Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▼ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
13 Jan 2024

Dealing with post-excavation data: the Omeka S TiMMA web-databaseBastien Rueff https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7989904Managing Archaeological Data with Omeka SRecommended by Jonathan Hanna based on reviews by Electra Tsaknaki and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Electra Tsaknaki and 1 anonymous reviewer
Managing data in archaeology is a perennial problem. As the adage goes, every day in the field equates to several days in the lab (and beyond). For better or worse, past archaeologists did all their organizing and synthesis manually, by hand, but since the 1970s ways of digitizing data for long term management and analysis have gained increasing attention [1]. It is debatable whether this ever actually made things easier, particularly given the associated problem of sustainable maintenance and accessibility of the data. Many older archaeologists, for instance, still have reels and tapes full of data that now require a new form of archaeology to excavate (see [2] for an unrealized idea on how to solve this). Today, the options for managing digital archaeological data are limited only by one’s imagination. There are systems built specifically for archaeology, such as Arches [3], Ark [4], Codifi [5], Heurist [6], InTerris Registries [7], OpenAtlas [8], S-Archeo [9], and Wild Note [10], as well as those geared towards museum collections like PastPerfect [11] and CatalogIt [12], among others. There are also mainstream databases that can be adapted to archaeological needs like MS Access [13] and Claris FileMaker [14], as well as various web database apps that function in much the same way (e.g., Caspio [15], dbBee [16], Amazon's Simpledb [17], Sci-Note [18], etc.) — all with their own limitations in size, price, and utility. One could also write the code for specific database needs using pre-built frameworks like those in Ruby-On-Rails [19] or similar languages. And of course, recent advances in machine-learning and AI will undoubtedly bring new solutions in the near future. But let’s be honest — most archaeologists probably just use Excel. That's partly because, given all the options, it is hard to decide the best tool and whether its worth changing from your current system, especially given few real-world examples in the literature. Bastien Rueff’s new paper [20] is therefore a welcomed presentation on the use of Omeka S [21] to manage data collected for the Timbers in Minoan and Mycenaean Architecture (TiMMA) project. Omeka S is an open-source web-database that is based in PHP and MySQL, and although it was built with the goal of connecting digital cultural heritage collections with other resources online, it has been rarely used in archaeology. Part of the issue is that Omeka Classic was built for use on individual sites, but this has now been scaled-up in Omeka S to accommodate a plurality of sites. Some of the strengths of Omeka S include its open-source availability (accessible regardless of budget), the way it links data stored elsewhere on the web (keeping the database itself lean), its ability to import data from common file types, and its multi-lingual support. The latter feature was particularly important to the TiMAA project because it allowed members of the team (ranging from English, Greek, French, and Italian, among others) to enter data into the system in whatever language they felt most comfortable. However, there are several limitations specific to Omeka S that will limit widespread adoption. Among these, Omeka S apparently lacks the ability to export metadata, auto-fill forms, produce summations or reports, or provide basic statistical analysis. Its internal search capabilities also appear extremely limited. And that is not to mention the barriers typical of any new software, such as onerous technical training, questionable long-term sustainability, or the need for the initial digitization and formatting of data. But given the rather restricted use-case for Omeka S, it appears that this is not a comprehensive tool but one merely for data entry and storage that requires complementary software to carry out common tasks. As such, Rueff has provided a review of a program that most archaeologists will likely not want or need. But if one was considering adopting Omeka S for a project, then this paper offers critical information for how to go about that. It is a thorough overview of the software package and offers an excellent example of its use in archaeological practice.
