Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 Feb 2024
Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias ReductionFumihiro Sakahira, Hiro’omi Tsumura https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7969330Evaluating Methods for Reducing Sampling Bias in Network AnalysisRecommended by James Allison based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewer
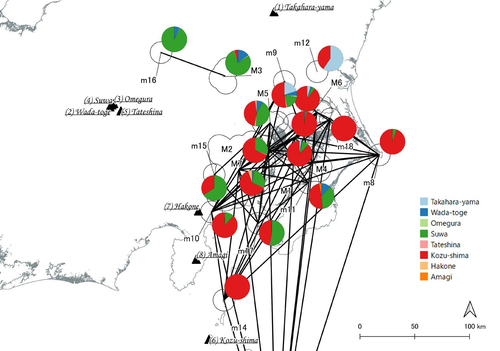
In a recent article, Fumihiro Sakahira and Hiro'omi Tsumura (2023) used social network analysis methods to analyze change in obsidian trade networks in Japan throughout the 13,000-year-long Jomon period. In the paper recommended here (Sakahira and Tsumura 2024), Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction they revisit that data and describe additional analyses that confirm the robustness of their social network analysis. The data, analysis methods, and substantive conclusions of the two papers overlap; what this new paper adds is a detailed examination of the data and methods, including use of bootstrap analysis to demonstrate the reasonableness of the methods they used to group sites into clusters. Both papers begin with a large dataset of approximately 21,000 artifacts from more than 250 sites dating to various times throughout the Jomon period. The number of sites and artifacts, varying sample sizes from the sites, as well as the length of the Jomon period, make interpretation of the data challenging. To help make the data easier to interpret and reduce problems with small sample sizes from some sites, the authors assign each site to one of five sub-periods, then define spatial clusters of sites within each period using the DBSCAN algorithm. Sites with at least three other sites within 10 km are joined into clusters, while sites that lack enough close neighbors are left as isolates. Clusters or isolated sites with sample sizes smaller than 30 were dropped, and the remaining sites and clusters became the nodes in the networks formed for each period, using cosine similarities of obsidian assemblages to define the strength of ties between clusters and sites. The main substantive result of Sakahira and Tsumura’s analysis is the demonstration that, during the Middle Jomon period (5500-4500 cal BP), clusters and isolated sites were much more connected than before or after that period. This is largely due to extensive distribution of obsidian from the Kozu-shima source, located on a small island off the Japanese mainland. Before the Middle Jomon period, Kozu-shima obsidian was mostly found at sites near the coast, but during the Middle Jomon, a trade network developed that took Kozu-shima obsidian far inland. This ended after the Middle Jomon period, and obsidian networks were less densely connected in the late and last Jomon periods. The methods and conclusions are all previously published (Sakahira and Tsumura 2023). What Sakahira and Tsumura add in Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction are: · an examination of the distribution of cosine similarities between their clusters for each period · a similar evaluation of the cosine similarities within each cluster (and among the unclustered sites) for each period · bootstrap analyses of the mean cosine similarities and network densities for each time period These additional analyses demonstrate that the methods used to cluster sites are reasonable, and that the use of spatially defined clusters as nodes (rather than the individual sites within the clusters) works well as a way of reducing bias from small, unrepresentative samples. An alternative way to reduce that bias would be to simply drop small assemblages, but that would mean ignoring data that could usefully contribute to the analysis. The cosine similarities between clusters show patterns that make sense given the results of the network analysis. The Middle Jomon period has, on average, the highest cosine similarities between clusters, and most cluster pairs have high cosine similarities, consistent with the densely connected, spatially expansive network from that time period. A few cluster pairs in the Middle Jomon have low similarities, apparently representing comparisons including one of the few nodes on the margins on the network that had little or no obsidian from the Kozu-shima source. The other four time periods all show lower average inter-cluster similarities and many cluster pairs have either high or low similarities. This probably reflects the tendency for nearby clusters to have very similar obsidian assemblages to each other and for geographically distant clusters to have dissimilar obsidian assemblages. The pattern is consistent with the less densely connected networks and regionalization shown in the network graphs. Thinking about this pattern makes me want to see a plot of the geographic distances between the clusters against the cosine similarities. There must be a very strong correlation, but it would be interesting to know whether there are any cluster pairs with similarities that deviate markedly from what would be predicted by their geographic separation. The similarities within clusters are also interesting. For each time period, almost every cluster has a higher average (mean and median) within-cluster similarity than the similarity for unclustered sites, with only two exceptions. This is partial validation of the method used for creating the spatial clusters; sites within the clusters are at least more similar to each other than unclustered sites are, suggesting that grouping them this way was reasonable. Although Sakahira and Tsumura say little about it, most clusters show quite a wide range of similarities between the site pairs they contain; average within-cluster similarities are relatively high, but many pairs of sites in most clusters appear to have low similarities (the individual values are not reported, but the pattern is clear in boxplots for the first four periods). There may be value in further exploring the occurrence of low site-to-site similarities within clusters. How often are they caused by small sample sizes? Clusters are retained in the analysis if they have a total of at least 30 artifacts, but clusters may contain sites with even smaller sample sizes, and small samples likely account for many of the low similarity values between sites in the same cluster. But is distance between sites in a cluster also a factor? If the most distant sites within a spatially extensive cluster are dissimilar, subdividing the cluster would likely improve the results. Further exploration of these within-cluster site-to-site similarity values might be worth doing, perhaps by plotting the similarities against the size of the smallest sample included in the comparison, as well as by plotting the