
MCLEAN Andrew
- CDCS, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
- Antiquity, Classic, Computational archaeology, Mediterranean, Spatial analysis
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Reviews: 0
Recommendation: 1
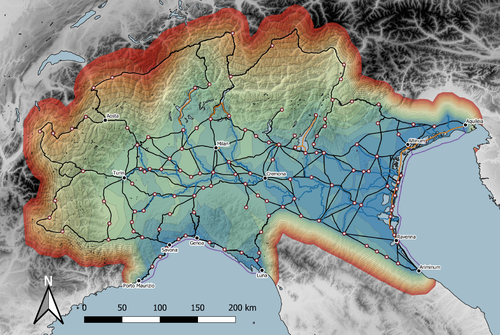
Rivers vs. Roads? A route network model of transport infrastructure in Northern Italy during the Roman period
Modelling Roman Transport Infrastructure in Northern Italy
Recommended by Andrew McLean based on reviews by Pau de Soto and Adam PažoutStudies of the economy of the Roman Empire have become increasingly interdisciplinary and nuanced in recent years, allowing the discipline to make great strides in data collection and importantly in the methods through which this increasing volume of data can be effectively and meaningfully analysed [see for example 1 and 2]. One of the key aspects of modelling the ancient economy is understanding movement and transport costs, and how these facilitated trade, communication and economic development. With archaeologists adopting more computational techniques and utilising GIS analysis beyond simply creating maps for simple visualisation, understanding and modelling the costs of traversing archaeological landscapes has become a much more fruitful avenue of research. Classical archaeologists are often slower to adopt these new computational techniques than others in the discipline. This is despite (or perhaps due to) the huge wealth of data available and the long period of time over which the Roman economy developed, thrived and evolved. This all means that the Roman Empire is a particularly useful proving ground for testing and perfecting new methodological developments, as well as being a particularly informative period of study for understanding ancient human behaviour more broadly. This paper by Page [3] then, is well placed and part of a much needed and growing trend of Roman archaeologists adopting these computational approaches in their research.
Page’s methodology builds upon De Soto’s earlier modelling of transport costs [4] and applies it in a new setting. This reflects an important practice which should be more widely adopted in archaeology. That of using existing, well documented methodologies in new contexts to offer wider comparisons. This allows existing methodologies to be perfected and tested more robustly without reinventing the wheel. Page does all this well, and not only builds upon De Soto’s work, but does so using a case study that is particularly interesting with convincing and significant results.
As Page highlights, Northern Italy is often thought of as relatively isolated in terms of economic exchange and transport, largely due to the distance from the sea and the barriers posed by the Alps and Apennines. However, in analysing this region, and not taking such presumptions for granted, Page quite convincingly shows that the waterways of the region played an important role in bringing down the cost of transport and allowed the region to be far more interconnected with the wider Roman world than previous studies have assumed.
This article is clearly a valuable and important contribution to our understanding of computational methods in archaeology as well as the economy and transport network of the Roman Empire. The article utilises innovative techniques to model transport in an area of the Roman Empire that is often overlooked, with the economic isolation of the area taken for granted. Having high quality research such as this specifically analysing the region using the most current methodologies is of great importance. Furthermore, developing and improving methodologies like this allow for different regions and case studies to be analysed and directly compared, in a way that more traditional analyses simply cannot do. As such, Page has demonstrated the importance of reanalysing traditional assumptions using the new data and analyses now available to archaeologists.
References
[1] Brughmans, T. and Wilson, A. (eds.) (2022). Simulating Roman Economies: Theories, Methods, and Computational Models. Oxford.
[2] Dodd, E.K. and Van Limbergen, D. (eds.) (2024). Methods in Ancient Wine Archaeology: Scientific Approaches in Roman Contexts. London ; New York.
[3] Page, J. (2024). Rivers vs. Roads? A route network model of transport infrastructure in Northern Italy during the Roman period, Zenodo, 7971399, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7971399
[4] De Soto P (2019). Network Analysis to Model and Analyse Roman Transport and Mobility. In: Finding the Limits of the Limes. Modelling Demography, Economy and Transport on the Edge of the Roman Empire. Ed. by Verhagen P, Joyce J, and Groenhuijzen M. Springer Open Access, pp. 271–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04576-0_13