Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract▲ | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
05 Jul 2023
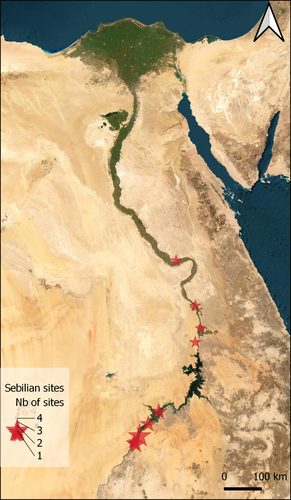
Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile ValleyAlice Leplongeon https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8115202Cultural taxonomic systems and the Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age prehistory of the Nile Valley – a critical reviewRecommended by Felix Riede, Sébastien Plutniak and Shumon Tobias Hussain and Shumon Tobias Hussain based on reviews by Giuseppina Mutri and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Giuseppina Mutri and 1 anonymous reviewer
The paper entitled “Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile Valley” submitted by A. Leplongeon offers a review of the many cultural taxonomic in use for the prehistory – especially the Late Palaeolithic/Late Stone Age – of the Nile Valley (Leplongeon 2023). This paper was first developed for a special conference session convened at the EAA annual meeting in 2021 and is intended for an edited volume on the topic of typology and taxonomy in archaeology. Issues of cultural taxonomy have recently risen to the forefront of archaeological debate (Reynolds and Riede 2019; Ivanovaitė et al. 2020; Lyman 2021). Archaeological systematics, most notably typology, have roots in the research history of a particular region and period (e.g. Plutniak 2022); commonly, different scholars employ different and at times incommensurable systems, often leading to a lack of clarity and inter-regional interoperability. African prehistory is not exempt from this debate (e.g. Wilkins 2020) and, in fact, such a situation is perhaps nowhere more apparent than in the iconic Nile Valley. The Nile Valley is marked by a complex colonial history and long-standing archaeological interest from a range of national and international actors. It is also a vital corridor for understanding human dispersals out of and into Africa, and along the North African coastal zone. As Leplongeon usefully reviews, early researchers have, as elsewhere, proposed a variety of archaeological cultures, the legacies of which still weigh in on contemporary discussions. In the Nile Valley, these are the Kubbaniyan (23.5-19.3 ka cal. BP), the Halfan (24-19 ka cal. BP), the Qadan (20.2-12 ka cal BP), the Afian (16.8-14 ka cal. BP) and the Isnan (16.6-13.2 ka cal. BP) but their temporal and spatial signatures remain in part poorly constrained, or their epistemic status debated. Leplongeon’s critical and timely chronicle of this debate highlights in particular the vital contributions of the many female prehistorians who have worked in the region – Angela Close (e.g. 1978; 1977) and Maxine Kleindienst (e.g. 2006) to name just a few of the more recent ones – and whose earlier work had already addressed, if not even solved many of the pressing cultural taxonomic issues that beleaguer the Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age record of this region. Leplongeon and colleagues (Leplongeon et al. 2020; Mesfin et al. 2020) have contributed themselves substantially to new cultural taxonomic research in the wider region, showing how novel quantitative methods coupled with research-historical acumen can flag up and overcome the shortcomings of previous systematics. Yet, as Leplongeon also notes, the cultural taxonomic framework for the Nile Valley specifically has proven rather robust and does seem to serve its purpose as a broad chronological shorthand well. By the same token, she urges due caution when it comes to interpreting these lithic-based taxonomic units in terms of past social groups. Cultural systematics are essential for such interpretations, but age-old frameworks are often not fit for this purpose. New work by Leplongeon is likely to not only continue the long tradition of female prehistorians working in the Nile Valley but also provides an epistemologically and empirically more robust platform for understanding the social and ecological dynamics of Late Palaeolithic/Later Stone Age communities there.
