Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract▼ | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
12 Feb 2024

3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, GermanyTharandt, Louise https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7948379Online presentation of the digital reconstruction process of a megalithic tomb : “3Duewelsteene”Recommended by Sophie C. Schmidt and James Allison based on reviews by Robert Bischoff, Ronald Visser and Scott Ure based on reviews by Robert Bischoff, Ronald Visser and Scott Ure
“3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, Germany” (Tharandt 2024) presents several 3-dimensional models of the Düwelsteene monument, along with contextual information about the grave and the process of creating the models. The website (https://3duewelsteene.github.io/) includes English and German versions, making it accessible to a wide audience. The website itself serves as the primary means of presenting the data, rather than as a supplement to a written text. This is an innovative and engaging way to present the research to a wider public. Düwelsteene (“Devil’s Stones”) is a megalithic passage grave from the Funnel Beaker culture, dating to approximately 3300 BC. to 2600 BC. that was excavated in 1932. The website displays three separate 3-dimensional models. They ares shown in the 3D viewer software 3DHOP, which enables viewers to interact with the models in several ways, Annotations on the models display further information. The first model was created by image-based modeling and shows the monument as it appears today. A second model uses historical photographs and excavation data to reconstruct the grave as it appeared prior to the 1932 archaeological excavation. Restoration work following the excavation relocated many of the stones. Pre-1932 photographs collected from residents of the nearby town of Heiden were then used to create a model showing what the tomb looked like before the restoration work. It is commendable that a “certainty view” of the model shows the certainty with which the stones can be put at the reconstructed place. Gaps in the 3D models of stones that were caused by overlap with other stones have been filled with a rough mesh and marked as such, thereby differentiating between known and unknown parts of the stones. The third model is the most imaginative and most interesting. As it shows as the grave as it might have appeared in approximately 3000 B.C., many aspects of this model are necessarily somewhat speculative. There is no direct evidence for exact size and shape of the capstones, the height of the mound, and other details. But enough is known about other similar constructions to allow these details to be inferred with some confidence. Again, care was taken to enable viewers to distinguish between the stones that are still in existence and those that were reconstructed. A video on the home page of the website adds a nice touch. It starts with the model of the Düwelsteene as it currently appears then shows, in reverse order, the changes to the grave, ending with the inferred original state. The 3D reconstructions are convincing and the methods well described. This project follows an open science approach and the FAIR principles, which is commendable and cutting edge in the field of Digital Archaeology. The preprint of the website hosted on zenodo includes all the photos, text, html files, and nine individual 3D model (.ply) files that are combined in the reconstructions exhibited on the website. A “readme.md” file includes details about building the models using CloudCompare and Blender, and modifications to the 3D viewer software (3DHOP) to get the website to improve the display of the reconstructions. We have to note that the link between the reconstructed models and the html page does not work when the files are downloaded from zenodo and opened offline. The html pages open in the browser, and the individual ply files work fine, but the 3D models do not display on the browser page when the html files are opened offline. The online version of the website is working perfectly. The 3Düwelsteene website combines the presentation of archaeological domain knowledge to a lay audience as well as in-depths information on the reconstruction process to make it an interesting contribution for researchers. By providing data and code for the website it also models an Open Science approach, which enables other researchers to re-use these materials. We congratulate the author on a successful reconstruction of the megalithic tomb, an admirable presentation of the archaeological work and the thoughtful outreach to a broad audience. Bibliography | 3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, Germany | Tharandt, Louise | <p>The Düwelsteene near Heiden, Westphalia, is one of the most southern megalithic tombs of the Funnel Beaker culture. In 1932 the Düwelsteene were restored and the appearance of the grave was changed. Even though the megalithic tomb was excavated... |  | Computational archaeology, Mesolithic, Neolithic | Sophie C. Schmidt | 2023-05-21 17:24:22 | View | |
24 Jan 2024
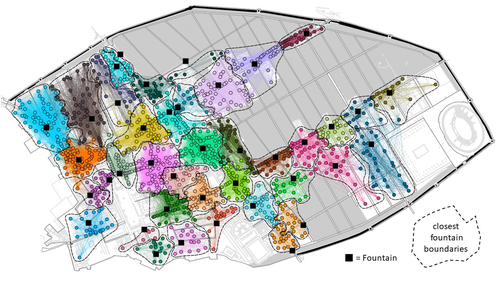
