
GOUDE Gwenaëlle
- UMR 7269 LAMPEA, CNRS, Aix en Provence, France
- Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Europe, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Physical anthropology, Protohistory
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Reviews: 0
Recommendation: 1
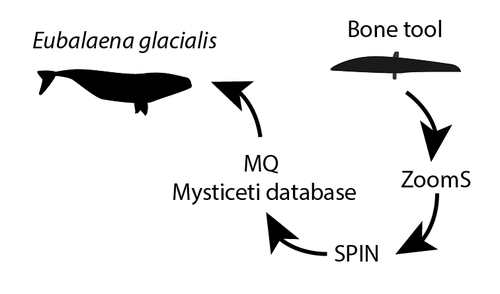
Palaeoproteomic identification of a whale bone tool from Bronze Age Heiloo, the Netherlands
Prehistoric whaling and tool industry evidenced by advanced proteomic methods
Recommended by Gwenaëlle Goude based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersProteomics is an increasingly applied field of study in archaeology. The characterisation of proteins in ancient biomaterials has been used extensively to determine the sex of certain animals (from dental enamel) or to identify species from non-diagnostic bone pieces or fragments of organic materials (glues and residues, for example). Paleoproteomics has been accompanied by methodological developments, in particular to reduce the size of samples affected by destructive analyses and to refine the level of species determination. The article by Joannes Dekker and colleagues (2024) - "Palaeoproteomic identification of a whale bone tool from Bronze Age Heiloo, the Netherlands" - provides a relevant and innovative example, incorporating ZooMS and SPIN techniques as well as the creation of a database of new reference collagens (cetaceans) specific to the site's natural environment (North Sea coast). The interest of this study also lies in the contribution of a use-wear analysis carried out prior to the sampling. This comparison of multidisciplinary data is essential for understanding the links between man and his natural environment and the technical and economic production that is closely linked to it. The tool studied (ca. 1500 BCE) comes from a coastal Bronze Age site in the Netherlands, where the economy was highly diversified, involving the exploitation of wild and domestic animals in both terrestrial and marine environments. The study shows that the bone of a North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) was shaped into a tool that was probably used to process plant fibres. This discovery supports other studies highlighting the intensive and non-opportunistic exploitation of whales in the North Sea since the Pleistocene.
Dekker, J. A. A., Mylopotamitaki, D., Verbaas, A., Sinet-Mathiot, V., Presslee, S., McCarthy, M. L., Olsen, M. T., Olsen, J. V., van den Hurk, Y., Brattinga, J. & Welker, F. (2024) Palaeoproteomic identification of a whale bone tool from Bronze Age Heiloo, the Netherlands. BioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.15.589626