[1] Doran, J. E., and F. R. Hodson (1975) Mathematics and Computers in Archaeology. Harvard University Press. [2] Snow, Dean R., Mark Gahegan, C. Lee Giles, Kenneth G. Hirth, George R. Milner, Prasenjit Mitra, and James Z. Wang (2006) Cybertools and Archaeology. Science 311(5763):958–959. [3] https://www.archesproject.org/ [4] https://ark.lparchaeology.com/ [5] https://codifi.com/ [6] https://heuristnetwork.org/ [7] https://www.interrisreg.org/ [8] https://openatlas.eu/ [9] https://www.skinsoft-lab.com/software/archaelogy-collection-management [10] https://wildnoteapp.com/ [11] https://museumsoftware.com/ [12] https://www.catalogit.app/ [13] https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/access [14] https://www.claris.com/filemaker/ [15] https://www.caspio.com/ [16] https://www.dbbee.com/ [17] https://aws.amazon.com/simpledb/ [18] https://www.scinote.net/ [19] https://rubyonrails.org/ [20] Rueff, Bastien (2023) Dealing with Post-Excavation Data: The Omeka S TiMMA Web-Database. peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://zenodo.org/records/7989905 [21] https://omeka.org/
| Dealing with post-excavation data: the Omeka S TiMMA web-database | Bastien Rueff | <p>This paper reports on the creation and use of a web database designed as part of the TiMMA project with the Content Management System Omeka S. Rather than resulting in a technical manual, its goal is to analyze the relevance of using Omeka S in... |  | Buildings archaeology, Computational archaeology | Jonathan Hanna | 2023-05-31 12:16:25 | View | |
02 Apr 2024
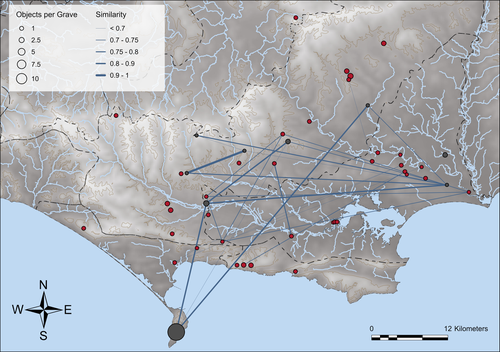
Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological DatasetsTimo Geitlinger https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239A different approach to similarity networks in Archaeology - Similarity Network FusionRecommended by Joel Santos based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewerThis is a fascinating paper for anyone interested in network analysis or the chronology and cultures of the case study, namely the Late prehistoric burial sites in Dorset, for which the author’s approach allowed a new perspective over an already deeply studied area [1]. This paper's implementation of Similarity Network Fusion (SNF) is noteworthy. This method is typically utilized within genetic research but has yet to be employed in Archaeology. SNF has the potential to benefit Archaeology due to its unique capabilities and approach significantly. The author exhibits a deep and thorough understanding of previous investigations concerning material and similarity networks while emphasizing the innovative nature of this particular study. The SNF approach intends to improve a lack of the most used (in Archaeology) similarity coefficient, the Brainerd-Robinson, in certain situations, mainly in heterogenous and noisy datasets containing a small number of samples but a large number of measurements, scale differences, and collection biases, among other things. The SNF technique, demonstrated in the case study, effectively incorporates various similarity networks derived from different datatypes into one network. As shown during the Dorset case study, the SNF application has a great application in archaeology, even in already available data, allowing us to go further and bring new visions to the existing interpretations. As stated by the author, SNF shows its potential for other applications and fields in archaeology coping with similar datasets, such as archaeobotany or archaeozoology, and seems to complement different multivariate statistical approaches, such as correspondence or cluster analysis. This paper has been subject to two excellent revisions, which the author mostly accepted. One of the revisions was more technical, improving the article in the metadata part, data availability and clarification, etc. Although the second revision was more conceptual and gave some excellent technical inputs, it focused more on complementary aspects that will allow the paper to reach a wider audience. I vividly recommend its publication. References [1] Geitlinger, T. (2024). Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets. Zenodo, 7998239, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239
| Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets | Timo Geitlinger | <p>Since its earliest application in the 1970s, network analysis has become increasingly popular in both theoretical and GIS-based archaeology. Yet, applications of material networks remained relatively restricted. This paper describes a specific ... |  | Computational archaeology, Protohistory | Joel Santos | 2023-06-02 16:51:19 | View | |
02 Feb 2024

Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley CollectionRaykovska Miglena, Jones Kristen, Klecherova Hristina, Alexandrov Stefan, Petkov Nikolay, Hristova Tanya, Ivanov Georgi https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8027548Out of the storeroom and into the virtualRecommended by Jitte Waagen based on reviews by Alicia Walsh and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Alicia Walsh and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Raykovska et al. 2023) discusses the digital documentation techniques and development of a virtual exhibition for artefacts retrieved from the necropolis of Baley, Bulgaria. The principal aim of this particular project is a solid one, trying to provide a solution to display artefacts that would otherwise remain hidden in museum storerooms. The paper describes how through a combination of 3D scanning and photogrammetry high quality 3D models have been produced, and provide content for an online virtual exhibition for the scientific community but also the larger public. It is a well-written and concise paper, in which the information on developed methods and techniques are transparently described, and various important aspects of digitization workflows, such as the importance of storing raw data, are addressed. The paper is a timely discussion on this subject, as strategies to develop digital artefact collections and what to do with those are increasingly being researched. Specifically, it discusses a workflow and its results, both in great detail. Although critical reflection on the process, goals and results from various perspectives would