Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * ▲ | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
28 Aug 2023
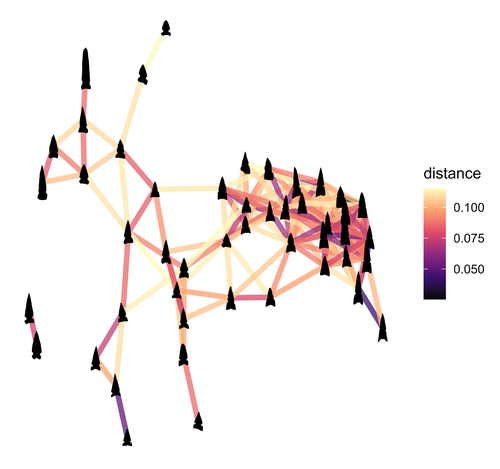
Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United StatesRobert J. Bischoff https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc2D Geometric Morphometrics of Projectile Points from the Southwestern United StatesRecommended by Adrian L. Burke based on reviews by James Conolly and 1 anonymous reviewerBischoff (2023) is a significant contribution to the growing field of geometric morphometric analysis in stone tool analysis. The subject is projectile points from the southwestern United States. Projectile point typologies or systematics remain an important part of North American archaeology, and in fact these typologies continue to be used primarily as cultural-historical markers. This article looks at projectile point types using a 2D image geometric morphometric analysis as a way of both improving on projectile point types but also testing if these types are in fact based in measurable reality. A total of 164 point outlines are analyzed using Elliptical Fourier, semilandmark and landmark analyses. The author also uses a network analysis to look at possible relationships between projectile point morphologies in space. This is a clever way of working around the predefined distributions of projectile point types, some of which are over 100 years old. Because of the dynamic nature of stone tools in terms of their use, reworking and reuse, this article can also provide solutions for studying the dynamic nature of stone tools. This article therefore also has a wide applicability to other stone tool analyses. Reference Bischoff, R. J. (2023) Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States, SocArXiv, a6wjc, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc | Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States | Robert J. Bischoff | <p style="text-align: justify;">Traditional analyses of projectile points often use visual identification, the presence or absence of discrete characteristics, or linear measurements and angles to classify points into distinct types. Geometric mor... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Lithic technology, North America | Adrian L. Burke | 2022-12-18 03:38:14 | View | |
20 Mar 2024
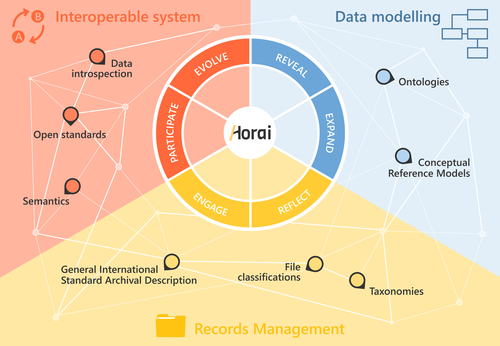
HORAI: An integrated management model for historical informationPablo del Fresno Bernal, Sonia Medina Gordo and Esther Travé Allepuz https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8185510A novel management model for historical informationRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by Leandro Sánchez Zufiaurre and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper “HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information” presents a novel model for managing historical information. The study draws from an extensive indepth work in historical information management and a multi-disciplinary corpus of research ranging from heritage infrastructure research and practice to information studies and archival management literature. The paper ties into several key debates and discussions in the field showing awareness of the state-of-the-art of data management practice and theory. The authors argue for a new semantic data model HORAI and link it to a four-phase data management lifecycle model. The conceptual work is discussed in relation to three existing information systems partly predating and partly developed from the outset of the HORAI-model. While the paper shows appreciable understanding of the practical and theoretical state-of-the-art and the model has a lot of potential, in its current form it is still somewhat rough on the edges. Many of the both practical and theoretical threads introduced in the text warrant also more indepth consideration and it will be interesting to follow how the work will proceed in the future. For example, the comparison of the HORAI model and the ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival Description standard in the figure 1 is interesting but would require more elaboration. A slightly more thorough copyediting of the text would have also been helpful to make it more approachable. As a whole, in spite of the critique, I find both the paper and the model as valuable contributions to the literature and the practice of managing historical information. The paper reports thorough work, provides a lot of food for thought and several interesting lines of inquiry in the future. ReferencesDel Fresno Bernal, P., Medina Gordo, S. and Travé Allepuz, E. (2024). HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information. CAA 2023, Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8185510 | HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information | Pablo del Fresno Bernal, Sonia Medina Gordo and Esther Travé Allepuz | <p>The archiving process goes beyond mere data storage, requiring a theoretical, methodological, and conceptual commitment to the sources of information. We present Horai as a semantic-based integration model designed to facilitate the development... |  | Computational archaeology, Spatial analysis | Isto Huvila | 2023-07-26 09:33:58 | View | |
27 Jun 2024