cosine similarity against the distance between sites. Any low similarity values not attributable to small sample sizes or geographic distance would surely be worth investigating further. Sakahira and Tsumura also use a bootstrap analysis to simulate, for each time period, mean cosine similarities between clusters and between site pairs without clustering. They also simulate the network density for each time period before and after clustering. These analyses show that, almost always, mean simulated cosine similarities and mean simulated network density are higher after clustering than before. The simulated mean values also match the actual mean values better after clustering than before. This improved match to actual values when the sites are clustered for the bootstrap reinforces the argument that clustering the sites for the network analysis was a reasonable result. The strength of this paper is that Sakahira and Tsumura return to reevaluate their previously published work, which demonstrated strong patterns through time in the nature and extent of Jomon obsidian trade networks. In the current paper they present further analyses demonstrating that several of their methodological decisions were reasonable and their results are robust. The specific clusters formed with the DBSCAN algorithm may or may not be optimal (which would be unreasonable to expect), but the authors present analyses showing that using spatial clusters does improve their network analysis. Clustering reduces problems with small sample sizes from individual sites and simplifies the network graphs by reducing the number of nodes, which makes the results easier to interpret. Reference Sakahira, F. and Tsumura, H. (2023). Tipping Points of Ancient Japanese Jomon Trade Networks from Social Network Analyses of Obsidian Artifacts. Frontiers in Physics 10:1015870. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2022.1015870 Sakahira, F. and Tsumura, H. (2024). Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction, Zenodo, 10057602, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7969330 | Social Network Analysis of Ancient Japanese Obsidian Artifacts Reflecting Sampling Bias Reduction | Fumihiro Sakahira, Hiro’omi Tsumura | <p>This study aims to investigate the dynamics of obsidian trade networks during the Jomon period (approximately 15,000 to 2,400 years ago), the hunting and gathering era in Japan. To improve regional representation and reduce the distortions caus... |  | Asia, Computational archaeology | James Allison | Thegn Ladefoged, Matthew Peeples | 2023-05-28 05:51:12 | View |
17 Jun 2022

Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5New method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in rock art contextsRecommended by Aitor Ruiz-Redondo based on reviews by Alain Queffelec, Laure Dayet and 1 anonymous reviewerSilica coating developed in cave art walls had an impact in the preservation of the paintings themselves. Despite it still exists a controversy about whether or not the effects contribute to the preservation of the artworks; it is evident that identifying these silica coatings would have an impact to assess the taphonomy of the walls and the paintings preserved on them. Unfortunately, current techniques -especially non-invasive ones- can hardly address amorphous silica characterisation. Thus, its presence is often detected on laboratory observations such as SEM or XRD analyses. In the paper “Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context - Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)”, Quiers and collaborators propose a new method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in a rock art context based on UV laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) and UV illumination [1]. The results from both methods presented by the authors are convincing for the detection of U-silica mineralisation (U-opal in the specific case of study presented). This would allow access to a fast and cheap method to identify this kind of formations in situ in decorated caves. Beyond the relationship between opal coating and the preservation of the rock art, the detection of silica mineralisation can have further implications. First, it can help to define spot for sampling for pigment compositions, as well as reconstruct the chronology of the natural history of the caves and its relation with the human frequentation and activities. In conclusion, I am glad to recommend this original research, which offers a new approach to the identification of geological processes that affect -and can be linked with- the Palaeolithic cave art. [1] Quiers, M., Chanteraud, C., Maris-Froelich, A., Chalmin-Aljanabi, E., Jaillet, S., Noûs, C., Pairis, S., Perrette, Y., Salomon, H., Monney, J. (2022) Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France). HAL, hal-03383193, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5 | Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France) | Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney | <p style="text-align: justify;">Silica coatings development on rock art walls in Points Cave questions the analytical access to pictorial matter specificities (geochemistry and petrography) and the rock art conservation state in the context of pig... |  | Archaeometry, Europe, Rock art, Taphonomy, Upper Palaeolithic | Aitor Ruiz-Redondo | 2021-10-25 11:12:48 | View | |
28 Aug 2023
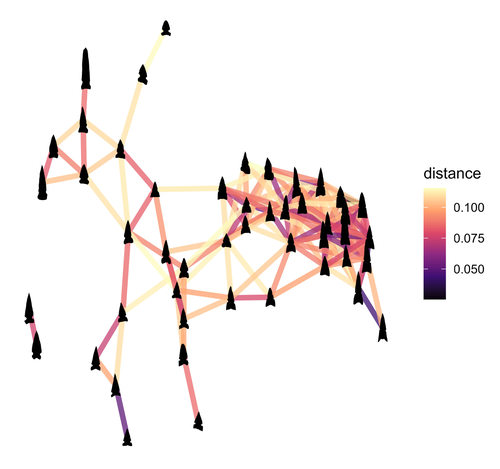
Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United StatesRobert J. Bischoff https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc2D Geometric Morphometrics of Projectile Points from the Southwestern United StatesRecommended by Adrian L. Burke based on reviews by James Conolly and 1 anonymous reviewerBischoff (2023) is a significant contribution to the growing field of geometric morphometric analysis in stone tool analysis. The subject is projectile points from the southwestern United States. Projectile point typologies or systematics remain an important part of North American archaeology, and in fact these typologies continue to be used primarily as cultural-historical markers. This article looks at projectile point types using a 2D image geometric morphometric analysis as a way of both improving on projectile point types but also testing if these types are in fact based in measurable reality. A total of 164 point outlines are analyzed using Elliptical Fourier, semilandmark and landmark analyses. The author also uses a network analysis to look at possible relationships between projectile point morphologies in space. This is a clever way of working around the predefined distributions of projectile point types, some of which are over 100 years old. Because of the dynamic nature of stone tools in terms of their use, reworking and reuse, this article can also provide solutions for studying the dynamic nature of stone tools. This article therefore also has a wide applicability to other stone tool analyses. Reference Bischoff, R. J. (2023) Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States, SocArXiv, a6wjc, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc | Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States | Robert J. Bischoff | <p style="text-align: justify;">Traditional analyses of projectile points often use visual identification, the presence or absence of discrete characteristics, or linear measurements and angles to classify points into distinct types. Geometric mor... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Lithic technology, North America | Adrian L. Burke | 2022-12-18 03:38:14 | View | |