have been a valuable addition to the paper (cf., Jeffra 2020, Paardekoper 2019), it nonetheless provides a good practice example of how to approach the creation of a virtual museum. Those who consider projects concerning digital documentation of archaeological artefacts as well as the creation of virtual spaces to use those in for research, education or valorisation purposes would do well to read this paper carefully. References Jeffra, C., Hilditch, J., Waagen, J., Lanjouw, T., Stoffer, M., de Gelder, L., and Kim, M. J. (2020). Blending the Material and the Digital: A Project at the Intersection of Museum Interpretation, Academic Research, and Experimental Archaeology. The EXARC Journal, 2020(4). https://exarc.net/ark:/88735/10541 Paardekooper, R.P. (2019). Everybody else is doing it, so why can’t we? Low-tech and High-tech approaches in archaeological Open-Air Museums. The EXARC Journal, 2019(4). https://exarc.net/ark:/88735/10457/ Raykovska, M., Jones, K., Klecherova, H., Alexandrov, S., Petkov, N., Hristova, T., and Ivanov, G. (2023). Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley Collection. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10091870 | Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley Collection | Raykovska Miglena, Jones Kristen, Klecherova Hristina, Alexandrov Stefan, Petkov Nikolay, Hristova Tanya, Ivanov Georgi | <p>Over the past decade, virtual reality has been quickly growing in popularity across disciplines including the field of archaeology and cultural heritage. Despite numerous artifacts being uncovered each year by archaeological excavations around ... |  | Ceramics, Computational archaeology, Conservation/Museum studies | Jitte Waagen | 2023-06-12 14:02:44 | View | |
12 Apr 2024
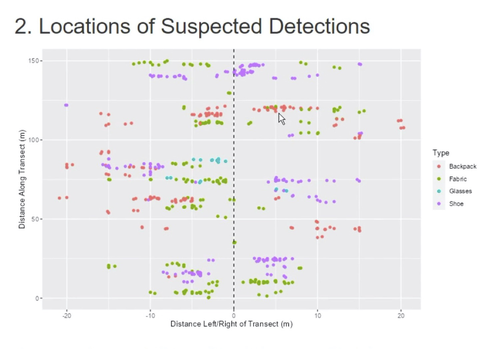
Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective SurveysE. B. Banning, Steven Edwards, and Isaac Ullah https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8072178A new tool to increase the robustness of archaeological field surveyRecommended by Jitte Waagen based on reviews by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas based on reviews by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas
This well-written and interesting paper ‘Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys’ deals with the development of a ‘modular, accessible, and simple web-based platform for survey planning and quality assurance’ in the area of pedestrian field survey methods (Banning et al. 2024). Although there have been excellent treatments of statistics in archaeological field survey (among which various by the first author: Banning 2020, 2021), and there is continuous methodological debate on platforms such as the International Mediterranean Survey Workshop (IMSW), in papers dealing with the current development and state of the field (Knodell et al. 2023), good practices (Attema et al. 2020) or the merits of a quantifying approach to archaeological densities (cf. de Haas et al. 2023), this paper rightfully addresses the lack of rigorous statistical approaches in archaeological field survey. As argued by several scholars such as Orton (2000), this mainly appears the result of lack of knowledge/familiarity/resources to bring in the required expertise etc. with the application of seemingly intricate statistics (cf. Waagen 2022). In this context this paper presents a welcome contribution to the feasibility of a robust archaeological field survey design. The SPACE application, under development by the authors, is introduced in this paper. It is a software tool that aims to provide different modules to assist archaeologists to make calculations for sample size, coverage, stratification, etc. under the conditions of survey goals and available resources. In the end, the goal is to ensure archaeological field surveys will attain their objectives effectively and permit more confidence in the eventual outcomes. The module concerning Sweep Widths, an issue introduced by the main author in 2006 (Banning 2006) is finished; the sweep width assessment is a methodology to calibrate one’s survey project for artefact types, landscape, visibility and person-bound performance, eventually increasing the quality (comparability) of the collected samples. This is by now a well-known calibration technique, yet little used, so this effort to make that more accessible is certainly laudable. An excellent idea, and another aim of this project, is indeed to build up a database with calibration data, so applying sweep-width corrections will become easier accessible to practitioners who lack time to set up calibration exercises. It will be very interesting to have a closer look at the eventual platform and to see if, and how, it will be adapted by the larger archaeological field survey community, both from an academic research perspective as from a heritage management point of view. I happily recommend this paper and all debate relating to it, including the excellent peer reviews of the manuscript by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas (available as part of this PCI recommendation procedure), to any practitioner of archaeological field survey. References Attema, P., Bintliff, J., Van Leusen, P.M., Bes, P., de Haas, T., Donev, D., Jongman, W., Kaptijn, E., Mayoral, V., Menchelli, S., Pasquinucci, M., Rosen, S., García Sánchez, J., Luis Gutierrez Soler, L., Stone, D., Tol, G., Vermeulen, F., and Vionis. A. 2020. “A guide to good practice in Mediterranean surface survey projects”, Journal of Greek Archaeology 5, 1–62. https://doi.org/10.32028/9781789697926-2 Banning, E.B., Alicia L. Hawkins, S.T. Stewart, Sweep widths and the detection of artifacts in archaeological survey, Journal of Archaeological Science, Volume 38, Issue 12, 2011, Pages 3447-3458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2011.08.007 Banning, E.B. 2020. Spatial Sampling. In: Gillings, M., Hacıgüzeller, P., Lock, G. (eds.) Archaeological Spatial Analysis. A Methodological Guide. Routledge. Banning, E.B. 2021. Sampled to Death? The Rise and Fall of Probability Sampling in Archaeology. American Antiquity, 86(1), 43-60. https://doi.org/10.1017/aaq.2020.39 Banning, E. B. Steven Edwards, & Isaac Ullah. (2024). Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys. Zenodo, 8072178, ver. 9 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8072178 Knodell, A.R., Wilkinson, T.C., Leppard, T.P. et al. 2023. Survey Archaeology in the Mediterranean World: Regional Traditions and Contributions to Long-Term History. J Archaeol Res 31, 263–329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10814-022-09175-7 Orton, C. 2000. Sampling in Archaeology. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139163996 Waagen, J. 2022. Sampling past landscapes. Methodological inquiries into the bias problems of recording archaeological surface assemblages. PhD-Thesis. https://hdl.handle.net/11245.1/e9cb922c-c7e4-40a1-b648-7b8065c46880 de Haas, T., Leppard, T. P., Waagen, J., & Wilkinson, T. (2023). Myopic Misunderstandings? A Reply to Meyer (JMA 35(2), 2022). Journal of Mediterranean Archaeology, 36(1), 127-137. https://doi.org/10.1558/jma.27148 | Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys | E. B. Banning, Steven Edwards, and Isaac Ullah | <p>Designing an effective archaeological survey can be complicated and confidence that it was effective requires post-survey evaluation. The goal of SPACE is to develop software to facilitate survey designers’ decisions and partially automate tool... |  | Computational archaeology, Landscape archaeology | Jitte Waagen | 2023-06-28 13:42:28 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information SystemsEric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732Exploring The Role of Archaeological Information Systems in Improving Data Management and InteroperabilityRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In response to the feedback provided by the reviewers, the authors have undertaken a comprehensive revision of the manuscript [1]. These revisions have specifically targeted the primary concerns raised regarding the clarity and structure of the argument concerning the transformative impact of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) on archaeological practices. In my view the revised manuscript now more clearly articulates the distinction between internal and external interoperability and emphasizes the critical importance of integrating contextual information with archaeological data. This approach directly addresses the previously identified need for enhanced traceability and usability of archaeological data, ensuring that the manuscript's contributions to the field are both clear and impactful. Moreover, the application of the proposed model at the Bibracte site is illustrated with greater clarity, serving as a concrete example of how the challenges associated with documentation and data management can be effectively addressed through the methodologies proposed in the paper. This practical demonstration enriches the manuscript, providing readers with a much clearer understanding of the model's applicability and benefits in real-world archaeological practice. The authors have also made significant efforts to refine the overall structure and coherence of the manuscript. By making complex concepts more accessible and ensuring a cohesive narrative flow throughout, the manuscript now offers a more engaging and comprehensible read. This has been achieved through careful rephrasing and restructuring of sections, particularly those relating to the T!O model's application and the conclusion, thereby enhancing reader engagement and comprehension. Alongside these structural and conceptual clarifications, explicit discussion of potential areas for future research, not only acknowledges the limitations of the current study but also highlights the significant potential for digital technologies to contribute to archaeological methodology and knowledge production. As such, the manuscript opens up new avenues for exploration and invites further scholarly engagement with the topics it addresses. I believe, these revisions address the earlier feedback quite comprehensively, presenting a robust and compelling argument for the adoption of collaborative and technologically informed approaches in the field of archaeology. The manuscript now stands as a strong example of the critical role AIS could/should play in transforming archaeological practices, offering valuable insights into how these kinds of systems might enhance the management, accessibility, and understanding of archaeological data. Through this revised submission, the authors have significantly strengthened their contribution to the ongoing discourse on digital archaeology, demonstrating the practical and theoretical implications of their work for the broader archaeological community. I am happy, therefore to recommend this paper for acceptence. Reference [1] Lacombe, E., Lukas, D. and Durost, S. (2024). The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems. Zenodo, 8309732, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732
| The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems | Eric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost | <p>The adoption of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) evolves according to multiple factors, both human and technical, as well as endogenous and exogenous. In consequence the ever increasing scope of digital tools, which allow for the organi... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Protohistory, Theoretical archaeology | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 18:58:26 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of MeaningsYael Alef, Yuval Shafriri https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309992How Semantic Technologies and Spatial Networks Can Enhance Archaeological Resource ManagementRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by Dominik Lukas and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Dominik Lukas and 1 anonymous reviewer
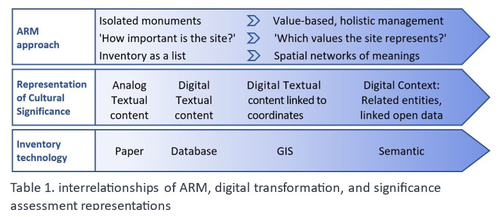
