Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▲ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 Jun 2020
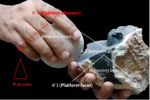
Platforms of Palaeolithic knappers reveal complex linguistic abilitiesCédric Gaucherel and Camille Noûs https://doi.org/10.31233/osf.io/wn5zaThe means of complexity in a lithic reduction sequenceRecommended by Marta Arzarello based on reviews by Antony Borel and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Antony Borel and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper entitled “Platforms of Palaeolithic knappers reveal complex linguistic abilities” [1] submitted by C. Gaucherel and C. Noûs represents an interesting reflection about the possibilities to detect the human cognitive abilities in relation to the lithic production. The definition and the study of human cognitive abilities during the Lower Palaeolithic it has always been a complex field of investigation. The relation between the technical skills (lithic production) and the emergence of the linguistic abilities is not easy to investigate due to the difficulty of finding objective data to refer to. The proposition, made by C. Gaucherel and C. Noûs, of a formal grammar of knapping as a method to study the syntactical organisation of the reduction sequences, constitute a new and theoretical useful approach. In order to effectively and precisely define the gestures linked to a specific reduction sequence, for example that of the handaxes shaping, a very large number of variables should be taken into consideration (morphology and quality of the raw material, experience of the knapper, context, percussion technique, forecast of use of the handaxe, etc.). But since a simplification, that brings more elements than the classic one [2,3] is needed, the “action grammar approach” can be a good instrument to detect the common element in a shaping reduction sequence. Furthermore, one of the advantages of the proposed methodology lies in the fact that the definition of the different STs (Stone Technology) can be done according to the technological specific characteristics to be studied and to the type of instrument produced. The deconstruction of knapping sequences could help to detect the degree of complexity of the different steps of the reduction sequences also thanks to the identification of the sub-actions types. The increasing/decreasing of complexity is a very complicate concept in lithic technology. Since at the base of the lithic production there are two basic concepts (angle between the striking platform and the debitage surface - convexity of the debitage/façonnage surface) which are simply declined in an increasingly complex way, it is not easy to define uniquely in what exactly consists the increase in complexity. The approach proposed in the paper “Platforms of Palaeolithic knappers reveal complex linguistic abilities” can help to have new evidences, according to the identification of the required cognitive abilities. The proposed example of formal grammar still needs to be confirmed on archaeological collections, but it is probable that a practical application will allow to further develop the methodology and possibly to highlight additional possibilities of the approach. Bibliography [1] Gaucherel, C. and Noûs C. (2020). Platforms of Palaeolithic knappers reveal complex linguistic abilities. Paleorxiv, wn5za, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology. doi: 10.31233/osf.io/wn5za | Platforms of Palaeolithic knappers reveal complex linguistic abilities | Cédric Gaucherel and Camille Noûs | <p>Recent studies in cognitive neurosciences have postulated a possible link between manual praxis such as tool-making and human languages. If confirmed, such a link opens significant avenues towards the study of the evolution of natural languages... |  | Africa, Ancient Palaeolithic, Lithic technology, Theoretical archaeology | Marta Arzarello | 2020-04-30 14:18:26 | View | |
01 Dec 2021
A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-MaatheideSonja Tomasso, Dries Cnuts, Justin Coppe, Marijn Van Gils, Ferdi Geerts, Marc De Bie, Veerle Rots https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pf3smPotential of a large-scale functional analysis to reconstructing past human activities at the Final Palaeolithic site of Lommel-MaatheideRecommended by Marta Arzarello and Alice Leplongeon based on reviews by Gabriele Luigi Francesco Berruti and Ana Abrunhosa and Alice Leplongeon based on reviews by Gabriele Luigi Francesco Berruti and Ana Abrunhosa
The paper “A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide” [1] focuses on the final Palaeolithic (Federmesser) site of Lommel-Maatheide. Federmesser sites from northern Belgium such as Lommel-Maatheide, Meer and Rekem, show evidence for dense human occupation of specific areas located on top of Tardiglacial dunes nearby water bodies [2]. Preserved spatial distribution of finds at the sites suggest different activity areas and the presence of habitat structures [2]. However, because of the low organic preservation at the sites, functional analyses of lithic assemblages have the potential to significantly contribute to the spatial organisation of activities at these sites. This study by Tomasso et al. [1], represents an excellent example of a large-scale integrated approach to the study of lithic industries. The article undoubtedly demonstrates the potential of the proposed methodology and the reliability of the results obtained. The article explores two different aspects (linked and excellently interconnected here): the possibility to apply use wear, residue and fracture analyses, on