26 Mar 2024
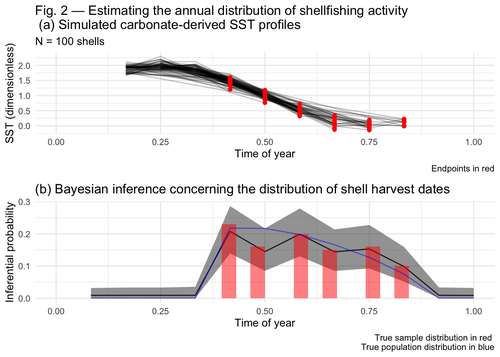
Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approachJordan Brown and Gabriel Lewis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7949547Mixture models and seasonal mobilityRecommended by Alfredo Cortell-Nicolau and Simon Carrignon based on reviews by Iza Romanowska and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper by Brown & Lewis [1] presents an approach to measure seasonal mobility and subsistence practices. In order to do so, the paper proposes a Bayesian mixture model to estimate the annual distribution of shellfish harvesting activity. Following the recommendations of the two reviewers, the paper presents a clear and innovative method to assess seasonal mobility for prehistoric groups, although it could benefit from additional references regarding isotopic literature. While the adequacy of isotope analysis for estimating mobility patterns in Archaeology has been extensively proven by now, work on specific seasonal mobility is not that much abundant. However, this is a key issue, since seasonal mobility is one of the main social components defining the differences between groups both considering farming vs hunting and gathering or even among hunter-gatherer groups themselves. In this regard, the paper brings a valuable methodological resources that can be used for further research in this issue. One of its greatest values is the fact that it can quantify the uncertainty present in previous isotope studies in seasonal mobility. As stated by the authors, the model can still undergo several optimisation aspects, but as it stands, it is already providing a valuable asset regarding the quantification of uncertainy in the isotopic studies of seasonal mobility. Reference [1] Brown, J. and Lewis, G. (2024). Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approach. Zenodo, 7949547, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7949547 | Inferring shellfishing seasonality from the isotopic composition of biogenic carbonate: A Bayesian approach | Jordan Brown and Gabriel Lewis | <p>The problem of accurately and reliably estimating the annual distribution of seasonally-varying human settlement and subsistence practices is a classic concern among archaeologists, which has only become more relevant with the increasing import... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Environmental archaeology, North America, Palaeontology, Paleoenvironment, Zooarchaeology | Alfredo Cortell-Nicolau | Iza Romanowska, Eduardo Herrera Malatesta, Alejandro Sierra Sainz-Aja, Sam Leggett, Christianne Fernee, Anonymous, Asier García-Escárzaga , Paul Szpak , Maria Elena Castiello , Jasmine Lundy , Tansy Branscombe | 2023-10-03 04:45:54 | View |
03 Nov 2023
The Dynamic Collections – a 3D Web Platform of Archaeological Artefacts designed for Data Reuse and Deep InteractionMarco Callieri, Åsa Berggren, Nicolò Dell’Unto, Paola Derudas, Domenica Dininno, Fredrik Ekengren, Giuseppe Naponiello https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10067103A comparative teaching and learning tool for 3D data: Dynamic CollectionsRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Alex Brandsen and Louise Tharandt based on reviews by Alex Brandsen and Louise Tharandt
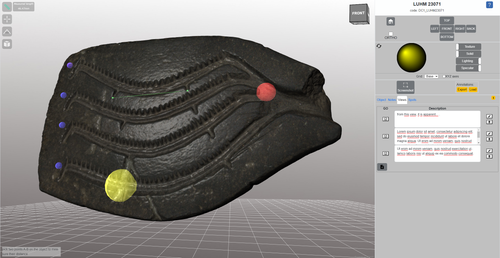
The paper (Callieri, M. et al. 2023) describes the “Dynamic Collections” project, an online platform initially created to showcase digital archaeological collections of Lund University. During a phase of testing by department members, new functionalities and artefacts were added resulting in an interactive platform adapted to university-level teaching and learning. The paper introduces into the topic and related works after which it starts to explain the project itself. The idea is to resemble the possibilities of interaction of non-digital collections in an online platform. Besides the objects themselves, the online platform offers annotations, measurement and other interactive tools based on the already known 3DHOP framework. With the possibility to create custom online collections a collaborative working/teaching environment can be created. The already wide-spread use of the 3DHOP framework enabled the authors to develop some functionalities that could be used in the “Dynamic Collections” project. Also, current and future plans of the project are discussed and will include multiple 3D models for one object or permanent identifiers, which are both important additions to the system. The paper then continues to explain some of its further planned improvements, like comparisons and support for teaching, which will make the tool an important asset for future university-level education. The paper in general is well-written and informative and introduces into the interactive tool, that is already available and working. It is very positive, that the authors rely on up-to-date methodologies in creating 3D online repositories and are in fact improving them by testing the tool in a teaching environment. They mention several times the alignment with upcoming EU efforts related to the European Collaborative Cloud for Cultural Heritage (ECCCH), which is anticipatory and far-sighted and adds to the longevity of the project. Comments of the reviewers were reasonably implemented and led to a clearer and more concise paper. I am very confident that this tool will find good use in heritage research and presentation as well as in university-level teaching and learning. Although the authors never answer the introductory question explicitly (What characteristics should a virtual environment have in order to trigger dynamic interaction?), the paper gives the implicit answer by showing what the "Dynamic Collections" project has achieved and is able to achieve in the future. BibliographyCallieri, M., Berggren, Å., Dell'Unto, N., Derudas, P., Dininno, D., Ekengren, F., and Naponiello, G. (2023). The Dynamic Collections – a 3D Web Platform of Archaeological Artefacts designed for Data Reuse and Deep Interaction, Zenodo, 10067103, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10067103 | The Dynamic Collections – a 3D Web Platform of Archaeological Artefacts designed for Data Reuse and Deep Interaction | Marco Callieri, Åsa Berggren, Nicolò Dell’Unto, Paola Derudas, Domenica Dininno, Fredrik Ekengren, Giuseppe Naponiello | <p>The Dynamic Collections project is an ongoing initiative pursued by the Visual Computing Lab ISTI-CNR in Italy and the Lund University Digital Archaeology Laboratory-DARKLab, Sweden. The aim of this project is to explore the possibilities offer... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology | Sebastian Hageneuer | 2023-08-31 15:05:32 | View | |