Social Network Analysis, Community Detection Algorithms, and Neighbourhood Identification in PompeiiNotarian, Matthew https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305968A Valuable Contribution to Archaeological Network Research: A Case Study of PompeiiRecommended by David Laguna-Palma based on reviews by Matthew Peeples, Isaac Ullah and Philip Verhagen based on reviews by Matthew Peeples, Isaac Ullah and Philip Verhagen
The paper entitled 'Social Network Analysis, Community Detection Algorithms, and Neighbourhood Identification in Pompeii' [1] presents a significant contribution to the field of archaeological network research, particularly in the challenging task of identifying urban neighborhoods within the context of Pompeii. This study focuses on the relational dynamics within urban neighborhoods and examines their indistinct boundaries through advanced analytical methods. The methodology employed provides a comprehensive analysis of community detection, including the Louvain and Leiden algorithms, and introduces a novel Convex Hull of Admissible Modularity Partitions (CHAMP) algorithm. The incorporation of a network approach into this domain is both innovative and timely. The potential impact of this research is substantial, offering new perspectives and analytical tools. This opens new avenues for understanding social structures in ancient urban settings, which can be applied to other archaeological contexts beyond Pompeii. Moreover, the manuscript is not only methodologically solid but also well-written and structured, making complex concepts accessible to a broad audience. In conclusion, this study represents a valuable contribution to the field of archaeology, particularly for archaeological network research. Their results not only enhance our knowledge of Pompeii but also provide a robust framework for future studies in similar historical contexts. Therefore, this publication advances our understanding of social dynamics in historical urban environments. The rigorous analysis, combined with the innovative application of network algorithms, makes this study a noteworthy addition to the existing body of network science literature. It is recommended for a wide range of scholars interested in the intersection of archaeology, history, and network science. Reference [1] Notarian, Matthew. 2024. Social Network Analysis, Community Detection Algorithms, and Neighbourhood Identification in Pompeii. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305968 | Social Network Analysis, Community Detection Algorithms, and Neighbourhood Identification in Pompeii | Notarian, Matthew | <p>The definition and identification of urban neighbourhoods in archaeological contexts remain complex and problematic, both theoretically and empirically. As constructs with both social and spatial characteristics, their detection through materia... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Computational archaeology, Mediterranean | David Laguna-Palma | 2023-08-31 19:28:35 | View | |
20 Feb 2024

Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of ArchaeologyWaagen, Jitte & Wijngaarden, Gert Jan van https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10061343Rewriting Archaeological Narratives: Archaeology of Archaeology through 3D Site Topography RecordingRecommended by Devi Taelman based on reviews by Geert Verhoeven, Jesús García-Sánchez and Catherine Scott based on reviews by Geert Verhoeven, Jesús García-Sánchez and Catherine Scott
Even though applications of 3D recording have existed in archaeology for a long time, it is only since the early 2000s that this field of research has become mainstream thanks to technological advances, and the availability of low-cost sensors and image-based modelling software. This has led to significant changes in the way archaeological sites are documented. This paper entitled "Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology" by Jitte Waagen & Gert Jan van Wijngaarden (2024) presents an overview of the current developments in the application possibilities of 3D site topography recording in archaeology. The paper is the result of the round table discussion "Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology" at the CAA conference on 5 April 2023 in Amsterdam, with contributions from Radu Brunchi, Nicola Lercari, Joep Orbons, Davide Tanasi, Alicia Walsh, Pawel Wolf and Teagan Zoldoske. The paper starts with a discussion of the Amsterdam Troy Project (ATP). In the frame of the ATP, the rich history of archaeological activity (over 150 years of fieldwork) at Troy is being studied to explore how previous archaeological research has helped to shape the current topography of the site and how these earlier research activities, embedded in their contemporary theoretical frameworks, have determined our understanding of the site (see Murray and M. Spriggs 2017, Carver 2011 for the influence of theory on archaeological fieldwork and archaeology as a discipline), the so-called 'Archaeology of Archaeology' approach. In addition to studying previous research records and re-excavating old excavation trenches, a central element of the project is the 3D recording of the