After a thorough review and consideration of the revised manuscript titled "Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text to Spatial Networks of Meanings" by Yael Alef and Yuval Shafriri [1], I am recommending the paper for publication. The authors have made significant strides in addressing the feedback from the initial review process, notably enhancing the manuscript's clarity, methodological detail, and overall contribution to the field of Archaeological Resource Management (ARM). On balance I think the paper competently navigates the shift from a traditional significance-focused assessment of isolated archaeological sites to a more holistic and interconnected approach, leveraging graph data models and spatial networks. This transition represents an advancement in the field, offering deeper insights into the sociocultural dynamics of archaeological sites. The case study of ancient synagogues in northern Israel, particularly the Huqoq Synagogue, serves as a compelling illustration of the potential of semantic technologies to enrich our understanding of cultural heritage. Significantly, the authors have responded to the call for a clearer methodological framework by providing a more detailed exposition of their use of knowledge graph visualization and semantic technologies. This response not only strengthens the paper's scientific rigor but also enhances its accessibility and applicability to a broader audience within the conservation and heritage management community. However, I do think it remains important to acknowledge areas where further work could enrich the paper's contribution. While the manuscript makes notable advancements in the technical and methodological domains, the exploration of the ethical and political implications of semantic technologies in ARM remains less developed. Recognizing the complex interplay of ethical and political considerations in archaeological assessments is crucial for the responsible advancement of the field. Thus, I suggest that future work could productively focus on these dimensions, offering a more comprehensive view of the implications of integrating semantic technologies into heritage management practices. I don't think that this omission is a reason to withold the paper for publication or seek further review. In fact I think it stands alone a paper quite well. Perhaps the authors might consider this as a complementary line of inquiry in their future work in the field. In conclusion then, I believe the revised manuscript represents a valuable addition to the literature, pushing boundaries of how we assess, understand, and manage archaeological resources. Its focus on semantic technologies and the creation of spatial networks of meanings marks a significant step forward in the field. I believe its publication will stimulate further research and discussion, particularly in the realms of ethical and political considerations, which remain ripe for exploration. Therefore, I'm happy to endorse the publication of this manuscript. Reference [1] Alef, Y and Shafriri, Y. (2024). Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of Meanings. Zenodo, 8309992, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309992 | Cultural Significance Assessment of Archaeological Sites for Heritage Management: From Text of Spatial Networks of Meanings | Yael Alef, Yuval Shafriri | <p>This study examines the shift towards a values-based approach for Archaeological Resource Management (ARM), emphasizing the integration of Context-Based Significance Assessment (CBSA) with semantic technologies into digital ARM inventories. We ... |  | Computational archaeology, Conservation/Museum studies, Spatial analysis | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 22:24:15 | View | |
23 Nov 2023
Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publicationSophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497Sharing Research Code in ArchaeologyRecommended by James Allison based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper “Percolation Package – From Script Sharing to Package Publication” by Sophie C. Schmidt and Simon Maddison (2023) describes the development of an R package designed to apply Percolation Analysis to archaeological spatial data. In an earlier publication, Maddison and Schmidt (2020) describe Percolation Analysis and provide case studies that demonstrate its usefulness at different spatial scales. In the current paper, the authors use their experience collaborating to develop the R package as part of a broader argument for the importance of code sharing to the research process. The paper begins by describing the development process of the R package, beginning with borrowing code from a geographer, refining it to fit archaeological case studies, and then collaborating to further refine and systematize the code into an R package that is more easily reusable by other researchers. As the review by Joe Roe noted, a strength of the paper is “presenting the development process as it actually happens rather than in an idealized form.” The authors also include a section about the lessons learned from their experience. Moving on from the anecdotal data of their own experience, the authors also explore code sharing practices in archaeology by briefly examining two datasets. One dataset comes from “open-archaeo” (https://open-archaeo.info/), an on-line list of open-source archaeological software maintained by Zack Batist. The other dataset includes articles published between 2018 and 2023 in the Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology. Schmidt and Maddison find that these two datasets provide contrasting views of code sharing in archaeology: many of the resources in the open-archaeo list are housed on Github, lack persistent object identifiers, and many are not easily findable (other than through the open-archaeo list). Research software attached to the published articles, on the other hand, is more easily findable either as a supplement to the published article, or in a repository with a DOI. The examination of code sharing in archaeology through these two datasets is preliminary and incomplete, but it does show that further research into archaeologists’ code-writing and code-sharing practices could be useful. Archaeologists often create software tools to facilitate their research, but how often? How often is research software shared with published articles? How much attention is given to documentation or making the software usable for other researchers? What are best (or good) practices for sharing code to make it findable and usable? Schmidt and Maddison’s paper provides partial answers to these questions, but a more thorough study of code sharing in archaeology would be