14 Sep 2020
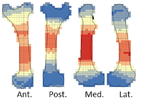
A way to break bones? The weight of intuitivenessDelphine Vettese, Trajanka Stavrova, Antony Borel, Juan Marin, Marie-Hélène Moncel, Marta Arzarello, Camille Daujeard https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/rebwtBreaking bones: Nature or Culture?Recommended by Beatrice Demarchi and Reuven Yeshurun based on reviews by Terry O'Connor, Alan Outram and 1 anonymous reviewerThe nature of breaking long bones for obtaining marrow is important in Paleolithic archaeology, due to its widespread, almost universal, character. Provided that hammer-stone percussion marks can be correctly identified using experimental datasets (e.g., [1]), the anatomical location and count of the marks may be taken to reflect recurrent “cultural” traditions in the Paleolithic [2]. Were MP humans breaking bones intuitively or did they abide by a strict “protocol”, and, if the latter, was this protocol optimized for marrow retrieval or geared towards another, less obvious goal? This paper provides a baseline for location analyses of percussion marks. Their dataset may therefore be regarded as a null hypothesis according to which the archaeological data could be tested. If Paleolithic patterns of percussion marks differ from Vettese et al.’s [3] “intuitive” patterns, then the null hypothesis is disproved and one can argue in favor of a learned pattern. The latter can be a result of ”culture”, as Vettese et al. [3] phrase it, in the sense of nonrandom action that draws on transmitted knowledge. Such comparisons bear a great potential for understanding the degree of technological behavior in the Paleolithic by factoring out the “natural” constraints of bone breakage patterns. Vettese et al. [3: fig. 14] started this discourse by comparing their experimental dataset to some Middle and Upper Paleolithic faunas; we are confident that many other studies will follow. Bibliography [1]Pickering, T.R., Egeland, C.P., 2006. Experimental patterns of hammerstone percussion damage on bones: Implications for inferences of carcass processing by humans. J. Archaeol. Sci. 33, 459–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2005.09.001 [2]Blasco, R., Rosell, J., Domínguez-Rodrigo, M., Lozano, S., Pastó, I., Riba, D., Vaquero, M., Peris, J.F., Arsuaga, J.L., de Castro, J.M.B., Carbonell, E., 2013. Learning by Heart: Cultural Patterns in the Faunal Processing Sequence during the Middle Pleistocene. PLoS One 8, e55863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055863 [3]Vettese, D., Stavrova, T., Borel, A., Marin, J., Moncel, M.-H., Arzarello, M., Daujeard, C. (2020) A way to break bones? The weight of intuitiveness. BioRxiv, 011320, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.31.011320 | A way to break bones? The weight of intuitiveness | Delphine Vettese, Trajanka Stavrova, Antony Borel, Juan Marin, Marie-Hélène Moncel, Marta Arzarello, Camille Daujeard | <p>During the Middle Paleolithic period, bone marrow extraction was an essential source of fat nutrients for hunter-gatherers especially throughout cold and dry seasons. This is attested by the recurrent findings of percussion marks in osteologica... |  | Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Spatial analysis, Taphonomy, Zooarchaeology | Beatrice Demarchi | 2020-04-01 11:52:05 | View | |
26 Apr 2022
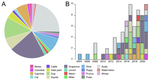
Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a reviewAllowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/skeu5Archaeophenomics: an up-and-coming field in bioarchaeologyRecommended by Anneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewerAnneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewer Phenomics is the analysis of high-dimensional phenotypic data [1]. Phenomics research strategies are capable of linking genetic variation to phenotypic variation [2], but a genetic component is not absolutely necessary. The paper “Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics: a review” by Evin and colleagues [3] examines the use of geometric morphometrics in bioarchaeology and coins the term archaeophenomics. Archaeophenomics can be described as the large-scale phenotyping of ancient remains, and both addresses taxonomic identification, as well as infers spatio-temporal agrobiodiversity dynamics. It is a relatively new field in bioarchaeology with the first paper using this approach stemming from 2004. This study by Evin et al. [3] presents an excellent review and unquestionably demonstrates the potential of archaeophenomics. The authors provide an exhaustive review specifically of bioarchaeological studies in international journals using geometric morphometrics to study archaeological remains of domestic species. Although geometric morphometrics lends itself well for archaeophenomics, readers should keep in mind that this is not the only method and other approaches might equally fall under archaeophenomics as long as high-dimensional phenotypic archaeological data are involved. Distinguishing archaeophenomics from phenomics is important because of a critical difference. Archaeological remains are often altered by taphonomical processes. As such data may not be as complete as when working with modern specimens. Although this poses difficulties, morphometric analyses can usually still be performed as long as the structures presenting the relevant geometrical features are present. Even fragmented remains can be studied with a restricted version of the original landmarking/measurement protocol. Evin et al. [3] define archaeophenomics as “phenomics of the past”. This is only partly correct. It can be deduced from their review that they really mean phenomics of our (human) past. This leaves a gap for phenomics of the non-human past, for which I suggest the term palaeophenomics. [1] Jin, L. (2021). Welcome to the Phenomics Journal. Phenomics, 1, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-020-00009-4.
| Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a review | Allowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral | <p>Geometric morphometrics revolutionized domestication studies through the precise quantification of the phenotype of ancient plant and animal remains. Geometric morphometrics allow for an increasingly detailed understanding of the past agrobiodi... |  | Archaeobotany, Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Zooarchaeology | Anneke H. van Heteren | 2022-02-17 09:50:39 | View | |
05 Jan 2024
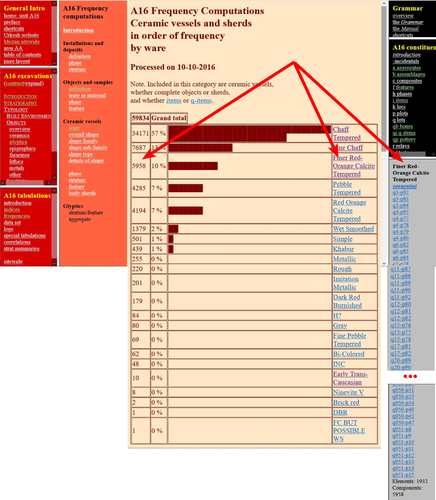
The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A Website Approach to Archaeological Typology.Giorgio Buccellati and Marilyn Kelly-Buccellati https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7743834Roster and Lexicon – A Radical Digital-Dialogical Approach to Questions of Typology and Categorization in ArchaeologyRecommended by Shumon Tobias Hussain , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann and 2 anonymous reviewers
“The density of types and the dignity of the fragment. A website approach to archaeological typology” by G. Buccellati and M. Kelly-Buccellati (1) is a contribution to the rapidly growing literature on digital approaches to archaeological data management, expertly showcasing the significant theoretical and epistemological impetus of such work. The authors offer a conceptually lucid discussion of key concepts in archaeological ordering practices surrounding the longstanding tension between so-called ‘etic’ and ‘emic’ approaches, thereby providing a thorough systematic of how to think through sameness and difference in the context of voluminous digital archaeological data. As a point of departure, the authors reconsider the relationship between archaeological fragments – spatiotemporally bounded artefacts and features – and their larger meaning-giving totality as the primary locus of archaeological knowledge. Typology can then be said to serve this overriding quest to resolve the conflict between parts and wholes, as the parts themselves are never sufficient to render the whole but the whole remains elusive without reference to the parts. Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati here make an interesting point about the importance to register the globality of the archaeological record – that is, literally everything encountered in the soil – without making any prior choices as to what supposedly matters and what not. The distinctiveness of the archaeological enterprise, according to them, indeed consists of the circumstance that merely disconnected fragments come to the attention of archaeologists and the only objective data that can be attained, because of this, are about the situated location of fragments in the ground and their relation to other fragments – what they call ‘emplacement’. This, we would add, includes the relationship of fragments with human observers and the employed methods of excavation as observation. As the authors say: “[i]t is in this sense that the fragments are natively digital: they are atoms that do not cohere into a typological whole”. The systematic exploration of how the so recovered fragments may be re-articulated is then essentially the goal of archaeological categorization and typology but these practices can only ever be successful if the whole context of original ‘emplacement’ is carefully taken into consideration. This reconstruction of the fundamental epistemological situation archaeology finds itself in leads the authors to a general rejection of ‘more’ vs. ‘less’ objective or even subjective ordering practices as such qualifications tend to miss the point. What matters is to enable the flexible and scalable confrontation of isolated archaeological fragments, to do experiment with and test different part-whole relations and their possible knowledge contributions. It is no coincidence that the authors insist on a dynamical approach to ordering practices and type-thinking in archaeology here, which in many ways comes often very close to the general conceptual orientation philosopher Stephen C. Pepper (2) has called ‘organicism’ – a preoccupation of resolving the tension between heterogeneous fragments and coherent wholes without losing sight of the specificity of each single fragment. In the view of organicist thinkers, and the authors seem to share this recognition, to take complexity seriously means to centre the dialectics between fragments and wholes in their entirety. This notion is directly reflected in the authors’ interesting definition of ‘big data’ in archaeology as a multi-layered and multi-referential system of organizing the totality of observations of emplacement (the Global record). Based on this broader exposition, Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati make some perceptive and noteworthy observations vis-à-vis the aforementioned emic-etic distinction that has caused so much archaeological confusion and debate (3–6). To begin with, emic and etic designate different systemic logics of organizing observable sameness and difference. Emic systems are closed and foreground the idea of the roster, they recognize only a limited set of types whose identity depends on relative differences. Etic systems, on the other hand, are in principle open (and even open-ended) and rely on the notion of the lexicon; they enlist a principally endless repertoire of traits, types and sub-types (classes and sub-classes may be added to this list of course). Difference in etic systems is moreover defined according to some general standards that appear to eclipse the standards of the system itself. Etic systems therefore tend to advocate supposedly universal principles of how to establish similarity vs. difference, although, in reality, there is substantial debate as to what these principles may be or whether such endeavour is a useful undertaking. In the wild, both etic and emic systems of ordering and categorization are of course encountered in the plural but etic systems deploy external standards of order while emic systems operate via internal standards. An