Bibliography Close, Angela E. 1977. The Identification of Style in Lithic Artefacts from North East Africa. Mémoires de l’Institut d’Égypte 61. Cairo: Geological Survey of Egypt. Close, Angela E. 1978. “The Identification of Style in Lithic Artefacts.” World Archaeology 10 (2): 223–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00438243.1978.9979732 Ivanovaitė, Livija, Serwatka, Kamil, Steven Hoggard, Christian, Sauer, Florian and Riede, Felix. 2020. “All These Fantastic Cultures? Research History and Regionalization in the Late Palaeolithic Tanged Point Cultures of Eastern Europe.” European Journal of Archaeology 23 (2): 162–85. https://doi.org/10.1017/eaa.2019.59 Kleindienst, M. R. 2006. “On Naming Things: Behavioral Changes in the Later Middle to Earlier Late Pleistocene, Viewed from the Eastern Sahara.” In Transitions Before the Transition. Evolution and Stability in the Middle Paleolithic and Middle Stone Age, edited by E. Hovers and Steven L. Kuhn, 13–28. New York, NY: Springer. Leplongeon, Alice. 2023. “Tool Types and the Establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) Cultural Taxonomic System in the Nile Valley.” https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8115202 Leplongeon, Alice, Ménard, Clément, Bonhomme, Vincent and Bortolini, Eugenio. 2020. “Backed Pieces and Their Variability in the Later Stone Age of the Horn of Africa.” African Archaeological Review 37 (3): 437–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10437-020-09401-x Lyman, R. Lee. 2021. “On the Importance of Systematics to Archaeological Research: The Covariation of Typological Diversity and Morphological Disparity.” Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology 4 (1): 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-021-00077-6 Mesfin, Isis, Leplongeon, Alice, Pleurdeau, David, and Borel, Antony. 2020. “Using Morphometrics to Reappraise Old Collections: The Study Case of the Congo Basin Middle Stone Age Bifacial Industry.” Journal of Lithic Studies 7 (1): 1–38. https://doi.org/10.2218/jls.4329 Plutniak, Sébastien. 2022. “What Makes the Identity of a Scientific Method? A History of the ‘Structural and Analytical Typology’ in the Growth of Evolutionary and Digital Archaeology in Southwestern Europe (1950s–2000s).” Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology 5 (1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-022-00119-7 Reynolds, Natasha, and Riede, Felix. 2019. “House of Cards: Cultural Taxonomy and the Study of the European Upper Palaeolithic.” Antiquity 93 (371): 1350–58. https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2019.49 Wilkins, Jayne. 2020. “Is It Time to Retire NASTIES in Southern Africa? Moving Beyond the Culture-Historical Framework for Middle Stone Age Lithic Assemblage Variability.” Lithic Technology 45 (4): 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/01977261.2020.1802848 | Tool types and the establishment of the Late Palaeolithic (Later Stone Age) cultural taxonomic system in the Nile Valley | Alice Leplongeon | <p>Research on the prehistory of the Nile Valley has a long history dating back to the late 19th century. But it is only between the 1960s and 1980s, that numerous cultural entities were defined based on tool and core typologies; this habit stoppe... |  | Africa, Lithic technology, Upper Palaeolithic | Felix Riede | 2023-03-08 19:25:28 | View | |
02 Apr 2024
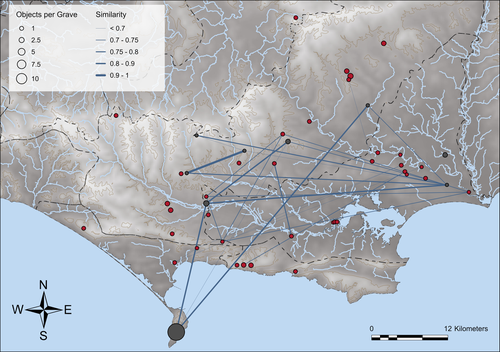
Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological DatasetsTimo Geitlinger https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239A different approach to similarity networks in Archaeology - Similarity Network FusionRecommended by Joel Santos based on reviews by Matthew Peeples and 1 anonymous reviewerThis is a fascinating paper for anyone interested in network analysis or the chronology and cultures of the case study, namely the Late prehistoric burial sites in Dorset, for which the author’s approach allowed a new perspective over an already deeply studied area [1]. This paper's implementation of Similarity Network Fusion (SNF) is noteworthy. This method is typically utilized within genetic research but has yet to be employed in Archaeology. SNF has the potential to benefit Archaeology due to its unique capabilities and approach significantly. The author exhibits a deep and thorough understanding of previous investigations concerning material and similarity networks while emphasizing the innovative nature of this particular study. The SNF approach intends to improve a lack of the most used (in