useful. Differences among journals in how often they publish articles with shared code, or the effects of age, gender, nationality, or context of employment on attitudes toward code sharing seem like obvious factors for a future study to consider. Shared code that is easy to find and easy to use benefits the researchers who adopt code written by others, but code authors also have much to gain by sharing. Properly shared code becomes a citable research product, and the act of code sharing can lead to productive research collaborations, as Schmidt and Maddison describe from their own experience. The strength of this paper is the attention it brings to current code-sharing practices in archaeology. I hope the paper will also help improve code sharing in archaeology by inspiring more archaeologists to share their research code so other researchers can find and use (and cite) it. References Maddison, M.S. and Schmidt, S.C. (2020). Percolation Analysis – Archaeological Applications at Widely Different Spatial Scales. Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology, 3(1), p.269–287. https://doi.org/10.5334/jcaa.54 Schmidt, S. C., and Maddison, M. S. (2023). Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication, Zenodo, 7966497, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497 | Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication | Sophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison | <p>In this paper we trace the development of an R-package starting with the adaptation of code from a different field, via scripts shared between colleagues, to a published package that is being successfully used by researchers world-wide. Our aim... |  | Computational archaeology | James Allison | 2023-05-24 15:40:15 | View | |
19 Feb 2024
Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias ReductionFumihiro Sakahira, Hiro’omi Tsumura https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7969330Evaluating Methods for Reducing Sampling Bias in Network AnalysisRecommended by James Allison based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewer
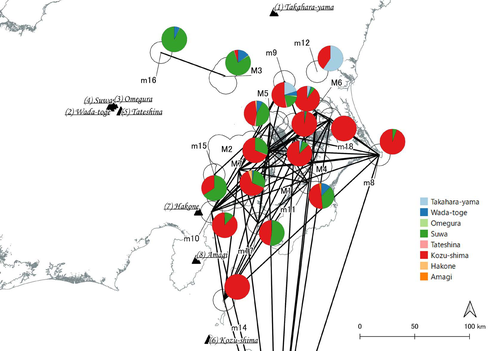
In a recent article, Fumihiro Sakahira and Hiro'omi Tsumura (2023) used social network analysis methods to analyze change in obsidian trade networks in Japan throughout the 13,000-year-long Jomon period. In the paper recommended here (Sakahira and Tsumura 2024), Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction they revisit that data and describe additional analyses that confirm the robustness of their social network analysis. The data, analysis methods, and substantive conclusions of the two papers overlap; what this new paper adds is a detailed examination of the data and methods, including use of bootstrap analysis to demonstrate the reasonableness of the methods they used to group sites into clusters. Both papers begin with a large dataset of approximately 21,000 artifacts from more than 250 sites dating to various times throughout the Jomon period. The number of sites and artifacts, varying sample sizes from the sites, as well as the length of the Jomon period, make interpretation of the data challenging. To help make the data easier to interpret and reduce problems with small sample sizes from some sites, the authors assign each site to one of five sub-periods, then define spatial clusters of sites within each period using the DBSCAN algorithm. Sites with at least three other sites within 10 km are joined into clusters, while sites that lack enough close neighbors are left as isolates. Clusters or isolated sites with sample sizes smaller than 30 were dropped, and the remaining sites and clusters became the nodes in the networks formed for each period, using cosine similarities of obsidian assemblages to define the strength of ties between clusters and sites. The main substantive result of Sakahira and Tsumura’s analysis is the demonstration that, during the Middle Jomon period (5500-4500 cal BP), clusters and isolated sites were much more connected than before or after that period. This is largely due to extensive distribution of obsidian from the Kozu-shima source, located on a small island off the Japanese mainland. Before the Middle Jomon period, Kozu-shima obsidian was mostly found at sites near the coast, but during the Middle Jomon, a trade network developed that took Kozu-shima obsidian far inland. This ended after the Middle Jomon period, and obsidian networks were less densely connected in the late and last Jomon periods. The methods and conclusions are all previously published (Sakahira and Tsumura 2023). What Sakahira and Tsumura add in Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction are: · an examination of the distribution of cosine similarities between their clusters for each period · a similar evaluation of the cosine similarities within each cluster (and among the unclustered sites) for each period · bootstrap analyses of the mean cosine similarities and network densities for each time period These additional analyses demonstrate that the methods used to cluster sites are reasonable, and that the use of spatially defined clusters as nodes (rather than the individual sites within the clusters) works well as a way of reducing bias from small, unrepresentative samples. An alternative way to reduce that bias would be to simply drop small assemblages, but that would mean ignoring data that could usefully contribute to the analysis. The cosine similarities between clusters show patterns that make sense given the results of the network analysis. The Middle Jomon period has, on average, the highest cosine similarities between clusters, and most cluster pairs have high cosine similarities, consistent with the densely connected, spatially expansive network from that time period. A few cluster pairs in the Middle Jomon have low similarities, apparently representing comparisons including one of the few nodes on the margins on the network that had little or no obsidian from the Kozu-shima source. The other four time periods all show lower average inter-cluster similarities and many cluster pairs have either high or low similarities. This probably reflects the tendency for nearby clusters to have very similar obsidian assemblages to each other and for geographically distant