paper to reach a wider audience. I vividly recommend its publication. References [1] Geitlinger, T. (2024). Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets. Zenodo, 7998239, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239
| Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets | Timo Geitlinger | <p>Since its earliest application in the 1970s, network analysis has become increasingly popular in both theoretical and GIS-based archaeology. Yet, applications of material networks remained relatively restricted. This paper describes a specific ... |  | Computational archaeology, Protohistory | Joel Santos | 2023-06-02 16:51:19 | View | |
29 Aug 2023
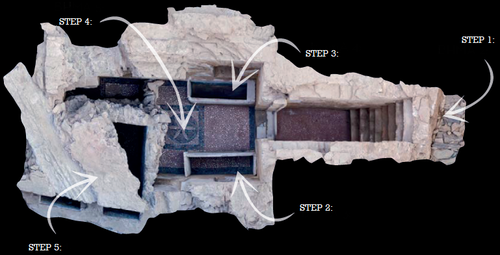
Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious GamesTsaknaki, Electra; Anastasovitis, Eleftherios; Georgiou, Georgia; Alagialoglou, Kleopatra; Mavrokostidou, Maria; Kartsiakli, Vasiliki; Aidonis, Asterios; Protopsalti, Tania; Nikolopoulos, Spiros; Kompatsiaris, Ioannis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981323AR and VR Gamification as a proof-of-conceptRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Sophie C. Schmidt and Tine Rassalle based on reviews by Sophie C. Schmidt and Tine Rassalle
Tsaknaki et al. (2023) discuss a work-in-progress project in which the presentation of Cultural Heritage is communicated using Serious Games techniques in a story-centric immersive narration instead of an exhibit-centered presentation with the use of Gamification, Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies. In the introduction the authors present the project called ECHOES, in which knowledge about the past of Thessaloniki, Greece is planned to be processed as an immersive and interactive experience. After presenting related work and the methodology, the authors describe the proposed design of the Serious Game and close the article with a discussion and conclusions. The paper is interesting because it highlights an ongoing process in the realm of the visualization of Cultural Heritage (see for example Champion 2016). The process described by the authors on how to accomplish this by using Serious Games, Gamification, Augmented and Virtual Reality is promising, although still hypothetical as the project is ongoing. It remains to be seen if the proposed visuals and interactive elements will work in the way intended and offer users an immersive experience after all. A preliminary questionnaire already showed that most of the respondents were not familiar with these technologies (AR, VR) and in my experience these numbers only change slowly. One way to overcome the technological barrier however might be the gamification of the experience, which the authors are planning to implement. I decided to recommend this article based on the remarks of the two reviewers, which the authors implemented perfectly, as well as my own evaluation of the paper. Although still in progress it seems worthwhile to have this article as a basis for discussion and comparison to similar projects. However, the article did not mention the possible longevity of data and in which ways the usability of the Serious Game will be secured for long-term storage. One eminent problem in these endeavors is, that we can read about these projects, but never find them anywhere to test them ourselves (see for example Gabellone et al. 2016). It is my intention with this review and the recommendation, that the ECHOES project will find a solution for this problem and that we are not only able to read this (and forthcoming) article(s) about the ECHOES project, but also play the Serious Game they are proposing in the near and distant future. References
Gabellone, Francesco, Antonio Lanorte, Nicola Masini, und Rosa Lasaponara. 2016. „From Remote Sensing to a Serious Game: Digital Reconstruction of an Abandoned Medieval Village in Southern Italy“. Journal of Cultural Heritage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2016.01.012 Tsaknaki, Electra, Anastasovitis, Eleftherios, Georgiou, Georgia, Alagialoglou, Kleopatra, Mavrokostidou, Maria, Kartsiakli, Vasiliki, Aidonis, Asterios, Protopsalti, Tania, Nikolopoulos, Spiros, and Kompatsiaris, Ioannis. (2023). Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious Games, Zenodo, 7981323, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981323 | Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious Games | Tsaknaki, Electra; Anastasovitis, Eleftherios; Georgiou, Georgia; Alagialoglou, Kleopatra; Mavrokostidou, Maria; Kartsiakli, Vasiliki; Aidonis, Asterios; Protopsalti, Tania; Nikolopoulos, Spiros; Kompatsiaris, Ioannis | <p>The main challenge of the current digital transition is to utilize computing media and cutting-edge technologyin a more meaningful way, which would make the archaeological and anthropological research outcomes relevant to a heterogeneous audien... |  | Bioarchaeology, Computational archaeology, Europe | Sebastian Hageneuer | 2023-05-29 13:19:46 | View | |