Archaeology) similarity coefficient, the Brainerd-Robinson, in certain situations, mainly in heterogenous and noisy datasets containing a small number of samples but a large number of measurements, scale differences, and collection biases, among other things. The SNF technique, demonstrated in the case study, effectively incorporates various similarity networks derived from different datatypes into one network. As shown during the Dorset case study, the SNF application has a great application in archaeology, even in already available data, allowing us to go further and bring new visions to the existing interpretations. As stated by the author, SNF shows its potential for other applications and fields in archaeology coping with similar datasets, such as archaeobotany or archaeozoology, and seems to complement different multivariate statistical approaches, such as correspondence or cluster analysis. This paper has been subject to two excellent revisions, which the author mostly accepted. One of the revisions was more technical, improving the article in the metadata part, data availability and clarification, etc. Although the second revision was more conceptual and gave some excellent technical inputs, it focused more on complementary aspects that will allow the paper to reach a wider audience. I vividly recommend its publication. References [1] Geitlinger, T. (2024). Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets. Zenodo, 7998239, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7998239
| Similarity Network Fusion: Understanding Patterns and their Spatial Significance in Archaeological Datasets | Timo Geitlinger | <p>Since its earliest application in the 1970s, network analysis has become increasingly popular in both theoretical and GIS-based archaeology. Yet, applications of material networks remained relatively restricted. This paper describes a specific ... |  | Computational archaeology, Protohistory | Joel Santos | 2023-06-02 16:51:19 | View | |
30 Sep 2022
Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF dataBharath Nair, Ismael Rodríguez Palomo, Bo Markussen, Carsten Wiuf, Sarah Fiddyment and Matthew Collins https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.13.483627Assessing glutamine deamination in ancient parchment samplesRecommended by Beatrice Demarchi based on reviews by Maria Codlin and 3 anonymous reviewersData authenticity and approaches to data authentication are crucial issues in ancient protein research. The advent of modern mass spectrometry has enabled the detection of traces of ancient biomolecules contained in fossils, including protein sequences. However, detecting proteins in ancient samples does not equate to demonstrating their endogenous nature: instead, if the mechanisms that drive protein preservation and degradation are understood, then the extent of protein diagenesis can be used for evaluating preservational quality, which in turn may be related to the authenticity of the protein data. The post-mortem deamidation of asparaginyl and glutamyl residues is a key degradation reaction, which can be assessed effectively on the basis of mass spectrometry data, and which has accrued a long history of research, both in terms of describing the mechanisms governing the reactions and with regard to the best strategies for assessing and quantifying the extent of glutamine (Gln) and asparagine (Asn) deamidation in ancient samples (Pal Chowdhury et al., 2019; Ramsøe et al., 2021, 2020; Schroeter and Cleland, 2016; Simpson et al., 2016; Solazzo et al., 2014; Welker et al., 2016; Wilson et al., 2012). In their paper, Nair and colleagues (2022) build on this wealth of knowledge and present a tool for quantifying the extent of Gln deamidation in parchment. Parchment is a collagen-based material which can yield extraordinary insights into manuscript manufacturing practices in the past, as well as on the daily lives of the people who assembled and used them (“biocodicology”) (Fiddyment et al., 2021, 2019, 2015; Teasdale et al., 2017). Importantly, the extent of deamidation can be directly related to the quality of the parchment produced: rapid direct deamidation of Gln is induced by the liming process, therefore high extents of deamidation are linked to prolonged exposure to the high pH conditions which are typical of liming, thus implying lower-quality parchment. Nair et al.’s approach focuses on collagen peptides which are typically detected during MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analyses of parchment and build a simple three-step workflow able to yield