interesting observation by the authors in this context is that archaeological reasoning in relation to sameness and difference is almost never either exclusively etic or exclusively emic. The simple reason is that any grouping of fragments according to technological (means/modes of production) or functional considerations (use-wear, tool design, relation between form and function) based on empirical evidence is typically already infused by emic standards. The classic example from the analysis of archaeological pottery is ware groups, which reference the nexus of technological know-how and concrete practices, and which rely, in a given context, on internal, relative differentiations between the respective observed practices. Yet ignoring these distinctions would sideline significant knowledge on the past. These discussions are refreshing as they may indicate that ordering practices – when considered as an end in themselves – misconstrue the archaeological process as static and so advocate for categories, classes, and types to be carved out before any serious analysis can begin. It could in fact be argued that in doing so, they merely construct a new closed system, then emic by definition. Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati propose an alternative without discarding the intuition that ordering archaeological materials is conditional to the inferential and knowledge-production process: they propose that typologies should be treated as arguments. Moreover, the sort of argument they have in mind is to a lesser extent ‘formal-logical’ but instead emphatically ‘dialogical’ in nature, as such argumentative form helps to combat the inherent static-ness of ordering practices the authors criticize, and so discloses a radically dynamic approach to the undertaking of fragment-whole matching. The organicist inclination to preserve ‘the dignity of fragments’ while working towards their resolution in attendant wholes and sub-wholes further gives rise to the idea that such ‘native digital fragments’ must be brought into systematic conversation with one another, acknowledging the involved complexity. To this end, the authors frame ordering work and typo-praxis as a ‘digital discourse’ and ask what the conditions and possibilities for such discourse are and how it can be facilitated. It is here that they put forward the idea that the webpage may provide an ideal epistemic model system to promote the preservation of emplaced archaeological fragments while simultaneously promoting multistranded and multi-context explorations of fragment coherence and articulation. The website enables unique forms of exploration and engagement with data and new arguments escaping the fixity of the analogue-printed which dominates current archaeological practice. Similar experiences were for example made in the context of Gardin’s ‘logicism’, leading to broadly comparable attempts to overcome the analogue with more dynamic, HTML/web-based forms of data presentation, exploration and discussion (7, 8). As such, Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati table a range of fresh arguments for re-thinking typology beyond and with text at the same time, to enable ‘dynamic reading’ of fragment-whole relationships in an increasingly digital world. Their proposal comes thereby close to what has been termed ‘deep mapping’ in the context of critical cartographies and other spatially-inclined scholarship in the Anglophone world (9, 10). Deep maps seek to transcend the epistemological limitations of 2D-representations of spatiality on traditional maps and introduce different layers of informational depth and heterogeneity, which, similarly to the living digital webpage proposed by the authors, can be continuously extended and revised and which may also greatly promote multidisciplinary and team-based research endeavours. In the same spirit as the authors’ ‘digital discourse’, deep mapping draws attention to the knowledge potential of bringing together the heterogeneous, the etic and the emic, and to pay more attention to ‘multiplanar’ and ‘multilinear’ relationships as well as the associated relations of relations. This proposal to deploy types and typology in general as dynamic arguments is linked to the ambition to contribute to and work on the narrativization of the archaeological record without tacit (and often unconscious) conceptual pre-subscription, countering typologies that remain largely in the abstract and so have contributed to the creeping anonymity of the past.
Bibliography 1. Buccellati, G. and Kelly-Buccellati, M. (2023). The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A website approach to archaeological typology, Zenodo, 7743834, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7743834. 2. Pepper, S C. (1972). World hypotheses: a study in evidence, 7. print (Univ. of California Press). 3. Hayden, B. (1984). Are Emic Types Relevant to Archaeology? Ethnohistory 31, 79–92. https://doi.org/10.2307/482057 4. Tostevin, G. B. (2011). An Introduction to the Special Issue: Reduction Sequence, Chaîne Opératoire, and Other Methods: The Epistemologies of Different Approaches to Lithic Analysis. PaleoAnthropology, 293−296. https://www.doi.org/10.4207/PA.2011.ART59 5. Tostevin, G. B. (2013). Seeing lithics: a middle-range theory for testing for cultural transmission in the pleistocene (Oakville, CT: Oxbow Books). 6. Boissinot, P. (2015). Qu’est-ce qu’un fait archéologique? (Éditions EHESS). https://doi.org/10.4000/lectures.19921 7. Gardin, J.-C. and Roux, V. (2004). The Arkeotek Project: a European Network of Knowledge Bases in the Archaeology of Techniques. Archeologia e Calcolatori 15, 25–40. 8. Husi, P. (2022). La céramique médiévale et moderne du bassin de la Loire moyenne, chrono-typologie et transformation des aires culturelles dans la longue durée (6e—17e s.) (FERACF). 9. Bodenhamer, D. J., Corrigan, J. and Harris, T. M. (2015). Deep Maps and Spatial Narratives (Indiana University Press). 10. Gillings, M., Hacigüzeller, P. and Lock, G. R. (2019). Re-mapping archaeology: critical perspectives, alternative mappings (Routledge).