At the edge of the city: the digital storyline of the Bronchotion Monastery of MystrasPanagiotidis V. Vayia; Valantou Vasiliki; Kazolias Anastasios; Zacharias Nikolaos https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8126952Mystras Captured from the Air – Digital Recording Techniques for Cultural Heritage Management of a Monumental Archaeological SiteRecommended by Jitte Waagen based on reviews by Nikolai Paukkonen and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Nikolai Paukkonen and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Panagiotidis et al. 2024) discusses the digital approach to the ‘digital storyline’ of the Monastery of Brontochion of Mystras, Peloponnese, Greece. Using drone and terrestrial photogrammetric recording techniques, their goal is to produce maps and 3D models that will be integrated in the overall study of the medieval city, as well as function as a comprehensive visualisation of the archaeological site throughout its history. This will take shape as a web application using ArcGIS Online that will be a valuable platform presenting interactive visual information to accompany written publications. In addition, the assets in the database will be available for further advanced purposes, such as suggested by the authors; xR applications, educational games or digital smart guides. The authors of the paper do a good job in describing the historical background of the site and the purpose of the digital documentation techniques, and the applied methods and the technical details of the produced models are dealt with in detail. The paper presents a compelling case for an integrative approach to using digital recording techniques at an architectonically complex site for Cultural Heritage Management. It can be placed in a series of studies discussing how monumental sites can benefit from advanced digital recording techniques such as those presented in this paper (see for example Waagen and Wijngaarden 2024). The paper is recommended as an interesting read for all who are involved in this field. References Panagiotidis V. Vayia, Valantou Vasiliki, Kazolias Anastasios, and Zacharias Nikolaos. (2024). At the Edge of a City: The Digital Storyline of the Brontochion Monastery of Mystras. Zenodo, 8126952, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8126952 Waagen, J., and van Wijngaarden, G. J. (2024). Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology. Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology, 7(1), 237–243. https://doi.org/10.5334/jcaa.157 | At the edge of the city: the digital storyline of the Bronchotion Monastery of Mystras | Panagiotidis V. Vayia; Valantou Vasiliki; Kazolias Anastasios; Zacharias Nikolaos | <p>This study focuses on the digital depiction of the storyline of the Monastery of Brontochion of Mystras, located at the southwest edge of the city of Mystras, situated at the foot of Mt. Taygetos, six kilometres west of the city of Sparta in th... |  | Computational archaeology, Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Remote sensing, Spatial analysis | Jitte Waagen | 2023-10-03 17:02:54 | View | |
10 Jun 2024

Hypercultural types: archaeological objects in fast times.Artur Ribeiro https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10567441The Postmodern Predicament of Type-Thinking in ArchaeologyRecommended by Shumon Tobias Hussain , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak based on reviews by Gavin Lucas, Miguel John Versluys and Anna S. Beck based on reviews by Gavin Lucas, Miguel John Versluys and Anna S. Beck
“Hypercultural types: archaeological objects in fast times” by A. Ribeiro (1) offers some timely, critical and creative reflections on the manifold struggles of and disappointments in type-thinking and typological approaches in recent archaeological scholarship. Ribeiro insightfully situates what has been identified as a “crisis” in archaeological typo-praxis in the historical conditions of postmodernity and late capitalism themselves. The author thereby attempts what he himself considers “quite hard”, namely “to understand the current Zeitgeist and how it affects how we think and do archaeology” (p. 4). This provides a sort of historical epistemology of the present which can of course only be preliminary and incomplete as it crystallizes, takes shape, and transforms as we write these lines, is available only in fragments and hints, and is generally difficult to talk about and describe as we (the author included) lack critical distance – present-day archaeologists and fellow academics are both enfolded in postmodernity and continue to contribute to its logics and trajectories. Ribeiro’s key argument is provocative as it is interesting: he contends that archaeologists’ difficulties of coming to terms with types and typologies – staple knowledge practices of the discipline ever since – are a symptom of the changing cultural matrix of our times. The diagnosis is multilayered and complex, and Ribeiro at times only scratches the surface of what may be at stake here as he openly admits himself. At the core of his proposal is a shift in attention away from classical questions of epistemological rank, which in archaeology have tended to orbit the contentious issue of the reality of types (see also 2). Instead of foregrounding the question of type-realities – whether types, once identified, can be meaningfully said to exist and to represent something significant in the world – archaeologists are urged to recognize that typo-praxis is culturally saturated in at least two profound ways. First, devising and mobilizing types and typologies is a cultural practice itself – it may indeed have long been a foundational ‘cultural technique’ (Kulturtechnik) (3) of archaeology as a disciplined community-venture of methodical knowledge production. Typo-centric understandings of the archaeological record are quite akin to definition-centric apprehensions of the same as in both cases order, discreteness, and one-to-one correspondence are considered overriding epistemic virtues and credible pointers to a subject-independent “reality”. As such, these practices have a location of their own and they may thus notably conflict with the particularities of alternate and ever-mutating phenomenal realities and historical conditions. Discreteness may for instance lose its paradigmatic status as a descriptor of worldly order, and this is precisely what Ribeiro argues to have happened in the wake of postmodern transformations, influentially said to have deeply reconfigured the relation between the local