an overall index of deamidation for a sample (the parchment glutamine index - PQI) 一 taking into account that different Gln residues degrade at different rates according to their micro-chemical environment. The first step involves pre-processing the MALDI spectra, since Nair et al. are specifically interested in maximising information which can be obtained by low-quality data. The second step builds on well-established methods for quantifying Q → E from MALDI-TOF data by modelling the convoluted isotope distributions (Wilson et al., 2012). Once relative rates of deamidation in selected peptides within a given sample are calculated, the third step uses a mixed effects model to combine the individual deamidation estimates and to obtain an overall estimate of the deamidation for a parchment sample (PQI). The PQI can be used effectively for assessing parchment quality, as the authors show for the dataset from Orval Abbey. However, PQI could also have wider applications to the study of processed collagen, which is widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In general, the study by Nair et al. is a welcome addition to a growing body of research on protein diagenesis, which will ultimately improve models for the assessment of the authenticity of biomolecular data in archaeology. References Chowdhury, P.M., Wogelius, R., Manning, P.L., Metz, L., Slimak, L., and Buckley, M. 2019. Collagen deamidation in archaeological bone as an assessment for relative decay rates. Archaeometry 61:1382–1398. https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.12492 Fiddyment, S., Goodison, N.J., Brenner, E., Signorello, S., Price, K., and Collins, M.J.. 2021. Girding the loins? Direct evidence of the use of a medieval parchment birthing girdle from biomolecular analysis. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.202055 Fiddyment,S., Holsinger, B., Ruzzier, C., Devine, A., Binois, A., Albarella, U., Fischer, R., Nichols, E., Curtis, A., Cheese, E., Teasdale, M.D., Checkley-Scott, C., Milner, S.J., Rudy, K.M., Johnson, E.J., Vnouček, J., Garrison, M., McGrory, S., Bradley, D.G., and Collins, M.J. 2015. Animal origin of 13th-century uterine vellum revealed using noninvasive peptide fingerprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15066–15071. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512264112 Fiddyment, S., Teasdale, M.D., Vnouček, J., Lévêque, É., Binois, A., and Collins, M.J. 2019. So you want to do biocodicology? A field guide to the biological analysis of parchment. Heritage Science 7:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-019-0278-6 Nair, B., Rodríguez Palomo, I., Markussen, B., Wiuf, C., Fiddyment, S., and Collins, M. Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF data. BiorRxiv, 2022.03.13.483627, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.13.483627 Ramsøe, A., Crispin, M., Mackie, M., McGrath, K., Fischer, R., Demarchi, B., Collins, M.J., Hendy, J., and Speller, C. 2021. Assessing the degradation of ancient milk proteins through site-specific deamidation patterns. Sci Rep 11:7795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87125-x Ramsøe, A., van Heekeren, V., Ponce, P., Fischer, R., Barnes, I., Speller, C., and Collins, M.J. 2020. DeamiDATE 1.0: Site-specific deamidation as a tool to assess authenticity of members of ancient proteomes. J Archaeol Sci 115:105080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2020.105080 Schroeter, E.R., and Cleland, T.P. 2016. Glutamine deamidation: an indicator of antiquity, or preservational quality? Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 30:251–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.7445 Simpson, J.P., Penkman, K.E.H., and Demarchi, B. 2016. The effects of demineralisation and sampling point variability on the measurement of glutamine deamidation in type I collagen extracted from bone. J Archaeol Sci 69: 29-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2016.02.002 Solazzo, C., Wilson, J., Dyer, J.M., Clerens, S., Plowman, J.E., von Holstein, I., Walton Rogers, P., Peacock, E.E., and Collins, M.J. 2014. Modeling deamidation in sheep α-keratin peptides and application to archeological wool textiles. Anal Chem 86:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4026362 Teasdale, M.D., Fiddyment, S., Vnouček, J., Mattiangeli, V., Speller, C., Binois, A., Carver, M., Dand, C., Newfield, T.P., Webb, C.C., Bradley, D.G., and Collins M.J. 2017. The York Gospels: a 1000-year biological palimpsest. R Soc Open Sci 4:170988. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.170988 Welker, F., Soressi, M.A., Roussel, M., van Riemsdijk, I., Hublin, J.-J., and Collins, M.J. 2016. Variations in glutamine deamidation for a Châtelperronian bone assemblage as measured by peptide mass fingerprinting of collagen. STAR: Science & Technology of Archaeological Research 3:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/20548923.2016.1258825 Wilson, J., van Doorn, N.L., and Collins, M.J. 2012. Assessing the extent of bone degradation using glutamine deamidation in collagen. Anal Chem 84:9041–9048. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301333t | Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF data | Bharath Nair, Ismael Rodríguez Palomo, Bo Markussen, Carsten Wiuf, Sarah Fiddyment and Matthew Collins | <p style="text-align: justify;">Parchment was used as a writing material in the Middle Ages and was made using animal skins by liming them with Ca(OH)<span class="math-tex">\( _2 \)</span>. During liming, collagen peptides containing Glutamine (Q)... | Bioarchaeology, Europe, Medieval, Zooarchaeology | Beatrice Demarchi | 2022-03-22 12:54:10 | View | ||
26 Oct 2022

Technological analysis and experimental reproduction of the techniques of perforation of quartz beads from the Ceramic period in the AntillesMadeleine Raymond, Pierrick Fouéré, Ronan Ledevin, Yannick Lefrais and Alain Queffelec https://osf.io/preprints/socarxiv/a5tgpUsing Cactus Thorns to Drill Quartz: A Proof of ConceptRecommended by Donatella Usai and Jonathan Hanna based on reviews by Viola Stefano, ? and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Viola Stefano, ? and 1 anonymous reviewer
Quartz adornments (beads, pendants, etc.) are frequent artifacts found in the Caribbean, particularly from Early Ceramic Age contexts (~500 BC-AD 700). As a form of specialization, these are sometimes seen as indicative of greater social complexity and craftsmanship during this time. Indeed, ethnographic analogy has purported that such stone adornments require enormous inputs of time and labor, as well as some technological sophistication with tools hard-enough to create the holes (e.g., metal or diamonds). However, given these limitations, one would expect unfinished beads to be a common artifact in the archaeological record. Yet, whereas unworked/raw materials are often found, beads with partial/unfinished perforations are not. References:
| Technological analysis and experimental reproduction of the techniques of perforation of quartz beads from the Ceramic period in the Antilles | Madeleine Raymond, Pierrick Fouéré, Ronan Ledevin, Yannick Lefrais and Alain Queffelec | <p style="text-align: justify;">Personal ornaments are a very specific kind of material production in human societies and are particularly valuable artifacts for the archaeologist seeking to understand past societies. In the Caribbean, Early Ceram... |  | Lithic technology, Neolithic, South America, Symbolic behaviours, Traceology | Donatella Usai | 2022-09-06 14:01:51 | View | |
12 Dec 2022
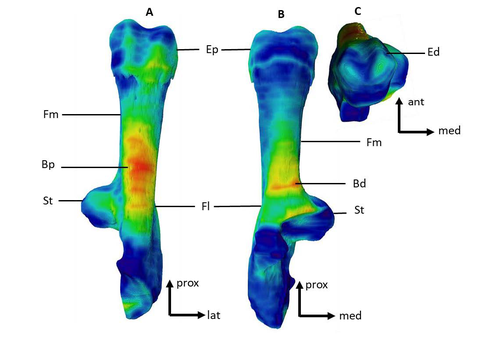
Can growth in captivity alter the calcaneal microanatomy of a wild ungulate?Romain Cottereau, Katia Ortiz, Yann Locatelli, Alexandra Houssaye*, Thomas Cucchi* https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504790Mobility in pigs: A microanatomical perspectiveRecommended by Nimrod Marom based on reviews by Max Price and Ignacio A. Lazagabaster based on reviews by Max Price and Ignacio A. Lazagabaster
Pig domestication and husbandry involved complex processes of introduction, introgression, and feralization that challenge our understanding of human/suid interactions in ancient times. This challenge is a constant stimulus for the development of novel methods and techniques to illuminate aspects of early pig husbandry, such as human-induced changes in mobility. Using geometric morphometrics, Harbers et al. (2020) have shown that the calcaneus records a plastic response to reduced mobility and hence to human management. In the present study, Cottereau et al. (2022) explore the possibility that a similar plastic response to different mobility regimes can be observed in the microanatomy of the calcaneus using CT scans. Their research utilizes a sample of calcanei obtained from Mesolithic specimens, and also from recent suids kept in natural habitat, large pen, and stall. Their results suggest that bone microanatomy is more affected by population differences than by mobility patterns, as illustrated by the similarity between Mesolitic boar calcanei and their difference from recent, free wild boar.