past and present topography of the site in order to reconstruct the archaeological research activities at the site and their impact on the archaeological landscape. The paper focuses on current trends in 3D recording of archaeological site topography and discusses three main areas where 3D recording of archaeological site topography can contribute to the "Archaeology of Archaeology" approach: (1) monitoring the topography of sites for preservation, conservation, research and dissemination purposes; (2) reconstructing, reevaluating and reinterpreting past archaeological research efforts; and (3) archiving in a 4D (GIS) environment. This is done using the example of the Amsterdam Troy project and comparing it with other projects using similar methods and approaches. Using these case studies, the authors effectively discuss the impact of these technologies on the understanding of the topography of archaeological sites and how 3D recording can enhance archaeological research methodologies and interpretations, for example, by not using such 3D approaches as a stand-alone product but integrating them with available information from previous research activities. They also recognise the limitations and challenges involved, such as the need for customised data acquisition strategies and the lack of ready-made software solutions for developing comprehensive data management strategies. One topic that could have been covered in more detail is how 3D site topography recording (and 3D recording in general) is affected by current theoretical developments in archaeology. Like any other archaeological fieldwork or data collection approach, it is a child of its time. Decisions such as what to record, how to record, what to store, how to store, what to visualise, and how to visualise influence our understanding of archaeological sites (Ward 2022). This minor critical reflection aside, the paper makes a timely and significant contribution to archaeology by addressing current trends and the limitations of the increasingly widespread use of 3D site topography recording technologies. References Carver, G. (2011). Reflections on the archaeology of archaeological excavation, Archaeological Dialogues 18(1), pp. 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1380203811000067 Murray, T. and Spriggs, M. (2017). The historiography of archaeology: exploring theory, contingency and rationality, World Archaeology 49(2), pp. 151–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/00438243.2017.1334583 Ward, C. (2022). Excavating the Archive / Archiving the Excavation: Archival Processes and Contexts in Archaeology, Advances in Archaeological Practice 10(2), pp. 160–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/aap.2022.1 Waagen, J. and van Wijngaarden, G.J. (2024). Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology, Zenodo, 10061343, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommonded by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10061343 | Understanding Archaeological Site Topography: 3D Archaeology of Archaeology | Waagen, Jitte & Wijngaarden, Gert Jan van | <p>The current ubiquitous use of 3D recording technologies in archaeological fieldwork, for a large part due to the application of budget-friendly (drone) sensors and the availability of many low-cost image-based 3D modelling software packages, ha... |  | Computational archaeology, Remote sensing | Devi Taelman | 2023-10-17 23:03:47 | View | |
20 Mar 2024
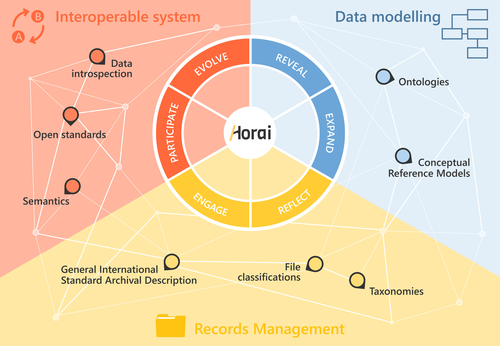
HORAI: An integrated management model for historical informationPablo del Fresno Bernal, Sonia Medina Gordo and Esther Travé Allepuz https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8185510A novel management model for historical informationRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by Leandro Sánchez Zufiaurre and 1 anonymous reviewerThe paper “HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information” presents a novel model for managing historical information. The study draws from an extensive indepth work in historical information management and a multi-disciplinary corpus of research ranging from heritage infrastructure research and practice to information studies and archival management literature. The paper ties into several key debates and discussions in the field showing awareness of the state-of-the-art of data management practice and theory. The authors argue for a new semantic data model HORAI and link it to a four-phase data management lifecycle model. The conceptual work is discussed in relation to three existing information systems partly predating and partly developed from the outset of the HORAI-model. While the paper shows appreciable understanding of the practical and theoretical state-of-the-art and the model has a lot of potential, in its current form it is still somewhat rough on the edges. Many of the both practical and theoretical threads introduced in the text warrant also more indepth consideration and it will be interesting to follow how the work will proceed in the future. For example, the comparison of the HORAI model and the ISAD(G): General International Standard Archival Description standard in the