lithic assemblages affected by taphonomical alterations and to study lithic assemblages from dune landscapes. The study allows to answer differentiated questions: what is the influence of taphonomical alterations on use wear analysis? How do excavation methods impact the formation of use wear and the preservation of residues? Can we recognize distinct domestic activities? The article also provides an interesting hypothesis about hunting activities and propulsion methods. The applied methodology is effectively interdisciplinary and innovative. It demonstrates how a truly integrated and articulated approach can represent the turning point for going beyond a mainly descriptive dimension to move towards a real understanding of the sites. Studies dedicated to the analysis of the propulsion mode are not very frequent, but they are surely very important to better understand human behaviour [3]. Here, the methodology developed for the evaluation of the propulsion mode represent an important starting point for the definition of a new approach. Morphological and morphometrical analysis are integrated to the evaluation of the mechanical stress, to fracture delineations and to the hafting system (the latter defined on experimental basis). This article therefore underlines the potential of combining different approaches to functional analysis associated with a ‘tailored’ reference collection and applying them to a high number of artefacts for reconstructing past human activities involving materials that are otherwise not preserved in these contexts. [1] Tomasso, S., Cnuts, D., Coppe, J., Geerts, F., Gils, M.V., Bie, M.D., Rots, V. (2021). A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pf3sm, ver 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology. [2] De Bie, M., Van Gils, M. (2006). Les habitats des groupes à Federmesser (aziliens) dans le Nord de la Belgique. Bulletin de la Société préhistorique française, 103, 781–790. [3] Coppe, J., Lepers, C., Clarenne, V., Delaunois, E., Pirlot, M. and Rots V. (2019). Ballistic Study Tackles Kinetic Energy Values of Palaeolithic Weaponry. Archaeometry, (61)4, 933-956. https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.12452 | A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide | Sonja Tomasso, Dries Cnuts, Justin Coppe, Marijn Van Gils, Ferdi Geerts, Marc De Bie, Veerle Rots | <p>The vast Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide, which is located in the Campine region (Northern Belgium), revealed the presence of numerous Final Palaeolithic concentrations situated on a large Late Glacial sand ridge on the northern edg... | Environmental archaeology, Landscape archaeology, Lithic technology, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Marta Arzarello | 2021-09-14 17:04:38 | View | ||
06 Oct 2023
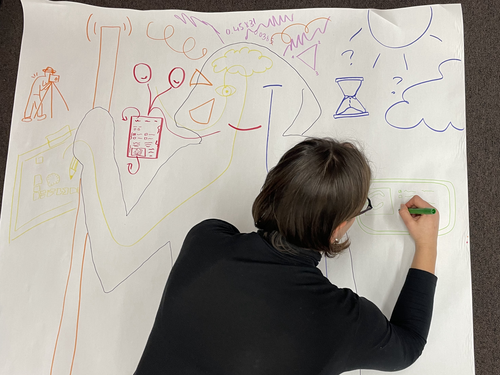
Body Mapping the Digital: Visually representing the impact of technology on archaeological practice.Araar, Leila; Morgan, Colleen; Fowler, Louise https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7990581Understanding archaeological documentation through a participatory, arts-based approachRecommended by Nicolo Dell'Unto based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThis paper presents the use of a participatory arts-based methodology to understand how digital and analogue tools affect individuals' participation in the process of archaeological recording and interpretation. The preliminary results of this work highlight the importance of rethinking archaeologists' relationship with different recording methods, emphasising the need to recognise the value of both approaches and to adopt a documentation strategy that exploits the strengths of both analogue and digital methods. Although a larger group of participants with broader and more varied experience would have provided a clearer picture of the impact of technology on current archaeological practice, the article makes an important contribution in highlighting the complex and not always easy transition that archaeologists trained in analogue methods are currently experiencing when using digital technology. This is assessed by using arts-based methodologies to enable archaeologists to consider how digital technologies are changing the relationship between mind, body and practice. I found the range of experiences described in the papers by the archaeologists involved in the experiment particularly interesting and very representative of the change in practice that we are all experiencing. As the article notes, the two approaches cannot be directly compared because they offer different possibilities: if analogue methods foster a deeper connection with the archaeological material, digital documentation seems to be perceived as more effective in terms of data capture, information exchange and data sharing (Araar et al., 2023). It seems to me that an important element to consider in such a study is the generational shift and the incredible divide between native and non-native digital. The critical issues highlighted in the paper are central and provide important directions for navigating this ongoing (digital) transition. References Araar, L., Morgan, C. and Fowler, L. (2023) Body Mapping the Digital: Visually representing the impact of technology on archaeological practice., Zenodo, 7990581, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7990581 | Body Mapping the Digital: Visually representing the impact of technology on archaeological practice. | Araar, Leila; Morgan, Colleen; Fowler, Louise | <p>This paper uses a participatory, art-based methodology to understand how digital and analog tools impact individuals' experience and perceptions of archaeological recording. Body mapping involves the co-creation of life-sized drawings and narra... |  | Computational archaeology, Theoretical archaeology | Nicolo Dell'Unto | 2023-06-01 09:06:52 | View | |