References Cottereau R, Ortiz K, Locatelli Y, Houssaye A, Cucchi T (2022), bioRxiv, 504790, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504790 Harbers H, Neaux D, Ortiz K, Blanc B, Laurens F, Baly I, Callou C, Schafberg R, Haruda A, Lecompte F, Casabianca F, Studer J, Renaud S, Cornette R, Locatelli Y, Vigne J-D, Herrel A, Cucchi T (2020) The mark of captivity: plastic responses in the ankle bone of a wild ungulate (Sus scrofa). Royal Society Open Science, 7, 192039. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.192039
| Can growth in captivity alter the calcaneal microanatomy of a wild ungulate? | Romain Cottereau, Katia Ortiz, Yann Locatelli, Alexandra Houssaye*, Thomas Cucchi* | <p style="text-align: justify;">Reduced mobility associated with captivity induce changes in biomechanical stress on the skeleton of domesticated animals. Due to bone plasticity, the morphology and the internal structure of the bones can respond t... |  | Neolithic, Zooarchaeology | Nimrod Marom | 2022-08-26 20:29:01 | View | |
17 Jun 2022

Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5New method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in rock art contextsRecommended by Aitor Ruiz-Redondo based on reviews by Alain Queffelec, Laure Dayet and 1 anonymous reviewerSilica coating developed in cave art walls had an impact in the preservation of the paintings themselves. Despite it still exists a controversy about whether or not the effects contribute to the preservation of the artworks; it is evident that identifying these silica coatings would have an impact to assess the taphonomy of the walls and the paintings preserved on them. Unfortunately, current techniques -especially non-invasive ones- can hardly address amorphous silica characterisation. Thus, its presence is often detected on laboratory observations such as SEM or XRD analyses. In the paper “Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context - Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)”, Quiers and collaborators propose a new method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in a rock art context based on UV laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) and UV illumination [1]. The results from both methods presented by the authors are convincing for the detection of U-silica mineralisation (U-opal in the specific case of study presented). This would allow access to a fast and cheap method to identify this kind of formations in situ in decorated caves. Beyond the relationship between opal coating and the preservation of the rock art, the detection of silica mineralisation can have further implications. First, it can help to define spot for sampling for pigment compositions, as well as reconstruct the chronology of the natural history of the caves and its relation with the human frequentation and activities. In conclusion, I am glad to recommend this original research, which offers a new approach to the identification of geological processes that affect -and can be linked with- the Palaeolithic cave art. [1] Quiers, M., Chanteraud, C., Maris-Froelich, A., Chalmin-Aljanabi, E., Jaillet, S., Noûs, C., Pairis, S., Perrette, Y., Salomon, H., Monney, J. (2022) Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France). HAL, hal-03383193, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5 | Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France) | Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney | <p style="text-align: justify;">Silica coatings development on rock art walls in Points Cave questions the analytical access to pictorial matter specificities (geochemistry and petrography) and the rock art conservation state in the context of pig... |  | Archaeometry, Europe, Rock art, Taphonomy, Upper Palaeolithic | Aitor Ruiz-Redondo | 2021-10-25 11:12:48 | View | |
15 Aug 2021
Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, IndiaNorbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675An insight into traditional method of food production in IndiaRecommended by Otis Crandell based on reviews by Antony Borel, Atefeh Shekofteh, Andrea Squitieri, Birgül Ögüt, Atefe Shekofte and 1 anonymous reviewerThis paper [1] covers an interesting topic in that it presents through ethnography an insight into a traditional method of food production which is gradually declining in use. In addition to preserving traditional knowledge, the ethnographic study of grinding stones has the potential for showing how similar tools may have been used by people in the past, particularly from the same geographic region. [1] Thongdok Norbu J., Nimasow Gibji, Nimasow Oyi D. (2021) Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Zenodo, 5118675, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeo. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5118675 | Ran-thok and Ling-chhom: indigenous grinding stones of Shertukpen tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, India | Norbu Jamchu Thongdok, Gibji Nimasow & Oyi Dai Nimasow | <p style="text-align: justify;">The Shertukpens are an Indigenous tribal group inhabiting the western and southern parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Northeast India. They are accomplished carvers of carving wood and stone. The paper aims to document the... | Antiquity, Asia, Environmental archaeology, Lithic technology, Peopling, Raw materials | Otis Crandell | 2021-02-10 10:26:12 | View | ||