| The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A Website Approach to Archaeological Typology. | Giorgio Buccellati and Marilyn Kelly-Buccellati | <p>Typology hinges on categorization, and the two main axes of categorization are the roster and the lexicon: the first defines elements from an -emic, and the second from an (e)-tic point of view, i. e., as a closed or an open system, respectivel... |  | Antiquity, Theoretical archaeology | Shumon Tobias Hussain | 2023-03-17 09:11:46 | View | |
06 Oct 2023
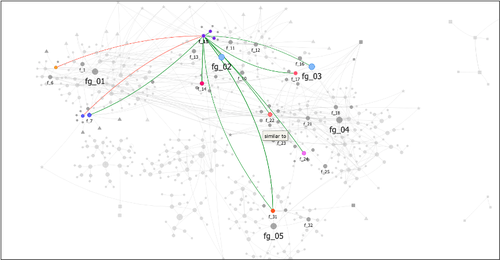
From paper to byte: An interim report on the digital transformation of two thing editionsAuth. Frederic; Rösler, Katja; Domscheit, Wenke; Hofmann, Kerstin P. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7304578Revitalising archaeological corpus publications through digitisation – the Corpus der römischen Funde im europäischen Barbaricum and the Conspectus Formarum Terrae Sigillatae Modo Confectae as exemplary casesRecommended by Felix Riede, Sébastien Plutniak and Shumon Tobias Hussain and Shumon Tobias Hussain based on reviews by Sebastian Hageneuer and Adéla Sobotkova based on reviews by Sebastian Hageneuer and Adéla Sobotkova
The paper entitled “From paper to byte: An interim report on the digital transformation of two thing editions” submitted by Frederic Auth and colleagues discusses how those rich and often meticulously illustrated catalogues of particular find classes that exist in many corners of archaeology can be brought to the cutting edge of contemporary research through digitisation. This paper was first developed for a special conference session convened at the EAA annual meeting in 2021 and is intended for an edited volume on the topic of typology, taxonomy, classification theory, and computational approaches in archaeology. Auth et al. (2023) begin with outlining the useful notion of the ‘thing-edition’ originally coined by Kerstin Hofmann in the context of her work with the many massive corpora of finds that have characterised, in particular, earlier archaeological knowledge production in Germany (Hofmann et al. 2019; Hofmann 2018). This work critically examines changing trends in the typological characterisation and recording of various find categories, their theoretical foundations or lack thereof and their legacy on contemporary practice. The present contribution focuses on what happens with such corpora when they are integrated into digitisation projects, specifically the efforts by the German Archaeological Institute (DAI), the so-called iDAI.world and in regard to two Roman-era material culture groups, the Corpus der römischen Funde im europäischen Barbaricum (Roman finds from beyond the empire’s borders in eight printed volumes covering thousands of finds of various categories), and the Conspectus Formarum Terrae Sigillatae Modo Confectae (Roman plain ware). Drawing on Bruno Latour’s (2005) actor-network theory (ANT), Auth et al. discuss and reflect on the challenges met and choices to be made when thing-editions are to be transformed into readily accessible data, that is as linked to open, usable data. The intellectual and infrastructural workload involved in such digitisation projects is not to be underestimated. Here, the contribution by Auth et al. excels in the manner that it does not present the finished product – the fully digitised corpora – but instead offers a glimpse ‘under the hood’ of the digitisation process as an interaction between analogue corpus, research team, and the technologies at hand. These aspects were rarely addressed in the literature, rooted in the 1970s early work (Borillo and Gardin 1974; Gaines 1981), on archaeological computerised databases, focused on technical dimensions (see Rösler 2016 for an exception). Their paper can so also be read in the broader context of heterogeneous computer-assisted knowledge ecologies and ‘mangles of practice’ (see Pickering and Guzik 2009) in which practitioners and technological structures respond to each other’s needs and attempt to cooperate in creative ways. As such, Auth et al.’s considerations not least offer valuable resources for Science and Technology Studies-inspired discussions on the cross-fertilization of archaeological theory, practice and currently emerging material and virtual research infrastructures and can be read in conjunction to Gavin Lucas’ (2022) paper on ‘machine epistemology’ due to appear in the same volume. Perhaps more importantly, however, the work by Auth and colleagues (2023) exemplifies the due diligence required in not merely turning a catalogue from paper to digital document but in transforming such catalogues into long-lasting and patently usable repositories of generations of scholars to come. Deploying the Latourian notions of trade-off and recursive reference, Auth et al. first examine the structure, strengths, and weakness of the two corpora before moving on to showing how the freshly digitised versions offer new and alternative ways of analysing the archaeological material at hand, notably through immediate visualisation opportunities, through ceramic form combinations, and relational network diagrams based on the data inherent in the respective thing-editions. Catalogues including basic descriptions and artefact illustrations exist for most if not all archaeological periods. They constitute an essential backbone of archaeological work as repeated access to primary material is impractical if not impossible. The catalogues addressed by Auth et al. themselves reflect major efforts on behalf of archaeological experts to arrive at clear and operational classifications in a pre-computerised era. The continued and expanded efforts by Auth and colleagues build on these works and clearly demonstrate the enormous analytical potential to make such data not merely more accessible but also more flexibly interoperable. Their paper will therefore be an important reference for future work with similar ambitions facing similar challenges. References Auth, Frederic, Katja Rösler, Wenke Domscheit, and Kerstin P. Hofmann. 