12 Dec 2022
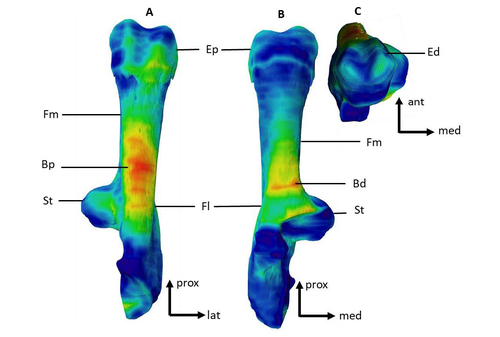
Can growth in captivity alter the calcaneal microanatomy of a wild ungulate?Romain Cottereau, Katia Ortiz, Yann Locatelli, Alexandra Houssaye*, Thomas Cucchi* https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504790Mobility in pigs: A microanatomical perspectiveRecommended by Nimrod Marom based on reviews by Max Price and Ignacio A. Lazagabaster based on reviews by Max Price and Ignacio A. Lazagabaster
Pig domestication and husbandry involved complex processes of introduction, introgression, and feralization that challenge our understanding of human/suid interactions in ancient times. This challenge is a constant stimulus for the development of novel methods and techniques to illuminate aspects of early pig husbandry, such as human-induced changes in mobility. Using geometric morphometrics, Harbers et al. (2020) have shown that the calcaneus records a plastic response to reduced mobility and hence to human management. In the present study, Cottereau et al. (2022) explore the possibility that a similar plastic response to different mobility regimes can be observed in the microanatomy of the calcaneus using CT scans. Their research utilizes a sample of calcanei obtained from Mesolithic specimens, and also from recent suids kept in natural habitat, large pen, and stall. Their results suggest that bone microanatomy is more affected by population differences than by mobility patterns, as illustrated by the similarity between Mesolitic boar calcanei and their difference from recent, free wild boar.
References Cottereau R, Ortiz K, Locatelli Y, Houssaye A, Cucchi T (2022), bioRxiv, 504790, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504790 Harbers H, Neaux D, Ortiz K, Blanc B, Laurens F, Baly I, Callou C, Schafberg R, Haruda A, Lecompte F, Casabianca F, Studer J, Renaud S, Cornette R, Locatelli Y, Vigne J-D, Herrel A, Cucchi T (2020) The mark of captivity: plastic responses in the ankle bone of a wild ungulate (Sus scrofa). Royal Society Open Science, 7, 192039. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.192039
| Can growth in captivity alter the calcaneal microanatomy of a wild ungulate? | Romain Cottereau, Katia Ortiz, Yann Locatelli, Alexandra Houssaye*, Thomas Cucchi* | <p style="text-align: justify;">Reduced mobility associated with captivity induce changes in biomechanical stress on the skeleton of domesticated animals. Due to bone plasticity, the morphology and the internal structure of the bones can respond t... |  | Neolithic, Zooarchaeology | Nimrod Marom | 2022-08-26 20:29:01 | View | |
02 Nov 2020
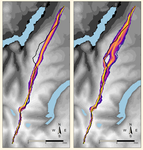
Probabilistic Modelling using Monte Carlo Simulation for Incorporating Uncertainty in Least Cost Path Results: a Roman Road Case StudyJoseph Lewis https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/mxas2A probabilistic method for Least Cost Path calculation.Recommended by Otis Crandell based on reviews by Georges Abou Diwan and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper entitled “Probabilistic Modelling using Monte Carlo Simulation for Incorporating Uncertainty in Least Cost Path Results: a Roman Road Case Study” [1] submitted by J. Lewis presents an innovative approach to applying Least Cost Path (LCP) analysis to incorporate uncertainty of the Digital Elevation Model used as the topographic surface on which the path is calculated. The proposition of using Monte Carlo simulations to produce numerous LCP, each with a slightly different DEM included in the error range of the model, allows one to strengthen the method by proposing a probabilistic LCP rather than a single and arbitrary one which does not take into account the uncertainty of the topographic reconstruction. This new method is integrated in the R package leastcostpath [2]. The author tests the method using a Roman road built along a ridge in Cumbria, England. The integration of the uncertainty of the DEM, thanks to Monte Carlo simulations, shows that two paths could have the same probability to be the real LCP. One of them is indeed the path that the Roman road took. In particular, it is one of two possibilities of LCP in the south to north direction. This new probabilistic method therefore strengthens the reconstruction of past pathways, while also allowing new hypotheses to be tested, and, in this case study, to suggest that the northern part of the Roman road’s location was selected to help the northward movements. [1] Lewis, J., 2020. Probabilistic Modelling using Monte Carlo Simulation for Incorporating Uncertainty in Least Cost Path Results: a Roman Road Case Study. SocArXiv, mxas2, ver 17 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology, 10.31235/osf.io/mxas2. [2] Lewis, J., 2020. leastcostpath: Modelling Pathways and Movement Potential Within a Landscape. R package. Version 1.7.4. | Probabilistic Modelling using Monte Carlo Simulation for Incorporating Uncertainty in Least Cost Path Results: a Roman Road Case Study | Joseph Lewis | <p>The movement of past peoples in the landscape has been studied extensively through the use of Least Cost Path (LCP) analysis. Although methodological issues of applying LCP analysis in Archaeology have frequently been discussed, the effect of v... |  | Spatial analysis | Otis Crandell | Adam Green, Georges Abou Diwan | 2020-08-05 12:10:46 | View |
15 Aug 2021
Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, IndiaNorbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675An insight into traditional method of food production in IndiaRecommended by Otis Crandell based on reviews by Antony Borel, Atefeh Shekofteh, Andrea Squitieri, Birgül Ögüt, Atefe Shekofte and 1 anonymous reviewerThis paper [1] covers an interesting topic in that it presents through ethnography an insight into a traditional method of food production which is gradually declining in use. In addition to preserving traditional knowledge, the ethnographic study of grinding stones has the potential for showing how similar tools may have been used by people in the past, particularly from the same geographic region. [1] Thongdok Norbu J., Nimasow Gibji, Nimasow Oyi D. (2021) Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Zenodo, 5118675, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeo. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675 | Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India | Norbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow | <p style="text-align: justify;">The Shertukpens are an Indigenous tribal group inhabiting the western and southern parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Northeast India. They are accomplished carvers of carving wood and stone. The paper aims to document the... | Antiquity, Asia, Environmental archaeology, Lithic technology, Peopling, Raw materials | Otis Crandell | 2021-02-10 10:26:12 | View | ||
05 Jun 2023

SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R ShinyROYER, Aurélien, DISCAMPS, Emmanuel, PLUTNIAK, Sébastien, THOMAS, Marc https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7957154Analyzing piece-plotted artifacts just got simpler: A good solution to the wrong problem?Recommended by Reuven Yeshurun based on reviews by Frédéric Santos, Jacqueline Meier and Maayan LevPaleolithic archaeologists habitually measure 3-coordinate data for artifacts in their excavations. This was first done manually, and in the last three decades it is usually performed by a total station and associated hardware. While the field recording procedure is quite straightforward, visualizing and analyzing the data are not, often requiring specialized proprietary software or coding expertise. Here, Royer and colleagues (2023) present the SEAHORS application, an elegant solution for the post-excavation analysis of artifact coordinate data that seems to be instantly useful for numerous archaeologists. SEAHORS allows one to import and organize field data (Cartesian coordinates and point description), which often comes in a variety of formats, and to create various density and distribution plots. It is specifically adapted to the needs of archaeologists, is free and accessible, and much simpler to use than many commercial programs. The authors further demonstrate the use of the application in the post-excavation analysis of the Cassenade Paleolithic site (see also Discamps et al., 2019). While in no way detracting from my appreciation of Royer et al.’s (2023) work, I would like to play the devil’s advocate by asking whether, in the majority of cases, field recording of artifacts in three coordinates is warranted. Royer et al. (2023) regard piece plotting as “…indispensable to propose reliable spatial planimetrical and stratigraphical interpretations” but this assertion does not hold in all (or most) cases, where careful stratigraphic excavation employing thin volumetric units would do just as well. Moreover, piece-plotting has some serious drawbacks. The recording often slows excavations considerably, beyond what is needed for carefully exposing and documenting the artifacts in their contexts, resulting in smaller horizontal and vertical exposures (e.g., Gilead, 2002). This typically hinders a fuller stratigraphic and contextual understanding of the excavated levels and features. Even worse, the method almost always creates a biased sample of “coordinated artifacts”, in which the most important items for understanding spatial patterns and site-formation processes – the small ones – are underrepresented. Some projects run the danger of treating the coordinated artifacts as bearing more significance than the sieve-recovered items, preferentially studying the former with no real justification. Finally, the coordinated items often go unassigned to a volumetric unit, effectively disconnecting them from other types of data found in the same depositional contexts. The advantages of piece-plotting may, in some cases, offset the disadvantages. But what I find missing in the general discourse (certainly not in the recommended preprint) is the “theory” behind the seemingly technical act of 3-coordinate recording (Yeshurun, 2022). Being in effect a form of sampling, this practice needs a rethink about where and how to be applied; what depositional contexts justify it, and what the goals are. These questions should determine if all “visible” artifacts are plotted, or just an explicitly defined sample of them (e.g., elongated items above a certain length threshold, which should be more reliable for fabric analysis), or whether the circumstances do not actually justify it. In the latter case, researchers sometimes opt for using “virtual coordinates” within in each spatial unit (typically 0.5x0.5 m), essentially replicating the data that is generated by “real” coordinates and integrating the sieve-recovered items as well. In either case, Royer et al.’s (2023) solution for plotting and visualizing labeled points within intra-site space would indeed be an important addition to the archaeologists’ tool kits.