05 Jun 2023

SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R ShinyROYER, Aurélien, DISCAMPS, Emmanuel, PLUTNIAK, Sébastien, THOMAS, Marc https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7957154Analyzing piece-plotted artifacts just got simpler: A good solution to the wrong problem?Recommended by Reuven Yeshurun based on reviews by Frédéric Santos, Jacqueline Meier and Maayan LevPaleolithic archaeologists habitually measure 3-coordinate data for artifacts in their excavations. This was first done manually, and in the last three decades it is usually performed by a total station and associated hardware. While the field recording procedure is quite straightforward, visualizing and analyzing the data are not, often requiring specialized proprietary software or coding expertise. Here, Royer and colleagues (2023) present the SEAHORS application, an elegant solution for the post-excavation analysis of artifact coordinate data that seems to be instantly useful for numerous archaeologists. SEAHORS allows one to import and organize field data (Cartesian coordinates and point description), which often comes in a variety of formats, and to create various density and distribution plots. It is specifically adapted to the needs of archaeologists, is free and accessible, and much simpler to use than many commercial programs. The authors further demonstrate the use of the application in the post-excavation analysis of the Cassenade Paleolithic site (see also Discamps et al., 2019). While in no way detracting from my appreciation of Royer et al.’s (2023) work, I would like to play the devil’s advocate by asking whether, in the majority of cases, field recording of artifacts in three coordinates is warranted. Royer et al. (2023) regard piece plotting as “…indispensable to propose reliable spatial planimetrical and stratigraphical interpretations” but this assertion does not hold in all (or most) cases, where careful stratigraphic excavation employing thin volumetric units would do just as well. Moreover, piece-plotting has some serious drawbacks. The recording often slows excavations considerably, beyond what is needed for carefully exposing and documenting the artifacts in their contexts, resulting in smaller horizontal and vertical exposures (e.g., Gilead, 2002). This typically hinders a fuller stratigraphic and contextual understanding of the excavated levels and features. Even worse, the method almost always creates a biased sample of “coordinated artifacts”, in which the most important items for understanding spatial patterns and site-formation processes – the small ones – are underrepresented. Some projects run the danger of treating the coordinated artifacts as bearing more significance than the sieve-recovered items, preferentially studying the former with no real justification. Finally, the coordinated items often go unassigned to a volumetric unit, effectively disconnecting them from other types of data found in the same depositional contexts. The advantages of piece-plotting may, in some cases, offset the disadvantages. But what I find missing in the general discourse (certainly not in the recommended preprint) is the “theory” behind the seemingly technical act of 3-coordinate recording (Yeshurun, 2022). Being in effect a form of sampling, this practice needs a rethink about where and how to be applied; what depositional contexts justify it, and what the goals are. These questions should determine if all “visible” artifacts are plotted, or just an explicitly defined sample of them (e.g., elongated items above a certain length threshold, which should be more reliable for fabric analysis), or whether the circumstances do not actually justify it. In the latter case, researchers sometimes opt for using “virtual coordinates” within in each spatial unit (typically 0.5x0.5 m), essentially replicating the data that is generated by “real” coordinates and integrating the sieve-recovered items as well. In either case, Royer et al.’s (2023) solution for plotting and visualizing labeled points within intra-site space would indeed be an important addition to the archaeologists’ tool kits.
References cited Discamps, E., Bachellerie, F., Baillet, M. and Sitzia, L. (2019). The use of spatial taphonomy for interpreting Pleistocene palimpsests: an interdisciplinary approach to the Châtelperronian and carnivore occupations at Cassenade (Dordogne, France). Paleoanthropology 2019, 362–388. https://doi.org/10.4207/PA.2019.ART136 Gilead, I. (2002). Too many notes? Virtual recording of artifacts provenance. In: Niccolucci, F. (Ed.). Virtual Archaeology: Proceedings of the VAST Euroconference, Arezzo 24–25 November 2000. BAR International Series 1075, Archaeopress, Oxford, pp. 41–44. Royer, A., Discamps, E., Plutniak, S. and Thomas, M. (2023). SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R Shiny Zenodo, 7957154, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7929462 Yeshurun, R. (2022). Intra-site analysis of repeatedly occupied camps: Sacrificing “resolution” to get the story. In: Clark A.E., Gingerich J.A.M. (Eds.). Intrasite Spatial Analysis of Mobile and Semisedentary Peoples: Analytical Approaches to Reconstructing Occupation History. University of Utah Press, pp. 27–35.