08 Feb 2024
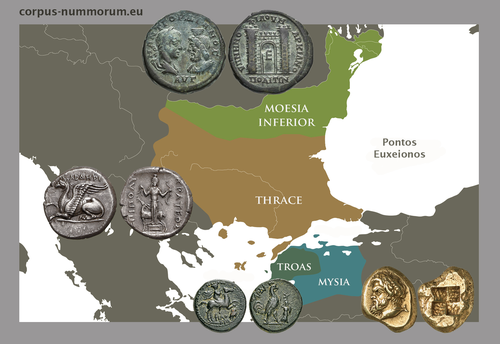
CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient CoinsUlrike Peter, Claus Franke, Jan Köster, Karsten Tolle, Sebastian Gampe, Vladimir F. Stolba https://zenodo.org/records/8263517The valuable Corpus Nummorum: a not so Little MinionRecommended by Ronald Visser based on reviews by Fleur Kemmers and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Fleur Kemmers and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper under review/recommendation deals with Corpus Nummorum (Peter et al. 2024). The Corpus Nummorum (CN) is web portal for ancient Greek coins from various collections (https://www.corpus-nummorum.eu/). The CN is a database and research tool for Greek coins dating between 600 BCE to 300 CE. While many traditional collection databases aim at collecting coins, CN also includes coin dies, coin types and issues. It aims at achieving a complete online coin type catalogue. The paper is not a paper in a traditional sense, but presents the CN as a tool and shows the functionalities in the system. The relevance and the possibilities of the CN for numismatists is made clear in the paper and the merits are clear even for me as a Roman archaeologist and non-numismatist. The CN was presented as a poster at the CAA 2023 in Amsterdam during “S03. Our Little Minions pt. V: small tools with major impact”, organized by Moritz Mennenga, Florian Thiery, Brigit Danthine and myself (Mennenga et al. 2023). Little Minions help us significantly in our daily work as small self-made scripts, home-grown small applications and small hardware devices. They often reduce our workload or optimize our workflows, but are generally under-represented during conferences and not often presented to the outside world. Therefore, the Little Minions form a platform that enables researchers and software engineers to share these tools (Thiery, Visser and Mennenga 2021). Little Minions have become a well known happening within the CAA-community since we started this in 2018, also because we do not only allow 10-minute lightning talks, but also spontaneous stand-up presentations during the conference. A full list of all minions presented in the past, can be found online: https://caa-minions.github.io/minions/. In a strict sense the CN would not count as a Little Minion, because it is a large project consisting of many minions that help a numismatist in his/her daily work. The CN seems a very Big Minion in that sense. Personally, I am very happy to see the database being developed as a fully open system and that code can be found on Github (https://github.com/telota/corpus-nummorum-editor), and also made citable with citation information in GitHub (see https://citation-file-format.github.io/) and a version deposited in Zenodo with DOI (Köster and Franke 2024). In addition, the authors claim that the CN will be shared based on the FAIR-principles (Wilkinson et al. 2016, 2019). These guidelines are developed to improve the Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reuse of digital data. I feel that CN will be a way forward in open numismatics and open archaeology. The CN is well known within the numismatist community and it was hard to find reviewers in this close community, because many potential reviewers work together with one or more of the authors, or are involved in the project. This also proves the relevance of the CN to the research community and beyond. Luckily, a Roman numismatist and a specialist in digital/computational archaeology were able to provide valuable feedback on the current paper. The reviewers only submitted feedback on the first version of the paper (Peter et al. 2023). The numismatist was positive on the content and the usefulness of CN for the discipline in general. However, she pointed out some important points that need to be addressed. The digital specialist was positive is various aspects, but also raised some important issues in relation to technical aspects and the explanation thereof. While both were positive on the project and the paper in general, both reviewers pointed out some issues that were largely addressed in the second version of this paper. The revised version was edited throughout and the paper was strongly improved. The Corpus Nummorum is well presented in this easy to read paper, although the explanations can sometimes be slightly technical. This paper gives a good introduction to the CN and I recommend this for publication. I sincerely hope that the CN will contribute and keep on contributing to the domains of numismatics, (digital) archaeology and open science in general. References Köster, J and Franke, C. 2024 Corpus Nummorum Editor. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10458195 Mennenga, M, Visser, RM, Thiery, F and Danthine, B. 2023 S03. Our Little Minions pt. V: small tools with major impact. In:. Book of Abstracts. CAA 2023: 50 Years of Synergy. Amsterdam: Zenodo. pp. 249–251. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.7930991 Peter, U, Franke, C, Köster, J, Tolle, K, Gampe, S and Stolba, VF. 2023 CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.8263518 Peter, U., Franke, C., Köster, J., Tolle, K., Gampe, S. and Stolba, V. F. (2024). CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins, Zenodo, 8263517, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8263517 Thiery, F, Visser, RM and Mennenga, M. 2021 Little Minions in Archaeology An open space for RSE software and small scripts in digital archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4575167 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Aalbersberg, IjJ, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, ’t Hoen, PAC, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Velterop, J, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2016 The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 3(1): 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Jan Aalbersberg, I, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, Hoen, PAC ’t, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Jan Velterop, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2019 Addendum: The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 6(1): 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0009-6 | CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins | Ulrike Peter, Claus Franke, Jan Köster, Karsten Tolle, Sebastian Gampe, Vladimir F. Stolba | <p>CORPUS NUMMORUM indexes ancient Greek coins from various landscapes and develops typologies. The coins and coin types are published on the multilingual website www.corpus-nummorum.eu utilizing numismatic authority data and adhering to FAIR prin... |  | Antiquity, Classic | Ronald Visser | 2023-08-18 17:37:51 | View | |
20 Feb 2024

Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of ArchaeologyWaagen, Jitte & Wijngaarden, Gert Jan van https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10061343Rewriting Archaeological Narratives: Archaeology of Archaeology through 3D Site Topography RecordingRecommended by Devi Taelman based on reviews by Geert Verhoeven, Jesús García-Sánchez and Catherine Scott based on reviews by Geert Verhoeven, Jesús García-Sánchez and Catherine Scott
Even though applications of 3D recording have existed in archaeology for a long time, it is only since the early 2000s that this field of research has become mainstream thanks to technological advances, and the availability of low-cost sensors and image-based modelling software. This has led to significant changes in the way archaeological sites are documented. This paper entitled "Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology" by Jitte Waagen & Gert Jan van Wijngaarden (2024) presents an overview of the current developments in the application possibilities of 3D site topography recording in archaeology. The paper is the result of the round table discussion "Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology" at the CAA conference on 5 April 2023 in Amsterdam, with contributions from Radu Brunchi, Nicola Lercari, Joep Orbons, Davide Tanasi, Alicia Walsh, Pawel Wolf and Teagan Zoldoske. The paper starts with a discussion of the Amsterdam Troy Project (ATP). In the frame of the ATP, the rich history of archaeological activity (over 150 years of fieldwork) at Troy is being studied to explore how previous archaeological research has helped to shape the current topography of the site and how these earlier research activities, embedded in their contemporary theoretical frameworks, have determined our understanding of the site (see Murray and M. Spriggs 2017, Carver 2011 for the influence of theory on archaeological fieldwork and archaeology as a discipline), the so-called 'Archaeology of Archaeology' approach. In addition to studying previous research records and re-excavating old excavation trenches, a central element of the project is the 3D recording of the past and present topography of the site in order to reconstruct the archaeological research activities at the site and their impact on the archaeological landscape. The paper focuses on current trends in 3D recording of archaeological site topography and discusses three main areas where 3D recording of archaeological site topography can contribute to the "Archaeology of Archaeology" approach: (1) monitoring the topography of sites for preservation, conservation, research and dissemination purposes; (2) reconstructing, reevaluating and reinterpreting past archaeological research efforts; and (3) archiving in a 4D (GIS) environment. This is done using the example of the Amsterdam Troy project and comparing it with other projects using similar methods and approaches. Using these case studies, the authors effectively discuss the impact of these technologies on the understanding of the topography of archaeological sites and how 3D recording can