2023. “From Paper to Byte: A Workshop Report on the Digital Transformation of Two Thing Editions.” Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8214563 Borillo, Mario, and Jean-Claude Gardin. 1974. Les Banques de Données Archéologiques. Marseille: Éditions du CNRS. Gaines, Sylvia W., ed. 1981. Data Bank Applications in Archaeology. Tucson, AZ: University of Arizona Press. Hofmann, Kerstin P. 2018. “Dingidentitäten Und Objekttransformationen. Einige Überlegungen Zur Edition von Archäologischen Funden.” In Objektepistemologien. Zum Verhältnis von Dingen Und Wissen, edited by Markus Hilgert, Kerstin P. Hofmann, and Henrike Simon, 179–215. Berlin Studies of the Ancient World 59. Berlin: Edition Topoi. https://dx.doi.org/10.17171/3-59 Hofmann, Kerstin P., Susanne Grunwald, Franziska Lang, Ulrike Peter, Katja Rösler, Louise Rokohl, Stefan Schreiber, Karsten Tolle, and David Wigg-Wolf. 2019. “Ding-Editionen. Vom Archäologischen (Be-)Fund Übers Corpus Ins Netz.” E-Forschungsberichte des DAI 2019/2. E-Forschungsberichte Des DAI. Berlin: Deutsches Archäologisches Institut. https://publications.dainst.org/journals/efb/2236/6674 Latour, Bruno. 2005. Reassembling the Social: An Introduction to Actor-Network-Theory. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Lucas, Gavin. 2022. “Archaeology, Typology and Machine Epistemology.” Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7622162 Pickering, Andrew, and Keith Guzik, eds. 2009. The Mangle in Practice: Science, Society, and Becoming. The Mangle in Practice. Science and Cultural Theory. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. Rösler, Katja. 2016. “Mit Den Dingen Rechnen: ‚Kulturen‘-Forschung Und Ihr Geselle Computer.” In Massendinghaltung in Der Archäologie. Der Material Turn Und Die Ur- Und Frühgeschichte, edited by Kerstin P. Hofmann, Thomas Meier, Doreen Mölders, and Stefan Schreiber, 93–110. Leiden: Sidestone Press. | From paper to byte: An interim report on the digital transformation of two thing editions | Auth. Frederic; Rösler, Katja; Domscheit, Wenke; Hofmann, Kerstin P. | <p>One specific form of publication for archaeological objects are catalogues, atlases and corpora. Kerstin Hofmann has introduced the term ‘Ding-Editionen’ (thing editions) for this category of publications that present their data in lists, short... |  | Antiquity, Computational archaeology, Dating, Theoretical archaeology | Felix Riede | 2022-11-08 16:00:49 | View | |
14 Nov 2023
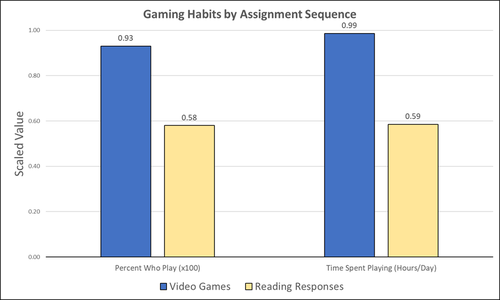
Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics ClassroomStephan, Robert https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286Learning with Archaeogaming? A study based on student feedbackRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Stephan 2023) is about the use of video games as a pedagogical tool in class. Instead of taking the perspective of a lecturer, the author seeks the student’s perspectives to evaluate the success of an interactive teaching method at the crossroads of history, archaeology, and classics. The paper starts with a literature review, that highlights the intensive use of video games among college students and high schoolers as well as the impact video games can have on learning about the past. The case study this paper is based on is made with the game Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey, which is introduced in the next part of the paper as well as previous works on the same game. The author then explains his method, which entailed the tasks students had to complete for a class in classics. They could either choose to play a video game or more classically read some texts. After the tasks were done, students filled out a 14-question-survey to collect data about prior gaming experience, assignment enjoyment, and other questions specific to the assignments. The results were based on only a fraction of the course participants (n=266) that completed the survey (n=26), which is a low number for doing statistical analysis. Besides some quantitative questions, students had also the possibility to freely give feedback on the assignments. Both survey types (quantitative answers and qualitative feedback) solely relied on the self-assessment of the students and one might wonder how representative a self-assessment is for evaluating learning outcomes. Both problems (size of the survey and actual achievements of learning outcomes) are getting discussed at the end of the paper, that rightly refers to its results as preliminary. I nevertheless think that this survey can help to better understand the role that video games can play in class. As the author rightly claims, this survey needs to be enhanced with a higher number of participants and a better way of determining the learning outcomes objectively. This paper can serve as a start into how we can determine the senseful use of video games in classrooms and what students think about doing so. References
Stephan, R. (2023). Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom, Zenodo, 8221286, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286
| Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom | Stephan, Robert | <p>This study assesses student feedback from the implementation of Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey as a teaching tool in a lower level, general education Classics course (CLAS 160B1 - Meet the Ancients: Gateway to Greece and Rome). In this course, which... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Mediterranean | Sebastian Hageneuer | Anonymous, Jeremiah McCall | 2023-08-07 16:45:31 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