References cited Discamps, E., Bachellerie, F., Baillet, M. and Sitzia, L. (2019). The use of spatial taphonomy for interpreting Pleistocene palimpsests: an interdisciplinary approach to the Châtelperronian and carnivore occupations at Cassenade (Dordogne, France). Paleoanthropology 2019, 362–388. https://doi.org/10.4207/PA.2019.ART136 Gilead, I. (2002). Too many notes? Virtual recording of artifacts provenance. In: Niccolucci, F. (Ed.). Virtual Archaeology: Proceedings of the VAST Euroconference, Arezzo 24–25 November 2000. BAR International Series 1075, Archaeopress, Oxford, pp. 41–44. Royer, A., Discamps, E., Plutniak, S. and Thomas, M. (2023). SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R Shiny Zenodo, 7957154, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7929462 Yeshurun, R. (2022). Intra-site analysis of repeatedly occupied camps: Sacrificing “resolution” to get the story. In: Clark A.E., Gingerich J.A.M. (Eds.). Intrasite Spatial Analysis of Mobile and Semisedentary Peoples: Analytical Approaches to Reconstructing Occupation History. University of Utah Press, pp. 27–35.
| SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R Shiny | ROYER, Aurélien, DISCAMPS, Emmanuel, PLUTNIAK, Sébastien, THOMAS, Marc | <p style="text-align: justify;">This paper presents SEAHORS, an R shiny application available as an R package, dedicated to the intra-site spatial analysis of piece-plotted archaeological remains. This open-source script generates 2D and 3D scatte... |  | Computational archaeology, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Reuven Yeshurun | 2023-02-24 16:01:44 | View | |
04 Oct 2023

IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A "para-description"Hagmann, Dominik; Reiner, Franziska https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/5vwg8The IUENNA project: integrating old data and documentation for future archaeologyRecommended by Ronald Visser based on reviews by Nina Richards and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Nina Richards and 3 anonymous reviewers
This recommended paper on the IUENNA project (Hagmann and Reiner 2023) is not a paper in the traditional sense, but it is a reworked version of a project proposal. It is refreshing to read about a project that has just started and see what the aims of the project are. This ties in with several open science ideas and standards (e.g. Brinkman et al. 2023). I am looking forward to see in a few years how the authors managed to reach the aims and goals of the project. The IUENNA project deals with the legacy data and old excavations on the Hemmaberg and in the Jauntal. Archaeological research in this small, but important region, has taken place for more than a century, revealing material from over 2000 years of human history. The Hemmaberg is well known for its late antique and early medieval structures, such as roads, villas and the various churches. The wider Jauntal reveals archaeological finds and features dating from the Iron Age to the recent past. The authors of the paper show the need to make sure that the documentation and data of these past archaeological studies and projects will be accessible in the future, or in their own words: "Acute action is needed to systematically transition these datasets from physical filing cabinets to a sustainable, networked virtual environment for long-term use" (Hagmann and Reiner 2023: 5). The papers clearly shows how this initiative fits within larger developments in both Digital Archaeology and the Digital Humanities. In addition, the project is well grounded within Austrian archaeology. While the project ties in with various international standards and initiatives, such as Ariadne (https://ariadne-infrastructure.eu/) and FAIR-data standards (Wilkinson et al. 2016, 2019), it would benefit from the long experience institutes as the ADS (https://archaeologydataservice.ac.uk/) and DANS (see Data Station Archaeology: https://dans.knaw.nl/en/data-stations/archaeology/) have on the storage of archaeological data. I would also like to suggest to have a look at the Dutch SIKB0102 standard (https://www.sikb.nl/datastandaarden/richtlijnen/sikb0102) for the exchange of archaeological data. The documentation is all in Dutch, but we wrote an English paper a few years back that explains the various concepts (Boasson and Visser 2017). However, these are a minor details or improvements compared to what the authors show in their project proposal. The integration of many standards in the project and the use of open software in a well-defined process is recommendable. The IUENNA project is an ambitious project, which will hopefully lead to better insights, guidelines and workflows on dealing with legacy data or documentation. These lessons will hopefully benefit archaeology as a discipline. This is important, because various (European) countries are dealing with similar problem, since many excavations of the past have never been properly published, digitalized or deposited. In the Netherlands, for example, various projects dealt with publication of legacy excavations in the Odyssee-project (https://www.nwo.nl/onderzoeksprogrammas/odyssee). This has led to the publication of various books and datasets (24) (https://easy.dans.knaw.nl/ui/datasets/id/easy-dataset:34359), but there are still many datasets (8) missing from the various projects. In addition, each project followed their own standards in creating digital data, while IUENNA will make an effort to standardize this. There are still more than 1000 Dutch legacy excavations still waiting to be published and made into a modern dataset (Kleijne 2010) and this is probably the case in many other countries. I sincerely hope that a successful end of IUENNA will be an inspiration for other regions and countries for future safekeeping of legacy data. References Boasson, W and Visser, RM. 2017 SIKB0102: Synchronizing Excavation Data for Preservation and Re-Use. Studies in Digital Heritage 1(2): 206–224. https://doi.org/10.14434/sdh.v1i2.23262 Brinkman, L, Dijk, E, Jonge, H de, Loorbach, N and Rutten, D. 2023 Open Science: A Practical Guide for Early-Career Researchers https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7716153 Hagmann, D and Reiner, F. 2023 IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A ‘para-description’. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/5vwg8 Kleijne, JP. 2010. Odysee in de breedte. Verslag van het NWO Odyssee programma, kortlopend onderzoek: ‘Odyssee, een oplossing in de breedte: de 1000 onuitgewerkte sites, die tot een substantiële kennisvermeerdering kunnen leiden, digitaal beschikbaar!’ ‐ ODYK‐09‐13. Den Haag: E‐depot Nederlandse Archeologie (EDNA). https://doi.org/10.17026/dans-z25-g4jw Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Aalbersberg, IjJ, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, ’t Hoen, PAC, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Velterop, J, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2016 The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 3(1): 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Jan Aalbersberg, I, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, Hoen, PAC ’t, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Jan Velterop, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2019 Addendum: The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 6(1): 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0009-6
| IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A "para-description" | Hagmann, Dominik; Reiner, Franziska | <p>The Go!Digital 3.0 project IUENNA – an acronym for “openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology” – embraces a comprehensive open science methodology. It focuses on the archaeological micro-region of the Jauntal Valley ... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Computational archaeology | Ronald Visser | 2023-04-06 13:36:16 | View | |
08 Feb 2024
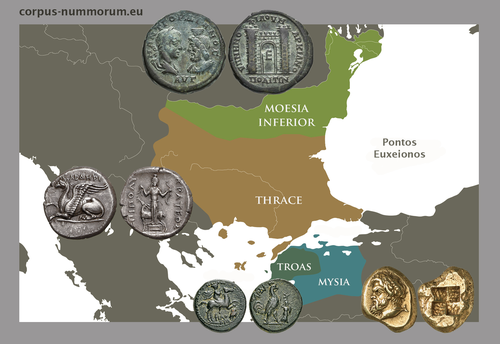
CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient CoinsUlrike Peter, Claus Franke, Jan Köster, Karsten Tolle, Sebastian Gampe, Vladimir F. Stolba https://zenodo.org/records/8263517The valuable Corpus Nummorum: a not so Little MinionRecommended by Ronald Visser based on reviews by Fleur Kemmers and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Fleur Kemmers and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper under review/recommendation deals with Corpus Nummorum (Peter et al. 2024). The Corpus Nummorum (CN) is web portal for ancient Greek coins from various collections (https://www.corpus-nummorum.eu/). The CN is a database and research tool for Greek coins dating between 600 BCE to 300 CE. While many traditional collection databases aim at collecting coins, CN also includes coin dies, coin types and issues. It aims at achieving a complete online coin type catalogue. The paper is not a paper in a traditional sense, but presents the CN as a tool and shows the functionalities in the system. The relevance and the possibilities of the CN for numismatists is made clear in the paper and the merits are clear even for me as a Roman archaeologist and non-numismatist. The CN was presented as a poster at the CAA 2023 in Amsterdam during “S03. Our Little Minions pt. V: small tools with major impact”, organized by Moritz Mennenga, Florian Thiery, Brigit Danthine and myself (Mennenga et al. 2023). Little Minions help us significantly in our daily work as small self-made scripts, home-grown small applications and small hardware devices. They often reduce our workload or optimize our workflows, but are generally under-represented during conferences and not often presented to the outside world. Therefore, the Little Minions form a platform that enables researchers and software engineers to share these tools (Thiery, Visser and Mennenga 2021). Little Minions have become a well known happening within the CAA-community since we started this in 2018, also because we do not only allow 10-minute lightning talks, but also spontaneous stand-up presentations during the conference. A full list of all minions presented in the past, can be found online: https://caa-minions.github.io/minions/. In a strict sense the CN would not count as a Little Minion, because it is a large project consisting of many minions that help a numismatist in his/her daily work. The CN seems a very Big Minion in that sense. Personally, I am very happy to