enhance archaeological research methodologies and interpretations, for example, by not using such 3D approaches as a stand-alone product but integrating them with available information from previous research activities. They also recognise the limitations and challenges involved, such as the need for customised data acquisition strategies and the lack of ready-made software solutions for developing comprehensive data management strategies. One topic that could have been covered in more detail is how 3D site topography recording (and 3D recording in general) is affected by current theoretical developments in archaeology. Like any other archaeological fieldwork or data collection approach, it is a child of its time. Decisions such as what to record, how to record, what to store, how to store, what to visualise, and how to visualise influence our understanding of archaeological sites (Ward 2022). This minor critical reflection aside, the paper makes a timely and significant contribution to archaeology by addressing current trends and the limitations of the increasingly widespread use of 3D site topography recording technologies. References Carver, G. (2011). Reflections on the archaeology of archaeological excavation, Archaeological Dialogues 18(1), pp. 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1380203811000067 Murray, T. and Spriggs, M. (2017). The historiography of archaeology: exploring theory, contingency and rationality, World Archaeology 49(2), pp. 151–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/00438243.2017.1334583 Ward, C. (2022). Excavating the Archive / Archiving the Excavation: Archival Processes and Contexts in Archaeology, Advances in Archaeological Practice 10(2), pp. 160–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/aap.2022.1 Waagen, J. and van Wijngaarden, G.J. (2024). Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology, Zenodo, 10061343, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommonded by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10061343 | Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology | Waagen, Jitte & Wijngaarden, Gert Jan van | <p>The current ubiquitous use of 3D recording technologies in archaeological fieldwork, for a large part due to the application of budget-friendly (drone) sensors and the availability of many low-cost image-based 3D modelling software packages, ha... |  | Computational archaeology, Remote sensing | Devi Taelman | 2023-10-17 23:03:47 | View | |
07 May 2024
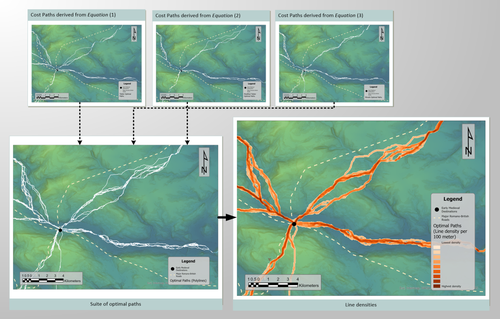
Mobility and the reuse of Roman Roads for the deposition of Viking Age silver hoards in North West EnglandWyatt Wilcox https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7999149Moving away from the ritual deposition: hoards from the Viking Age, Least Cost Paths and reused Roman RoadsRecommended by Ronald Visser based on reviews by Sam Leggett and Scott Madry based on reviews by Sam Leggett and Scott Madry
I had the pleasure of reading ‘Mobility and the reuse of Roman Roads for the deposition of Viking Age silver hoards in North West England’ by Wyatt O. Wilcox (Wilcox 2024a). It is an honour to recommend this paper. The aim of this study is to research the relationship of 18 Viking Age hoards and their transport and depositional locations. This is studied in relation to the Roman road network and the landscape using least cost path analyses. Single finds from the Portable Antiquities Scheme (https://finds.org.uk/) are also incorporated in the study. The study deals with the distance of these Viking Age finds to these roads/least-cost-paths and the final interpretation moves away from ritual interpretation of these finds to a more mundane explanation. I feel that this could potentially open discussion also for hoards from other periods. While both reviewers (Sam Leggett and Scott Madry) presented various suggestions to improve the first submitted version of the paper, the author has done a tremendous job to improve the paper based on the comments and even beyond these comments. The author has also deposited the Jypiter-notebook online (Wilcox 2024b), showing that he is contributing to Open Science. The first version of the dataset has been improved and updated based on the comments by the reviewers and me, improving the reproducibility of the analyses. All in all, this paper has improved and I am very glad that I can recommend this for publication, and I’d like to do so with a sentence from the review by Sam Leggett: “this study has a lot of potential to be deployed across other regions, and time periods for similar purposes (Iron Age hoards for instance). And it will be of great interest to Viking Age experts interested in hoards, but also early medieval transport and travel.” References Wilcox, W. 2024a Mobility and the reuse of Roman Roads for the deposition of Viking Age silver hoards in North West England. Zenodo, 7999149, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7999149 Wilcox, W. 2024b Mobility and the reuse of Roman Roads for the deposition of Viking Age silver hoards in North West England (Supplemental Material). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11067607 | Mobility and the reuse of Roman Roads for the deposition of Viking Age silver hoards in North West England | Wyatt Wilcox | <p>Discussions on Viking Age silver hoards in North West England have been dominated by analysis of the material compositions of the hoards. Despite a multi-century research legacy concerning the material composition of the Viking Age silver... |  | Europe, Landscape archaeology, Medieval, Spatial analysis | Ronald Visser | 2023-06-04 22:29:18 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