figure 1 is interesting but would require more elaboration. A slightly more thorough copyediting of the text would have also been helpful to make it more approachable. As a whole, in spite of the critique, I find both the paper and the model as valuable contributions to the literature and the practice of managing historical information. The paper reports thorough work, provides a lot of food for thought and several interesting lines of inquiry in the future. ReferencesDel Fresno Bernal, P., Medina Gordo, S. and Travé Allepuz, E. (2024). HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information. CAA 2023, Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8185510 | HORAI: An integrated management model for historical information | Pablo del Fresno Bernal, Sonia Medina Gordo and Esther Travé Allepuz | <p>The archiving process goes beyond mere data storage, requiring a theoretical, methodological, and conceptual commitment to the sources of information. We present Horai as a semantic-based integration model designed to facilitate the development... |  | Computational archaeology, Spatial analysis | Isto Huvila | 2023-07-26 09:33:58 | View | |
16 May 2022

Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool culturesAnnemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger https://osf.io/x8m4jOpen glossary for wood technologiesRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé
Wood is a widely available and versatile material, so it is not surprising that it has been a key resource throughout human history. However, it is more vulnerable to decomposition than other materials, and its direct use is only rarely recorded in prehistoric sites. Despite this, there are exceptions (e.g., [1-5] [6] and references therein), and indirect evidence of its use has been attested through use-wear analyses, residue analyses (e.g., [7]) and imprints on the ground (e.g., [8]). One interesting finding of note is that the technology required to make, for example, wooden spears was quite complex [9], leading some authors to propose that this type of tool production represented a cognitive leap for Pleistocene hominids [10]. Other researchers, however, have proposed that the production process for wooden tools could have been much easier than is currently thought [11]. Be that as it may, in recent years researchers have begun to approach wood remains systematically, developing analyses of natural and anthropogenic damage, often with the help of experimental reference samples. In this work, the authors elaborate a comprehensive glossary as a first step towards the understanding of the use of wood for technological purposes in different times and places, as there is still a general gap in the established nomenclature. Thus, this glossary is a synthesis and standardisation of analytical terms for early wood technologies that includes clear definitions and descriptions of traces from stone tool-using cultures, to avoid confusion in ongoing and future studies of wood tools. For this, the authors have carried out a detailed search of the current literature to select appropriate terms associated with additional readings that provide a wide, state-of-the-art description of the field of wood technology. An interesting point is that the glossary has been organised within a chaîne opératoire framework divided into categories including general terms and natural traces, and then complemented by an appendix of images. It is important to define the natural traces –understanding these as alterations caused by natural processes–because they can mask those modifications produced by other agents affecting both unmodified and modified wood before, during or after its human use. In short, the work carried out by Milks et al. [6] is an excellent and complete assessment and vital to the technological approach to wooden artifacts from archaeological contexts and establishing a common point for a standardised nomenclature. One of its particular strengths is that the glossary is a preprint that will remain open during the coming years, so that other researchers can continue to make suggestions and refinements to improve the definitions, terms and citations within it. [1] Oakley, K., Andrews, P., Keeley, L., Clark, J. (1977). A reappraisal of the Clacton spearpoint. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 43, 13-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0079497X00010343 [2] Thieme, H. (1997). Lower Palaeolithic hunting spears from Germany. Nature 385, 807-810. https://doi.org/10.1038/385807a0 [3] Schoch, W.H., Bigga, G., Böhner, U., Richter, P., Terberger, T. (2015). New insights on the wooden weapons from the Paleolithic site of Schöningen. Journal of Human Evolution 89, 214-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.08.004 [4] Aranguren, B., Revedin, A., Amico, N., Cavulli, F., Giachi, G., Grimaldi, S. et al. (2018). Wooden tools and fire technology in the early Neanderthal site of Poggetti Vecchi (Italy). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115, 2054-2059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716068115 [5] Rios-Garaizar, J., López-Bultó, O., Iriarte, E., Pérez-Garrido, C., Piqué, R., Aranburu, A., et al. (2018). A Middle Palaeolithic wooden digging stick from Aranbaltza III, Spain. PLoS ONE 13(3): e0195044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195044 [6] Milks, A. G., Lehmann, J., Böhner, U., Leder, D., Koddenberg, T., Sietz, M., Vogel, M., Terberger, T. (2022). Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures. Peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/x8m4j [7] Nugent, S. (2006). Applying use-wear and residue analyses to digging sticks. Mem Qld Mus Cult Herit Ser 4, 89-105. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.890092331962439 [8] Allué, E., Cabanes, D., Solé, A., Sala, R. (2012). Hearth Functioning and Forest Resource Exploitation Based on the Archeobotanical Assemblage from Level J, in: i Roura E. (Ed.), High Resolution Archaeology and Neanderthal Behavior: Time and Space in Level J of Abric Romaní (Capellades, Spain). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3922-2_9 [9] Ennos, A.R., Chan, T.L. (2016). "Fire hardening" spear wood does slightly harden it, but makes it much weaker and more brittle. Biology Letters 12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2016.0174 [10] Haidle, M.N. (2009). How to think a simple spear?, in: de Beaune S.A., Coolidge F.L., Wynn T. (Eds.), Cognitive Archaeology and Human Evolution. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 57-73. [11] Garofoli, D. (2015). A Radical Embodied Approach to Lower Palaeolithic Spear-making. Journal of Mind and Behavior 36, 1-26. | Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures | Annemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger | <p>The analysis of wood technologies created by stone tool-using cultures remains underdeveloped relative to the study of lithic and bone technologies. In recent years archaeologists have begun to approach wood assemblages systematically, developi... |  | Ancient Palaeolithic, Archaeobotany, Mesolithic, Middle Palaeolithic, Neolithic, Raw materials, Taphonomy, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Ruth Blasco | 2021-12-01 12:18:53 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information SystemsEric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732Exploring The Role of Archaeological Information Systems in Improving Data Management and InteroperabilityRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In response to the feedback provided by the reviewers, the authors have undertaken a comprehensive revision of the manuscript [1]. These revisions have specifically targeted the primary concerns raised regarding the clarity and structure of the argument concerning the transformative impact of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) on archaeological practices. In my view the revised manuscript now more clearly articulates the distinction between internal and external interoperability and emphasizes the critical importance of integrating contextual information with archaeological data. This approach directly addresses the previously identified need for enhanced traceability and usability of archaeological data, ensuring that the manuscript's contributions to the field are both clear and impactful. Moreover, the application of the proposed model at the Bibracte site is illustrated with greater clarity, serving as a concrete example of how the challenges associated with documentation and data management can be effectively addressed through the methodologies proposed in the paper. This practical demonstration enriches the manuscript, providing readers with a much clearer understanding of the model's applicability and benefits in real-world archaeological practice. The authors have also made significant efforts to refine the overall structure and coherence of the manuscript. By making complex concepts more accessible and ensuring a cohesive narrative flow throughout, the manuscript now offers a more engaging and comprehensible read. This has been achieved through careful rephrasing and restructuring of sections, particularly those relating to the T!O model's application and the conclusion, thereby enhancing reader engagement and comprehension. Alongside these structural and conceptual clarifications, explicit discussion of potential areas for future research, not only acknowledges the limitations of the current study but also highlights the significant potential for digital technologies to contribute to archaeological methodology and knowledge production. As such, the manuscript opens up new avenues for exploration and invites further scholarly engagement with the topics it addresses. I believe, these revisions address the earlier feedback quite comprehensively, presenting a robust and compelling argument for the adoption of collaborative and technologically informed approaches in the field of archaeology. The manuscript now stands as a strong example of the critical role AIS could/should play in transforming archaeological practices, offering valuable insights into how these kinds of systems might enhance the management, accessibility, and understanding of archaeological data. Through this revised submission, the authors have significantly strengthened their contribution to the ongoing discourse on digital archaeology, demonstrating the practical and theoretical implications of their work for the broader archaeological community. I am happy, therefore to recommend this paper for acceptence. Reference [1] Lacombe, E., Lukas, D. and Durost, S. (2024). The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems. Zenodo, 8309732, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732