and the global, at times even superseding such distinctions altogether. When coupled to questions of reality, types, in a similar fashion as definitions, quickly become vehicles to affirm epistemic power and knowledge authority and so help certify certain kinds of realities while supressing others. This is the paradox of modernity: to insist on monolithic understandings of the world while professing radical difference. Second, and for Ribeiro more importantly, typo-praxis is not just subject to cultural variation and thus by implication is plural, it also always has its proper associated cultural milieu in which it exerts some sort of efficacy, i.e. enables action and insight. Ribeiro maintains that this sort of efficacy has become contentious under postmodern conditions and this is because culture, under the gaze of global consumerism, has lost much of its classical significance, and as “hyperculture” (4) developed new logics, significations, and material culture correspondences, essentially “flattening” the highly textured and differentiated world of modernity (p. 6). Some of these new configurations sharply violate the expectations of traditional views of culture. The postmodern situation has in this way effectively emerged as a resistant force proffering much caution and growing scepticism among archaeologists and other academics alike as received ideas about “types” and “cultures” do not seem to work anymore the same way as before. The credibility of different modes of typo-praxis, archaeological or not, in other words, may depend much more on the cultural ecology of lived experience and contemporary diagnosis than is often realized. With Ribeiro, we may say that culture concepts and type concepts are indeed co-constitutive, and what sort of types and typologies archaeologists can persuasively deploy thus also depends greatly on how we construct the link between culture and type, and how (well) we grapple with our own realities and the lessons we draw from them – yet another important reminder of how our own subjectivities figure in such foundational debates (see esp. 5). The crisis of typo-praxis in archaeology, then, is intricately linked to the crisis of modernity, broached by Ribeiro with the labels of postmodernity and late capitalism. Upon reflection, this is not surprising at all since Tylor’s (6) influential definition of culture for example, which is extensively referenced in the paper, was both reflective of and conducive to the project of modernity and its distinctive historical formations such as empire and colonialism. Ribeiro reminds us that questions of justification and credibility, be it in the domain of type-thinking or other epistemic contexts, can never be fully divorced from the contemporary situation, and archaeologists thus need to be vigilant observers of the present, too. Typo-praxis ultimately is motivated by and draws authority from what Foucault (7) has called épistémè, the totality of pertinent parameters forming the historical a priori of understanding or the guiding unconsciousness of subjectivity within a given epoch. The crisis of archaeological typo-praxis, in this view, signifies a calling into question of the historical a priori on which much traditional type-work in archaeology was premised. Archaeologists still have to come to terms with the implications and consequences of this assessment. “Hypercultural types: archaeological objects in fast times” offers a first poignant analysis of some of these challenges of postmodern archaeological type-thinking.
Bibliography 1. Ribeiro, A. (2024). Hypercultural types: archaeological objects in fast times. Zenodo, 10567441, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10567441 2. Hussain, S. T. (2024). The Loss of Typological Innocence: An Archaeology of Archaeological Typo-Praxis. Zenodo, 10567441. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10547264 3. Macho, T. (2013). Second-Order Animals: Cultural Techniques of Identity and Identification. Theory, Culture & Society 30, 30–47. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263276413499189 4. Han, B.-C. (2022). Hyperculture: culture and globalization (Polity Press). 5. Frank, A., Gleiser, M. and Thompson, E. (2024). The blind spot: why science cannot ignore human experience (The MIT Press). https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/13711.001.0001 6. E. B. Tylor, E. B. (1871). Primitive Culture: Researches Into the Development of Mythology, Philosophy, Religion, Art, and Custom (J. Murray). 7. Foucault, M. (2007). The order of things: an archaeology of the human sciences, Repr (Routledge). | Hypercultural types: archaeological objects in fast times. | Artur Ribeiro | <p>Although artifact typologies still play a big role in archaeology, they have certainly lost some repute in recent decades. More than just a collection of items with similar attributes, typologies are a reflection of cultural behaviour and pract... |  | Theoretical archaeology | Shumon Tobias Hussain | 2024-01-25 13:40:08 | View | |
05 Jul 2023
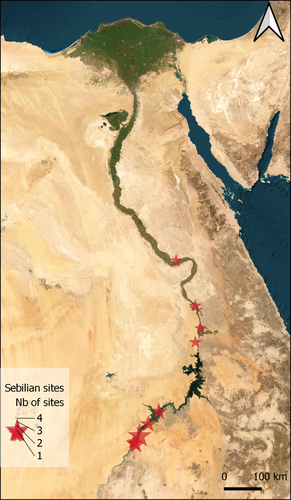
Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile ValleyAlice Leplongeon https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8115202Cultural taxonomic systems and the Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age prehistory of the Nile Valley – a critical reviewRecommended by Felix Riede, Sébastien Plutniak and Shumon Tobias Hussain and Shumon Tobias Hussain based on reviews by Giuseppina Mutri and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Giuseppina Mutri and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper entitled “Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile Valley” submitted by A. Leplongeon offers a review of the many cultural taxonomic in use for the prehistory – especially the Late Palaeolithic/Late Stone Age – of the Nile Valley (Leplongeon 2023). This paper was first developed for a special conference session convened at the EAA annual meeting in 2021 and is intended for an edited volume on the topic of typology and taxonomy in archaeology. Issues of cultural taxonomy have recently risen to the forefront of archaeological debate (Reynolds and Riede 2019; Ivanovaitė et al. 2020; Lyman 2021). Archaeological systematics, most notably typology, have roots in the research history of a particular region and period (e.g. Plutniak 2022); commonly, different scholars employ different and at times incommensurable systems, often leading to a lack of clarity and inter-regional interoperability. African prehistory is not exempt from this debate (e.g. Wilkins 2020) and, in fact, such a situation is perhaps nowhere more apparent than in the iconic Nile Valley. The Nile Valley is marked by a complex colonial history and long-standing archaeological interest from a range of national and international actors. It is also a vital corridor for understanding human dispersals out of and into Africa, and along the North African coastal zone. As Leplongeon usefully reviews, early researchers have, as elsewhere, proposed a variety of archaeological cultures, the legacies of which still weigh in on contemporary discussions. In the Nile Valley, these are the Kubbaniyan (23.5-19.3 ka cal. BP), the Halfan (24-19 ka cal. BP), the Qadan (20.2-12 ka cal BP), the Afian (16.8-14 ka cal. BP) and the Isnan (16.6-13.2 ka cal. BP) but their temporal and spatial signatures remain in part poorly constrained, or their epistemic status debated. Leplongeon’s critical and timely chronicle of this debate highlights in particular the vital contributions of the many female prehistorians who have worked in the region – Angela Close (e.g. 1978; 1977) and Maxine Kleindienst (e.g. 2006) to name just a few of the more recent ones – and whose earlier work had already addressed, if not even solved many of the pressing cultural taxonomic issues that beleaguer the Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age record of this region. Leplongeon and colleagues (Leplongeon et al. 2020; Mesfin et al. 2020) have contributed themselves substantially to new cultural taxonomic research in the wider region, showing how novel quantitative methods coupled with research-historical acumen can flag up and overcome the shortcomings of previous systematics. Yet, as Leplongeon also notes, the cultural taxonomic framework for the Nile Valley specifically has proven rather robust and does seem to serve its purpose as a broad chronological shorthand well. By the same token, she urges due caution when it comes to interpreting these lithic-based taxonomic units in terms of past social groups. Cultural systematics are essential for such interpretations, but age-old frameworks are often not fit for this purpose. New work by Leplongeon is likely to not only continue the long tradition of female prehistorians working in the Nile Valley but also provides an epistemologically and empirically more robust platform for understanding the social and ecological dynamics of Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age communities there.
Bibliography Close, Angela E. 1977. The Identification of Style in Lithic Artefacts from North East Africa. Mémoires de l’Institut d’Égypte 61. Cairo: Geological Survey of Egypt. Close, Angela E. 1978. “The Identification of Style in Lithic Artefacts.” World Archaeology 10 (2): 223–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00438243.1978.9979732 Ivanovaitė, Livija, Serwatka, Kamil, Steven Hoggard, Christian, Sauer, Florian and Riede, Felix. 2020. “All These Fantastic Cultures? Research History and Regionalization in the Late Palaeolithic Tanged Point Cultures of Eastern Europe.” European Journal of Archaeology 23 (2): 162–85. https://doi.org/10.1017/eaa.2019.59 Kleindienst, M. R. 2006. “On Naming Things: Behavioral Changes in the Later Middle to Earlier Late Pleistocene, Viewed from the Eastern Sahara.” In Transitions Before the Transition. Evolution and Stability in the Middle Paleolithic and Middle Stone Age, edited by E. Hovers and Steven L. Kuhn, 13–28. New York, NY: Springer. Leplongeon, Alice. 2023. “Tool Types and the Establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) Cultural Taxonomic System in the Nile Valley.” https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8115202 Leplongeon, Alice, Ménard, Clément, Bonhomme, Vincent and Bortolini, Eugenio. 2020. “Backed Pieces and Their Variability in the Later Stone Age of the Horn of Africa.” African Archaeological Review 37 (3): 437–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10437-020-09401-x Lyman, R. Lee. 2021. “On the Importance of Systematics to Archaeological Research: The Covariation of Typological Diversity and Morphological Disparity.” Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology 4 (1): 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-021-00077-6 Mesfin, Isis, Leplongeon, Alice, Pleurdeau, David, and Borel, Antony. 2020. “Using Morphometrics to Reappraise Old Collections: The Study Case of the Congo Basin Middle Stone Age Bifacial Industry.” Journal of Lithic Studies 7 (1): 1–38. https://doi.org/10.2218/jls.4329 Plutniak, Sébastien. 2022. “What Makes the Identity of a Scientific Method? A History of the ‘Structural and Analytical Typology’ in the Growth of Evolutionary and Digital Archaeology in Southwestern Europe (1950s–2000s).” Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology 5 (1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-022-00119-7 Reynolds, Natasha, and Riede, Felix. 2019. “House of Cards: Cultural Taxonomy and the Study of the European Upper Palaeolithic.” Antiquity 93 (371): 1350–58. https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2019.49 Wilkins, Jayne. 2020. “Is It Time to Retire NASTIES in Southern Africa? Moving Beyond the Culture-Historical Framework for Middle Stone Age Lithic Assemblage Variability.” Lithic Technology 45 (4): 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/01977261.2020.1802848 | Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile Valley | Alice Leplongeon | <p>Research on the prehistory of the Nile Valley has a long history dating back to the late 19th century. But it is only between the 1960s and 1980s, that numerous cultural entities were defined based on tool and core typologies; this habit stoppe... |  | Africa, Lithic technology, Upper Palaeolithic | Felix Riede | 2023-03-08 19:25:28 | View | |