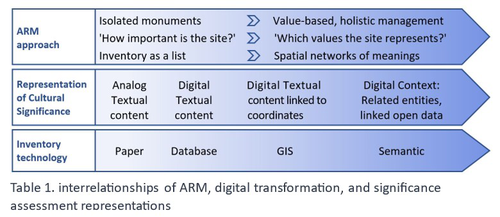
Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of MeaningsYael Alef, Yuval Shafriri https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309992How Semantic Technologies and Spatial Networks Can Enhance Archaeological Resource ManagementRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by Dominik Lukas and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Dominik Lukas and 1 anonymous reviewer
After a thorough review and consideration of the revised manuscript titled "Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text to Spatial Networks of Meanings" by Yael Alef and Yuval Shafriri [1], I am recommending the paper for publication. The authors have made significant strides in addressing the feedback from the initial review process, notably enhancing the manuscript's clarity, methodological detail, and overall contribution to the field of Archaeological Resource Management (ARM). On balance I think the paper competently navigates the shift from a traditional significance-focused assessment of isolated archaeological sites to a more holistic and interconnected approach, leveraging graph data models and spatial networks. This transition represents an advancement in the field, offering deeper insights into the sociocultural dynamics of archaeological sites. The case study of ancient synagogues in northern Israel, particularly the Huqoq Synagogue, serves as a compelling illustration of the potential of semantic technologies to enrich our understanding of cultural heritage. Significantly, the authors have responded to the call for a clearer methodological framework by providing a more detailed exposition of their use of knowledge graph visualization and semantic technologies. This response not only strengthens the paper's scientific rigor but also enhances its accessibility and applicability to a broader audience within the conservation and heritage management community. However, I do think it remains important to acknowledge areas where further work could enrich the paper's contribution. While the manuscript makes notable advancements in the technical and methodological domains, the exploration of the ethical and political implications of semantic technologies in ARM remains less developed. Recognizing the complex interplay of ethical and political considerations in archaeological assessments is crucial for the responsible advancement of the field. Thus, I suggest that future work could productively focus on these dimensions, offering a more comprehensive view of the implications of integrating semantic technologies into heritage management practices. I don't think that this omission is a reason to withold the paper for publication or seek further review. In fact I think it stands alone a paper quite well. Perhaps the authors might consider this as a complementary line of inquiry in their future work in the field. In conclusion then, I believe the revised manuscript represents a valuable addition to the literature, pushing boundaries of how we assess, understand, and manage archaeological resources. Its focus on semantic technologies and the creation of spatial networks of meanings marks a significant step forward in the field. I believe its publication will stimulate further research and discussion, particularly in the realms of ethical and political considerations, which remain ripe for exploration. Therefore, I'm happy to endorse the publication of this manuscript. Reference [1] Alef, Y and Shafriri, Y. (2024). Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of Meanings. Zenodo, 8309992, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309992 | Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of Meanings | Yael Alef, Yuval Shafriri | <p>This study examines the shift towards a values-based approach for Archaeological Resource Management (ARM), emphasizing the integration of Context-Based Significance Assessment (CBSA) with semantic technologies into digital ARM inventories. We ... |  | Computational archaeology, Conservation/Museum studies, Spatial analysis | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 22:24:15 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