| SEAHORS: Spatial Exploration of ArcHaeological Objects in R Shiny | ROYER, Aurélien, DISCAMPS, Emmanuel, PLUTNIAK, Sébastien, THOMAS, Marc | <p style="text-align: justify;">This paper presents SEAHORS, an R shiny application available as an R package, dedicated to the intra-site spatial analysis of piece-plotted archaeological remains. This open-source script generates 2D and 3D scatte... |  | Computational archaeology, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Reuven Yeshurun | 2023-02-24 16:01:44 | View | |
14 Nov 2022
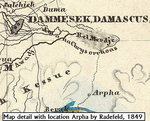
Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman CityJens Kleb https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021Cross-comparison of classical sources, explorer and scientific reports and maps in the search of an ancient city: The example of Raphana of the DecapolisRecommended by Luc Doyon based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli
Establishing the precise location of ancient cities constitutes a challenging task that requires the implementation of multi-disciplinary approaches. In his manuscript entitled “Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha: The search of an eminent Greco-Roman city”, Kleb (2022) proposes a convincing argument building on in-depth research of classical literary sources, literature review of explorer accounts and scientific publications from the 19th and 20th century as well as analysis of old and new maps, aerial photographs, and satellite images. This research report clearly emphasizes the importance of undertaking systematic interdisciplinary work on the topic to mitigate the uncertainties associated with the identification of Raphana, the Decapolis city first mentioned by Pliny the Elder. The Decapolis refers to a group of ten cities of Hellenistic traditions located on the eastern borders of the Roman Empire. This group of cities plays an important role in research that aims to contextualize the Judaean and Galilean history and to investigate urban centers in which different local and Greco-Roman influences met (Lichtenberger, 2021). While the location of most of the Decapolis cities is known and is (or was) subjected to systematic archaeological investigations (e.g., Eisenberg and Kowalewska, 2022; Makhadmeh et al., 2020; Shiyab et al., 2019), the location of others remain speculative. This is the case of Raphana for which the precise location remains difficult to establish owing in part to numerous name changes, limited information on the city structure, architecture, and size, etc. The research presented by Kleb (2022) has some merits, which is emphasized here, although the report is presented in an unusual format compared to traditional scientific articles, i.e., introduction, research background, methodology, results, and discussion. First, the extensive review of classical works allows the reader to gain a historical perspective on the change of names from Raepta/Raphana to Arpha/Arefa. The author argues these different names likely refer to a single location. Second, the author combs through an impressive literature from the 19th and 20th century and emphasize how some assumptions by explorers who visited the region were introduced in the scientific literature and remained unchallenged. Finally, the author gathers a remarkable quantity of old and new maps of the Golan, el-Ledja and Hauran regions and compare them with multiple lines of evidence to hypothesize that the location of Raphana may lie near Ar-Rafi’ah, also known as Bir Qassab, in the Ard el Fanah plain, a conclusion that now requires to be tested through fieldwork investigations. References Kleb, J. (2022) Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City. Figshare, 20550021, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021 Eisenberg, M. and Kowalewska, A. (2022). Funerary podia of Hippos of the Decapolis and the phenomenon in the Roman world. J. Roman Archaeol. 35, 107–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047759421000465 Lichtenberger, A. (2021). The Decapolis, in: A Companion to the Hellenistic and Roman Near East. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119037354.ch18 Makhadmeh, A., Al-Badarneh, M., Rawashdeh, A. and Al-Shorman, A. (2020). Evaluating the carrying capacity at the archaeological site of Jerash (Gerasa) using mathematical GIS modeling. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 23, 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.09.002 Shiyab, A., Al-Shorman, A., Turshan, N., Tarboush, M., Alawneh, F. and Rahabneh, A. (2019). Investigation of late Roman pottery from Gadara of the Decapolis, Jordan using multi-methodic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 25, 100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2019.04.003 | Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City | Jens Kleb | <p style="text-align: justify;">This research paper presents a detailed analysis of ancient literature and archaeological and geographical research until the present day for an important ancient location in the southern part of Syria. This one had... |  | Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Luc Doyon | 2021-12-30 13:54:32 | View | |
28 Aug 2023
Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United StatesRobert J. Bischoff https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc2D Geometric Morphometrics of Projectile Points from the Southwestern United StatesRecommended by Adrian L. Burke based on reviews by James Conolly and 1 anonymous reviewerBischoff (2023) is a significant contribution to the growing field of geometric morphometric analysis in stone tool analysis. The subject is projectile points from the southwestern United States. Projectile point typologies or systematics remain an important part of North American archaeology, and in fact these typologies continue to be used primarily as cultural-historical markers. This article looks at projectile point types using a 2D image geometric morphometric analysis as a way of both improving on projectile point types but also testing if these types are in fact based in measurable reality. A total of 164 point outlines are analyzed using Elliptical Fourier, semilandmark and landmark analyses. The author also uses a network analysis to look at possible relationships between projectile point morphologies in space. This is a clever way of working around the predefined distributions of projectile point types, some of which are over 100 years old. Because of the dynamic nature of stone tools in terms of their use, reworking and reuse, this article can also provide solutions for studying the dynamic nature of stone tools. This article therefore also has a wide applicability to other stone tool analyses. Reference Bischoff, R. J. (2023) Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States, SocArXiv, a6wjc, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc | Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States | Robert J. Bischoff | <p style="text-align: justify;">Traditional analyses of projectile points often use visual identification, the presence or absence of discrete characteristics, or linear measurements and angles to classify points into distinct types. Geometric mor... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Lithic technology, North America | Adrian L. Burke | 2022-12-18 03:38:14 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