14 Nov 2022
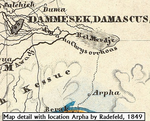
Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman CityJens Kleb https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021Cross-comparison of classical sources, explorer and scientific reports and maps in the search of an ancient city: The example of Raphana of the DecapolisRecommended by Luc Doyon based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli
Establishing the precise location of ancient cities constitutes a challenging task that requires the implementation of multi-disciplinary approaches. In his manuscript entitled “Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha: The search of an eminent Greco-Roman city”, Kleb (2022) proposes a convincing argument building on in-depth research of classical literary sources, literature review of explorer accounts and scientific publications from the 19th and 20th century as well as analysis of old and new maps, aerial photographs, and satellite images. This research report clearly emphasizes the importance of undertaking systematic interdisciplinary work on the topic to mitigate the uncertainties associated with the identification of Raphana, the Decapolis city first mentioned by Pliny the Elder. The Decapolis refers to a group of ten cities of Hellenistic traditions located on the eastern borders of the Roman Empire. This group of cities plays an important role in research that aims to contextualize the Judaean and Galilean history and to investigate urban centers in which different local and Greco-Roman influences met (Lichtenberger, 2021). While the location of most of the Decapolis cities is known and is (or was) subjected to systematic archaeological investigations (e.g., Eisenberg and Kowalewska, 2022; Makhadmeh et al., 2020; Shiyab et al., 2019), the location of others remain speculative. This is the case of Raphana for which the precise location remains difficult to establish owing in part to numerous name changes, limited information on the city structure, architecture, and size, etc. The research presented by Kleb (2022) has some merits, which is emphasized here, although the report is presented in an unusual format compared to traditional scientific articles, i.e., introduction, research background, methodology, results, and discussion. First, the extensive review of classical works allows the reader to gain a historical perspective on the change of names from Raepta/Raphana to Arpha/Arefa. The author argues these different names likely refer to a single location. Second, the author combs through an impressive literature from the 19th and 20th century and emphasize how some assumptions by explorers who visited the region were introduced in the scientific literature and remained unchallenged. Finally, the author gathers a remarkable quantity of old and new maps of the Golan, el-Ledja and Hauran regions and compare them with multiple lines of evidence to hypothesize that the location of Raphana may lie near Ar-Rafi’ah, also known as Bir Qassab, in the Ard el Fanah plain, a conclusion that now requires to be tested through fieldwork investigations. References Kleb, J. (2022) Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City. Figshare, 20550021, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021 Eisenberg, M. and Kowalewska, A. (2022). Funerary podia of Hippos of the Decapolis and the phenomenon in the Roman world. J. Roman Archaeol. 35, 107–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047759421000465 Lichtenberger, A. (2021). The Decapolis, in: A Companion to the Hellenistic and Roman Near East. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119037354.ch18 Makhadmeh, A., Al-Badarneh, M., Rawashdeh, A. and Al-Shorman, A. (2020). Evaluating the carrying capacity at the archaeological site of Jerash (Gerasa) using mathematical GIS modeling. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 23, 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.09.002 Shiyab, A., Al-Shorman, A., Turshan, N., Tarboush, M., Alawneh, F. and Rahabneh, A. (2019). Investigation of late Roman pottery from Gadara of the Decapolis, Jordan using multi-methodic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 25, 100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2019.04.003 | Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City | Jens Kleb | <p style="text-align: justify;">This research paper presents a detailed analysis of ancient literature and archaeological and geographical research until the present day for an important ancient location in the southern part of Syria. This one had... |  | Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Luc Doyon | 2021-12-30 13:54:32 | View | |
29 Aug 2023
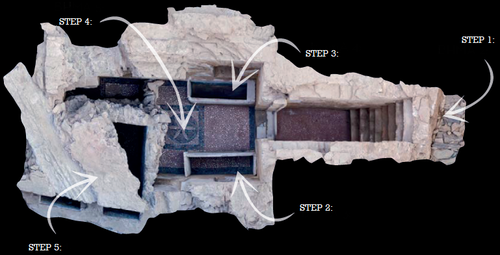
Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious GamesTsaknaki, Electra; Anastasovitis, Eleftherios; Georgiou, Georgia; Alagialoglou, Kleopatra; Mavrokostidou, Maria; Kartsiakli, Vasiliki; Aidonis, Asterios; Protopsalti, Tania; Nikolopoulos, Spiros; Kompatsiaris, Ioannis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981323AR and VR Gamification as a proof-of-conceptRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Sophie C. Schmidt and Tine Rassalle based on reviews by Sophie C. Schmidt and Tine Rassalle