clusters to have dissimilar obsidian assemblages. The pattern is consistent with the less densely connected networks and regionalization shown in the network graphs. Thinking about this pattern makes me want to see a plot of the geographic distances between the clusters against the cosine similarities. There must be a very strong correlation, but it would be interesting to know whether there are any cluster pairs with similarities that deviate markedly from what would be predicted by their geographic separation. The similarities within clusters are also interesting. For each time period, almost every cluster has a higher average (mean and median) within-cluster similarity than the similarity for unclustered sites, with only two exceptions. This is partial validation of the method used for creating the spatial clusters; sites within the clusters are at least more similar to each other than unclustered sites are, suggesting that grouping them this way was reasonable. Although Sakahira and Tsumura say little about it, most clusters show quite a wide range of similarities between the site pairs they contain; average within-cluster similarities are relatively high, but many pairs of sites in most clusters appear to have low similarities (the individual values are not reported, but the pattern is clear in boxplots for the first four periods). There may be value in further exploring the occurrence of low site-to-site similarities within clusters. How often are they caused by small sample sizes? Clusters are retained in the analysis if they have a total of at least 30 artifacts, but clusters may contain sites with even smaller sample sizes, and small samples likely account for many of the low similarity values between sites in the same cluster. But is distance between sites in a cluster also a factor? If the most distant sites within a spatially extensive cluster are dissimilar, subdividing the cluster would likely improve the results. Further exploration of these within-cluster site-to-site similarity values might be worth doing, perhaps by plotting the similarities against the size of the smallest sample included in the comparison, as well as by plotting the cosine similarity against the distance between sites. Any low similarity values not attributable to small sample sizes or geographic distance would surely be worth investigating further. Sakahira and Tsumura also use a bootstrap analysis to simulate, for each time period, mean cosine similarities between clusters and between site pairs without clustering. They also simulate the network density for each time period before and after clustering. These analyses show that, almost always, mean simulated cosine similarities and mean simulated network density are higher after clustering than before. The simulated mean values also match the actual mean values better after clustering than before. This improved match to actual values when the sites are clustered for the bootstrap reinforces the argument that clustering the sites for the network analysis was a reasonable result. The strength of this paper is that Sakahira and Tsumura return to reevaluate their previously published work, which demonstrated strong patterns through time in the nature and extent of Jomon obsidian trade networks. In the current paper they present further analyses demonstrating that several of their methodological decisions were reasonable and their results are robust. The specific clusters formed with the DBSCAN algorithm may or may not be optimal (which would be unreasonable to expect), but the authors present analyses showing that using spatial clusters does improve their network analysis. Clustering reduces problems with small sample sizes from individual sites and simplifies the network graphs by reducing the number of nodes, which makes the results easier to interpret. Reference Sakahira, F. and Tsumura, H. (2023). Tipping Points of Ancient Japanese Jomon Trade Networks from Social Network Analyses of Obsidian Artifacts. Frontiers in Physics 10:1015870. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2022.1015870 Sakahira, F. and Tsumura, H. (2024). Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction, Zenodo, 10057602, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7969330 | Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction | Fumihiro Sakahira, Hiro’omi Tsumura | <p>This study aims to investigate the dynamics of obsidian trade networks during the Jomon period (approximately 15,000 to 2,400 years ago), the hunting and gathering era in Japan. To improve regional representation and reduce the distortions caus... |  | Asia, Computational archaeology | James Allison | Thegn Ladefoged, Matthew Peeples | 2023-05-28 05:51:12 | View |
02 Sep 2023

Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA ISDudek Iwona, Blaise Jean-Yves https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8311129Using information visualisation to improve traceability, transmissibility and verifiability in research workflowsRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by Adéla Sobotkova and 2 anonymous reviewersThe paper “Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS” (Dudek & Blaise, 2023) describes a prototype of an information system developed to improve the traceability, transmissibility and verifiability of archaeological research workflows. A key aspect of the work with MEMORIA is to make research documentation and the workflows underpinning the conducted research more approachable and understandable using a series of visual interfaces that allow users of the system to explore archaeological documentation, including metadata describing the data and paradata that describes its underlying processes. The work of Dudek and Blaise address one of the central barriers to reproducibility and transparency of research data and propose a set of both theoretically and practically well-founded tools and methods to solve this major problem. From the reported work on MEMORIA IS, information visualisation and the proposed tools emerge as an interesting and potentially powerful approach for a major push in improving the traceability, transmissibility and verifiability of research data through making research workflows easier to approach and understand. In comparison to technical