see the database being developed as a fully open system and that code can be found on Github (https://github.com/telota/corpus-nummorum-editor), and also made citable with citation information in GitHub (see https://citation-file-format.github.io/) and a version deposited in Zenodo with DOI (Köster and Franke 2024). In addition, the authors claim that the CN will be shared based on the FAIR-principles (Wilkinson et al. 2016, 2019). These guidelines are developed to improve the Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reuse of digital data. I feel that CN will be a way forward in open numismatics and open archaeology. The CN is well known within the numismatist community and it was hard to find reviewers in this close community, because many potential reviewers work together with one or more of the authors, or are involved in the project. This also proves the relevance of the CN to the research community and beyond. Luckily, a Roman numismatist and a specialist in digital/computational archaeology were able to provide valuable feedback on the current paper. The reviewers only submitted feedback on the first version of the paper (Peter et al. 2023). The numismatist was positive on the content and the usefulness of CN for the discipline in general. However, she pointed out some important points that need to be addressed. The digital specialist was positive is various aspects, but also raised some important issues in relation to technical aspects and the explanation thereof. While both were positive on the project and the paper in general, both reviewers pointed out some issues that were largely addressed in the second version of this paper. The revised version was edited throughout and the paper was strongly improved. The Corpus Nummorum is well presented in this easy to read paper, although the explanations can sometimes be slightly technical. This paper gives a good introduction to the CN and I recommend this for publication. I sincerely hope that the CN will contribute and keep on contributing to the domains of numismatics, (digital) archaeology and open science in general. References Köster, J and Franke, C. 2024 Corpus Nummorum Editor. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10458195 Mennenga, M, Visser, RM, Thiery, F and Danthine, B. 2023 S03. Our Little Minions pt. V: small tools with major impact. In:. Book of Abstracts. CAA 2023: 50 Years of Synergy. Amsterdam: Zenodo. pp. 249–251. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.7930991 Peter, U, Franke, C, Köster, J, Tolle, K, Gampe, S and Stolba, VF. 2023 CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.8263518 Peter, U., Franke, C., Köster, J., Tolle, K., Gampe, S. and Stolba, V. F. (2024). CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins, Zenodo, 8263517, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8263517 Thiery, F, Visser, RM and Mennenga, M. 2021 Little Minions in Archaeology An open space for RSE software and small scripts in digital archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4575167 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Aalbersberg, IjJ, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, ’t Hoen, PAC, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Velterop, J, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2016 The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 3(1): 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Jan Aalbersberg, I, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, Hoen, PAC ’t, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Jan Velterop, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2019 Addendum: The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 6(1): 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0009-6 | CORPUS NUMMORUM – A Digital Research Infrastructure for Ancient Coins | Ulrike Peter, Claus Franke, Jan Köster, Karsten Tolle, Sebastian Gampe, Vladimir F. Stolba | <p>CORPUS NUMMORUM indexes ancient Greek coins from various landscapes and develops typologies. The coins and coin types are published on the multilingual website www.corpus-nummorum.eu utilizing numismatic authority data and adhering to FAIR prin... |  | Antiquity, Classic | Ronald Visser | 2023-08-18 17:37:51 | View | |
16 May 2022

Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool culturesAnnemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger https://osf.io/x8m4jOpen glossary for wood technologiesRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé
Wood is a widely available and versatile material, so it is not surprising that it has been a key resource throughout human history. However, it is more vulnerable to decomposition than other materials, and its direct use is only rarely recorded in prehistoric sites. Despite this, there are exceptions (e.g., [1-5] [6] and references therein), and indirect evidence of its use has been attested through use-wear analyses, residue analyses (e.g., [7]) and imprints on the ground (e.g., [8]). One interesting finding of note is that the technology required to make, for example, wooden spears was quite complex [9], leading some authors to propose that this type of tool production represented a cognitive leap for Pleistocene hominids [10]. Other researchers, however, have proposed that the production process for wooden tools could have been much easier than is currently thought [11]. Be that as it may, in recent years researchers have begun to approach wood remains systematically, developing analyses of natural and anthropogenic damage, often with the help of experimental reference samples. In this work, the authors elaborate a comprehensive glossary as a first step towards the understanding of the use of wood for technological purposes in different times and places, as there is still a general gap in the established nomenclature. Thus, this glossary is a synthesis and standardisation of analytical terms for early wood technologies that includes clear definitions and descriptions of traces from stone tool-using cultures, to avoid confusion in ongoing and future studies of wood tools. For this, the authors have carried out a detailed search of the current literature to select appropriate terms associated with additional readings that provide a wide, state-of-the-art description of the field of wood technology. An interesting point is that the glossary has been organised within a chaîne opératoire framework divided into categories including general terms and natural traces, and then complemented by an appendix of images. It is important to define the natural traces –understanding these as alterations caused by natural processes–because they can mask those modifications produced by other agents affecting both unmodified and modified wood before, during or after its human use. In short, the work carried out by Milks et al. [6] is an excellent and complete assessment and vital to the technological approach to wooden artifacts from archaeological contexts and establishing a common point for a standardised nomenclature. One of its particular strengths is that the glossary is a preprint that will remain open during the coming years, so that other researchers can continue to make suggestions and refinements to improve the definitions, terms and citations within it. [1] Oakley, K., Andrews, P., Keeley, L., Clark, J. (1977). A reappraisal of the Clacton spearpoint. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 43, 13-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0079497X00010343 [2] Thieme, H. (1997). Lower Palaeolithic hunting spears from Germany. Nature 385, 807-810. https://doi.org/10.1038/385807a0 [3] Schoch, W.H., Bigga, G., Böhner, U., Richter, P., Terberger, T. (2015). New insights on the wooden weapons from the Paleolithic site of Schöningen. Journal of Human Evolution 89, 214-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.08.004 [4] Aranguren, B., Revedin, A., Amico, N., Cavulli, F., Giachi, G., Grimaldi, S. et al. (2018). Wooden tools and fire technology in the early Neanderthal site of Poggetti Vecchi (Italy). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115, 2054-2059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716068115 [5] Rios-Garaizar, J., López-Bultó, O., Iriarte, E., Pérez-Garrido, C., Piqué, R., Aranburu, A., et al. (2018). A Middle Palaeolithic wooden digging stick from Aranbaltza III, Spain. PLoS ONE 13(3): e0195044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195044 [6] Milks, A. G., Lehmann, J., Böhner, U., Leder, D., Koddenberg, T., Sietz, M., Vogel, M., Terberger, T. (2022). Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures. Peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/x8m4j [7] Nugent, S. (2006). Applying use-wear and residue analyses to digging sticks. Mem Qld Mus Cult Herit Ser 4, 89-105. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.890092331962439 [8] Allué, E., Cabanes, D., Solé, A., Sala, R. (2012). Hearth Functioning and Forest Resource Exploitation Based on the Archeobotanical Assemblage from Level J, in: i Roura E. (Ed.), High Resolution Archaeology and Neanderthal Behavior: Time and Space in Level J of Abric Romaní (Capellades, Spain). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3922-2_9 [9] Ennos, A.R., Chan, T.L. (2016). "Fire hardening" spear wood does slightly harden it, but makes it much weaker and more brittle. Biology Letters 12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2016.0174 [10] Haidle, M.N. (2009). How to think a simple spear?, in: de Beaune S.A., Coolidge F.L., Wynn T. (Eds.), Cognitive Archaeology and Human Evolution. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 57-73. [11] Garofoli, D. (2015). A Radical Embodied Approach to Lower Palaeolithic Spear-making. Journal of Mind and Behavior 36, 1-26. | Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures | Annemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger | <p>The analysis of wood technologies created by stone tool-using cultures remains underdeveloped relative to the study of lithic and bone technologies. In recent years archaeologists have begun to approach wood assemblages systematically, developi... |  | Ancient Palaeolithic, Archaeobotany, Mesolithic, Middle Palaeolithic, Neolithic, Raw materials, Taphonomy, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Ruth Blasco | 2021-12-01 12:18:53 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