Tsaknaki et al. (2023) discuss a work-in-progress project in which the presentation of Cultural Heritage is communicated using Serious Games techniques in a story-centric immersive narration instead of an exhibit-centered presentation with the use of Gamification, Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies. In the introduction the authors present the project called ECHOES, in which knowledge about the past of Thessaloniki, Greece is planned to be processed as an immersive and interactive experience. After presenting related work and the methodology, the authors describe the proposed design of the Serious Game and close the article with a discussion and conclusions. The paper is interesting because it highlights an ongoing process in the realm of the visualization of Cultural Heritage (see for example Champion 2016). The process described by the authors on how to accomplish this by using Serious Games, Gamification, Augmented and Virtual Reality is promising, although still hypothetical as the project is ongoing. It remains to be seen if the proposed visuals and interactive elements will work in the way intended and offer users an immersive experience after all. A preliminary questionnaire already showed that most of the respondents were not familiar with these technologies (AR, VR) and in my experience these numbers only change slowly. One way to overcome the technological barrier however might be the gamification of the experience, which the authors are planning to implement. I decided to recommend this article based on the remarks of the two reviewers, which the authors implemented perfectly, as well as my own evaluation of the paper. Although still in progress it seems worthwhile to have this article as a basis for discussion and comparison to similar projects. However, the article did not mention the possible longevity of data and in which ways the usability of the Serious Game will be secured for long-term storage. One eminent problem in these endeavors is, that we can read about these projects, but never find them anywhere to test them ourselves (see for example Gabellone et al. 2016). It is my intention with this review and the recommendation, that the ECHOES project will find a solution for this problem and that we are not only able to read this (and forthcoming) article(s) about the ECHOES project, but also play the Serious Game they are proposing in the near and distant future. References
Gabellone, Francesco, Antonio Lanorte, Nicola Masini, und Rosa Lasaponara. 2016. „From Remote Sensing to a Serious Game: Digital Reconstruction of an Abandoned Medieval Village in Southern Italy“. Journal of Cultural Heritage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2016.01.012 Tsaknaki, Electra, Anastasovitis, Eleftherios, Georgiou, Georgia, Alagialoglou, Kleopatra, Mavrokostidou, Maria, Kartsiakli, Vasiliki, Aidonis, Asterios, Protopsalti, Tania, Nikolopoulos, Spiros, and Kompatsiaris, Ioannis. (2023). Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious Games, Zenodo, 7981323, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981323 | Designing Stories from the Grave: Reviving the History of a City through Human Remains and Serious Games | Tsaknaki, Electra; Anastasovitis, Eleftherios; Georgiou, Georgia; Alagialoglou, Kleopatra; Mavrokostidou, Maria; Kartsiakli, Vasiliki; Aidonis, Asterios; Protopsalti, Tania; Nikolopoulos, Spiros; Kompatsiaris, Ioannis | <p>The main challenge of the current digital transition is to utilize computing media and cutting-edge technologyin a more meaningful way, which would make the archaeological and anthropological research outcomes relevant to a heterogeneous audien... |  | Bioarchaeology, Computational archaeology, Europe | Sebastian Hageneuer | 2023-05-29 13:19:46 | View | |
15 Aug 2021
Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, IndiaNorbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675An insight into traditional method of food production in IndiaRecommended by Otis Crandell based on reviews by Antony Borel, Atefeh Shekofteh, Andrea Squitieri, Birgül Ögüt, Atefe Shekofte and 1 anonymous reviewerThis paper [1] covers an interesting topic in that it presents through ethnography an insight into a traditional method of food production which is gradually declining in use. In addition to preserving traditional knowledge, the ethnographic study of grinding stones has the potential for showing how similar tools may have been used by people in the past, particularly from the same geographic region. [1] Thongdok Norbu J., Nimasow Gibji, Nimasow Oyi D. (2021) Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Zenodo, 5118675, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeo. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675 | Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India | Norbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow | <p style="text-align: justify;">The Shertukpens are an Indigenous tribal group inhabiting the western and southern parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Northeast India. They are accomplished carvers of carving wood and stone. The paper aims to document the... | Antiquity, Asia, Environmental archaeology, Lithic technology, Peopling, Raw materials | Otis Crandell | 2021-02-10 10:26:12 | View | ||
02 May 2023
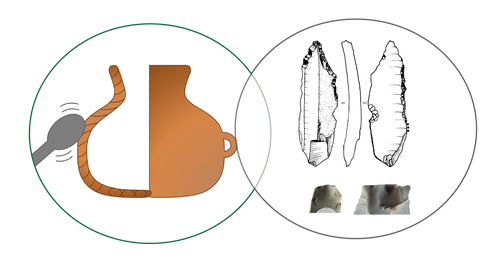