work relating to archaeological data management, this paper starts commendably with a careful explication of the conceptual and epistemic underpinnings of the MEMORIA IS both in documentation research, knowledge organisation and information visualisation literature. Rather than being developed on the basis of a set of opaque assumptions, the meticulous description of the MEMORIA IS and its theoretical and technical premises is exemplary in its transparence and richness and has potential for a long-term impact as a part of the body of literature relating to the development of archaeological documentation and documentation tools. While the text is sometimes fairly densely written, it is worth taking the effort to read it through. Another major strength of the paper is that it provides a rich set of examples of the workings of the prototype system that makes it possible to develop a comprehensive understanding of the proposed approaches and assess their validity. As a whole, this paper and the reported work on MEMORIA IS forms a worthy addition to the literature on and practical work for developing critical infrastructures for data documentation, management and access in archaeology. Beyond archaeology and the specific context of the discussed work discussed this paper has obvious relevance to comparable work in other fields. ReferencesDudek, I. and Blaise, J.-Y. (2023) Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS, Zenodo, 8252923, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8252923
| Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS | Dudek Iwona, Blaise Jean-Yves | <p>The paper presents an exploratory web information system developed as a reaction to practical and epistemological questions, in the context of a scientific unit studying the architectural heritage (from both historical sciences perspective, and... |  | Computational archaeology | Isto Huvila | 2023-05-02 12:50:39 | View | |
06 Aug 2023
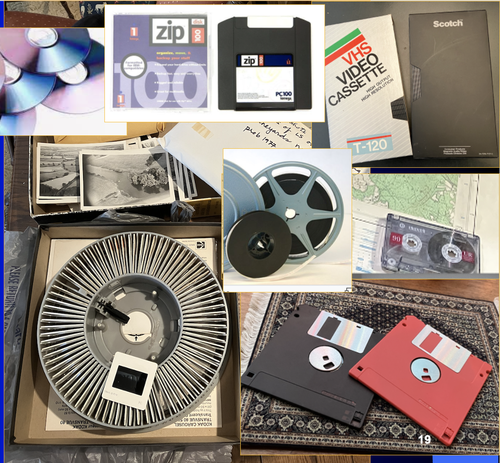

A Focus on the Future of our Tiny Piece of the Past: Digital Archiving of a Long-term Multi-participant Regional ProjectScott Madry, Gregory Jansen, Seth Murray, Elizabeth Jones, Lia Willcoxon, Ebtihal Alhashem https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7967035A meticulous description of archiving research data from a long-running landscape research projectRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann and Iwona DudekThe paper “A Focus on the Future of our Tiny Piece of the Past: Digital Archiving of a Long-term Multi-participant Regional Project” (Madry et al., 2023) describes practices, challenges and opportunities encountered in digital archiving of a landscape research project running in Burgundy, France for more than 45 years. As an unusually long-running multi-disciplinary undertaking working with a large variety of multi-modal digital and non-digital data, the Burgundy project has lived through the development of documentation and archiving technologies from the 1970s until today and faced many of the challenges relating to data management, preservation and migration. The major strenght of the paper is that it provides a detailed description of the evolution of digital data archiving practices in the project including considerations about why some approaches were tested and abandoned. This differs from much of the earlier literature where it has been more common to describe individual solutions how digital archiving was either planned or was performed at one point of time. A longitudinal description of what was planned, how and why it has worked or failed so far, as described in the paper, provides important insights in the everyday hurdles and ways forward in digital archiving. As a description of a digital archiving initiative, the paper makes a valuable contribution for the data archiving scholarship as a case description of practices and considerations in one research project. For anyone working with data management in a research project either as a researcher or data manager, the text provides useful advice on important practical matters to consider ahead, during and after the project. The main advice the authors are giving, is to plan and act for data preservation from the beginning of the project rather than doing it afterwards. To succeed in this, it is crucial to be knowledgeable of the key concepts of data management—such as “digital data fixity, redundant backups, paradata, metadata, and appropriate keywords” as the authors underline—including their rationale and practical implications. The paper shows also that when and if unexpected issues raise, it is important to be open for different alternatives, explore ways forward, and in general be flexible. The paper makes also a timely contribution to the discussion started at the session “Archiving information on archaeological practices and work in the digital environment: workflows, paradata and beyond” at the Computer Applications and Quantitative 2023 conference in Amsterdam where it was first presented. It underlines the importance of understanding and communicating the premises and practices of how data was collected (and made) and used in research for successful digital archiving, and the similar pertinence of documenting digital archiving processes to secure the keeping, preservation and effective reuse of digital archives possible. ReferencesMadry, S., Jansen, G., Murray, S., Jones, E., Willcoxon, L. and Alhashem, E. (2023) A Focus on the Future of our Tiny Piece of the Past: Digital Archiving of a Long-term Multi-participant Regional Project, Zenodo, 7967035, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7967035 | A Focus on the Future of our Tiny Piece of the Past: Digital Archiving of a Long-term Multi-participant Regional Project | Scott Madry, Gregory Jansen, Seth Murray, Elizabeth Jones, Lia Willcoxon, Ebtihal Alhashem | <p>This paper will consider the practical realities that have been encountered while seeking to create a usable Digital Archiving system of a long-term and multi-participant research project. The lead author has been involved in archaeologic... |  | Computational archaeology, Environmental archaeology, Landscape archaeology | Isto Huvila | 2023-05-24 18:46:34 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