Transmission of lithic and ceramic technical know-how in the Early Neolithic of central-western Europe: Shedding Light on the Social Mechanisms underlying Cultural TransitionSolène Denis, Louise Gomart, Laurence Burnez-Lanotte, Pierre Allard https://osf.io/gqnht/A Thought Provoking Consideration of Craft in the NeolithicRecommended by Clare Burke based on reviews by Bogdana Milić and 1 anonymous reviewerThe pioneering work of Leroi-Gourhan introduced archaeologists to the concept of the chaîne opératoire[1], whereby, like his supervisor Mauss[2], Leroi-Gourhan proposed direct links between bodily actions and aspects of cultural identity. The chaîne opératoire offers a powerful conceptual tool with which to reconstruct and describe the technological practices undertaken by craftspeople, linking material objects to the cultural context in which crafts are learnt. Although initially applied to lithics, the concept today is well known in ceramic studies, as well as, other material crafts, in order to identify aspects of tradition and identity through ideas linked to technological style[3,4] and communities of practice[5]. Utilizing this approach, Denis et al.[6] use the chaîne opératoire to look at both lithics and ceramics together from a diachronic viewpoint, to examine technical systems present over the transition between Linearbandkeramic (LBK) and post LBK Blicquy/Villeneuve-Saint German (BQY/VSG) timeframes. This much needed comparative and diachronic perspective, focuses on material from the sites of Vaux-et-Borset and Verlaine in Belgium, and has enabled the authors to consider the impact of changing social dynamics on these two crafts simultaneously. The authors examine the ceramic and lithic assemblages from a macroscopic and morphological perspective in order to identify techniques of production. The data gathered testifies to the dominance of one production technique for each craft within the LBK. There is particularly striking homogeneity noted for the lithics that suggests the transmission of a single tradition over the Hesbaye area, whilst the ceramics display greater regional diversity. The picture alters somewhat for the BQY/VSG material where it seems there is an increase in the diversity of production techniques, with both the introduction of new techniques, as well as a degree of hybridization of earlier techniques to form new BQY/VSG chaînes opératoires that have LBK roots. The BQY/VSG diversity noted for the lithics is especially interesting, with the introduction of techniques that attest to increased expertise which the authors attest to the migration of an external group. The results of this work have allowed Denis et al. to discuss multiple influences on the technical systems they identify. Rather than trying to fit the data within a single model, the authors demonstrate the need for nuance, considering the social changes associated with Neolithic migration and interactions, as multifaced and dynamic. As such, they are able to show not only the influence of contact with other groups, but that the apparent migration of external groups does not simply lead to the replacement of the crafting heritage already established at the sites they have examined. In concluding the authors acknowledge, that as scholars push the existing state of knowledge (in this respect analysis of raw materials would make an especially important contribution), the picture presented in the paper may alter. Future work will hopefully fill in current gaps, particularly in terms of how far the trends identified extend, and the extent to which the lithic and ceramic pictures diversify on a broader geographical scale. It is certain that based on such results, future work should adopt the comparative approach presented by the authors, who have demonstrated its explanatory potential for understanding the technical and cultural groups we all study. [2] Mauss, M. 2009 [1934]. Techniques, Technology and Civilisation. Edited and introduced by N. Schlanger. New York/Oxford: Durkheim Press/Berghahn Books. [3] Lechtman, H. 1977. Style in Technology: some early thoughts. In H. Lechtman and R.S. Merrill (eds.) Material Culture: styles, organization and dynamics of technology. Proceedings of the American Ethnological Society 1975, St. Paul, 3-20. [4] Gosselain, O. 1992. Technology and Style: Potters and Pottery Among Bafia of Cameroon. Man 27(3) 559- 586. htpps://doi.org/10.2307/2803929. [5] Wenger, E. 1998. Communities of practice: Learning, meaning, and identity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [6] Denis, S., Gomart, L., Burnez-Lanotte, L. and Allard, P. (2023). Transmission of lithic and ceramic technical know-how in the Early Neolithic of central-western Europe: Shedding Light on the Social Mechanisms underlying Cultural Transition. OSF Preprints, gqnht, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/gqnht
| Transmission of lithic and ceramic technical know-how in the Early Neolithic of central-western Europe: Shedding Light on the Social Mechanisms underlying Cultural Transition | Solène Denis, Louise Gomart, Laurence Burnez-Lanotte, Pierre Allard | <p>Research on the European Neolithisation agrees that a process of colonisation throughout the sixth millennium BC underlies the spread of agricultural ways of life on the continent. From central to central-western Europe, this colonisation path ... |  | Ceramics, Europe, Lithic technology, Neolithic | Clare Burke | 2022-11-18 12:03:55 | View | |
03 Nov 2023
Multiproxy analysis exploring patterns of diet and disease in dental calculus and skeletal remains from a 19th century Dutch populationBartholdy, Bjørn Peare; Hasselstrøm, Jørgen B.; Sørensen, Lambert K.; Casna, Maia; Hoogland, Menno; Historisch Genootschap Beemster; Henry, Amanda G. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7649150Detection of plant-derived compounds in XIXth c. Dutch dental calculusRecommended by Louise Le Meillour based on reviews by Mario Zimmerman and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Mario Zimmerman and 2 anonymous reviewers
The advent of biomolecular methods has certainly increased our overall comprehension of archaeological societies. One of the materials of choice to perform ancient DNA or proteomics analyses is dental calculus[1,2], a mineralised biofilm formed during the life of one individual. Research conducted in the past few decades has demonstrated the potential of dental calculus to retrieve information about past societies health[3–6], diet[7–11], and more recently, as a putative proxy for isotopic analyses[12].
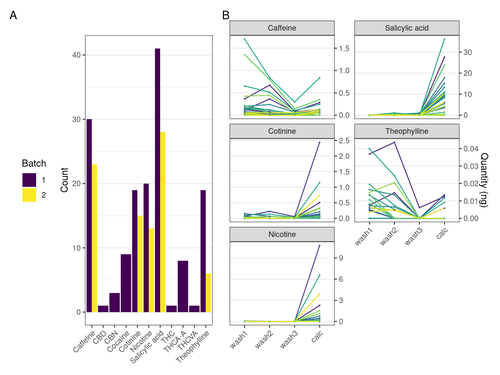
Bartholdy et al. utilised the developed LC-MS/MS method to 41 buried individuals, most of them bearing pipe notches on their teeth, from the cemetery of the 19th rural settlement of Middenbeemster, the Netherlands. Along with dental calculus sampling and analysis, they undertook the skeletal and dental examination of all of the specimens in order to assess sex, age-at-death, and pathology on the two tissues. The results obtained on the dental calculus of the sampled individuals show probable consumption of tea, coffee and tobacco indicated by the detection of the various plant compounds and associated metabolites (caffeine, nicotine and salicylic acid, amongst others). The authors were able to place their results in perspective and propose several interpretations concerning the ingestion of plant-derived products, their survival in dental calculus and the importance of their findings for our overall comprehension of health and habits of the XIXth c. Dutch population. The paper is well-written and accessible to a non-specialist audience, maximising the impact of their study. I personally really enjoyed handling this manuscript that is not only a good piece of scientific literature but also a pleasant read, the reason why I warmly recommend this paper to be accessible through PCI Archaeology. References 1. Fagernäs, Z. and Warinner, C. (2023) Dental Calculus. in Handbook of Archaeological Sciences 575–590. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119592112.ch28 2. Wright, S. L., Dobney, K. & Weyrich, L. S. (2021) Advancing and refining archaeological dental calculus research using multiomic frameworks. STAR: Science & Technology of Archaeological Research 7, 13–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/20548923.2021.1882122 3. Fotakis, A. K. et al. (2020) Multi-omic detection of Mycobacterium leprae in archaeological human dental calculus. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 375, 20190584. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0584 4. Warinner, C. et al. (2014) Pathogens and host immunity in the ancient human oral cavity. Nat. Genet. 46, 336–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2906 5. Weyrich, L. S. et al. (2017) Neanderthal behaviour, diet, and disease inferred from ancient DNA in dental calculus. Nature 544, 357–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21674 6. Jersie-Christensen, R. R. et al. (2018) Quantitative metaproteomics of medieval dental calculus reveals individual oral health status. Nat. Commun. 9, 4744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07148-3 7. Hendy, J. et al. (2018) Proteomic evidence of dietary sources in ancient dental calculus. Proc. Biol. Sci. 285. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.0977 8. Wilkin, S. et al. (2020) Dairy pastoralism sustained eastern Eurasian steppe populations for 5,000 years. Nat Ecol Evol 4, 346–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-020-1120-y 9. Bleasdale, M. et al. (2021) Ancient proteins provide evidence of dairy consumption in eastern Africa. Nat. Commun. 12, 632. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20682-3 10. Warinner, C. et al. (2014) Direct evidence of milk consumption from ancient human dental calculus. Sci. Rep. 4, 7104. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07104 11. Buckley, S., Usai, D., Jakob, T., Radini, A. and Hardy, K. (2014) Dental Calculus Reveals Unique Insights into Food Items, Cooking and Plant Processing in Prehistoric Central Sudan. PLoS One 9, e100808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100808 12. Salazar-García, D. C., Warinner, C., Eerkens, J. W. and Henry, A. G. (2023) The Potential of Dental Calculus as a Novel Source of Biological Isotopic Data. in Exploring Human Behavior Through Isotope Analysis: Applications in Archaeological Research (eds. Beasley, M. M. & Somerville, A. D.) 125–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-32268-6_6 13. Sørensen, L. K., Hasselstrøm, J. B., Larsen, L. S. and Bindslev, D. A. (2021) Entrapment of drugs in dental calculus - Detection validation based on test results from post-mortem investigations. Forensic Sci. Int. 319, 110647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2020.110647 14. Bartholdy, Bjørn Peare, Hasselstrøm, Jørgen B., Sørensen, Lambert K., Casna, Maia, Hoogland, Menno, Historisch Genootschap Beemster and Henry, Amanda G. (2023) Multiproxy analysis exploring patterns of diet and disease in dental calculus and skeletal remains from a 19th century Dutch population, Zenodo, 7649150, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7649150 | Multiproxy analysis exploring patterns of diet and disease in dental calculus and skeletal remains from a 19th century Dutch population | Bartholdy, Bjørn Peare; Hasselstrøm, Jørgen B.; Sørensen, Lambert K.; Casna, Maia; Hoogland, Menno; Historisch Genootschap Beemster; Henry, Amanda G. | <p>Dental calculus is an excellent source of information on the dietary patterns of past populations, including consumption of plant-based items. The detection of plant-derived residues such as alkaloids and their metabolites in dental calculus pr... |  | Bioarchaeology, Post-medieval | Louise Le Meillour | Mario Zimmerman, Anonymous | 2023-07-31 17:21:40 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