| The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems | Eric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost | <p>The adoption of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) evolves according to multiple factors, both human and technical, as well as endogenous and exogenous. In consequence the ever increasing scope of digital tools, which allow for the organi... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Protohistory, Theoretical archaeology | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 18:58:26 | View | |
11 Jan 2022
Tektite geoarchaeology in mainland Southeast AsiaBen Marwick, Son Thanh Pham, Rachel Brewer, Li-Ying Wang https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/93fpaTektites as chronological markers: after careful geoarchaeological validation only!Recommended by Alain Queffelec and Shanti Pappu based on reviews by Sheila Mishra, Toshihiro Tada, Mike Morley and 1 anonymous reviewer and Shanti Pappu based on reviews by Sheila Mishra, Toshihiro Tada, Mike Morley and 1 anonymous reviewer
Tektites, a naturally occurring glass produced by major cosmic impacts and ejected at long distances, are known from five impacts worldwide [1]. The presence of this impact-generated glass, which can be dated in the same way as a volcanic rock, has been used to date archaeological sites in several regions of the world. This paper by Marwick and colleagues [2] reviews and adds new data on the use and misuse of this specific material as a chronological marker in Australia, East and Southeast Asia, where an impact dated to 0.78 Ma created and widely distributed tektites. This material, found in archaeological excavations in China, Laos, Thaïland, Australia, Borneo, and Vietnam, has been used to date layers containing lithic artifacts, sometimes creating a strong debate about the antiquity of the occupation and lithic production in certain regions. The review of existing data shows that geomorphological data and stratigraphic integrity can be questioned at many sites that have yielded tektites. The new data provided by this paper for five archaeological sites located in Vietnam confirm that many deposits containing tektites are indeed lag deposits and that these artifacts, thus in secondary position, cannot be considered to date the layer. This study also emphasizes the general lack of other dating methods that would allow comparison with the tektite age. In the Vietnamese archaeological sites presented here, discrepancies between methods, and the presence of historical artifacts, confirm that the layers do not share similar age with the cosmic impact that created the tektites. Based on this review and these new results, and following previous propositions [3], Marwick and colleagues conclude that, if tektites can be used as chronological markers, one has to prove that they are in situ. They propose that geomorphological assessment of the archaeological layer as primary deposit must first be attained, in addition to several parameters of the tektites themselves (shape, size distribution, chemical composition). Large error can be made by using only tektites to date an archaeological layer, and this material should not be used solely due to risks of high overestimation of the age of the archaeological production. [1] Rochette, P., Beck, P., Bizzarro, M., Braucher, R., Cornec, J., Debaille, V., Devouard, B., Gattacceca, J., Jourdan, F., Moustard, F., Moynier, F., Nomade, S., Reynard, B. (2021). Impact glasses from Belize represent tektites from the Pleistocene Pantasma impact crater in Nicaragua. Communications Earth & Environment, 2(1), 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00155-1 [2] Marwick, B., Son, P. T., Brewer, R., Wang, L.-Y. (2022). Tektite geoarchaeology in mainland Southeast Asia. SocArXiv, 93fpa, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology, https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/93fpa. [3] Tada, T., Tada, R., Chansom, P., Songtham, W., Carling, P. A., Tajika, E. (2020). In Situ Occurrence of Muong Nong-Type Australasian Tektite Fragments from the Quaternary Deposits near Huai Om, Northeastern Thailand. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science 7(1), 1–15, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-020-00378-4 | Tektite geoarchaeology in mainland Southeast Asia | Ben Marwick, Son Thanh Pham, Rachel Brewer, Li-Ying Wang | <p>Tektites formed by an extraterrestrial impact event in Southeast Asia at 0.78 Ma have been found in geological contexts and archaeological sites throughout Australia, East and Southeast Asia. At some archaeological sites, especially in Bose Bas... |  | Asia, Geoarchaeology | Alain Queffelec | 2021-08-14 18:04:18 | View | |
01 Sep 2023
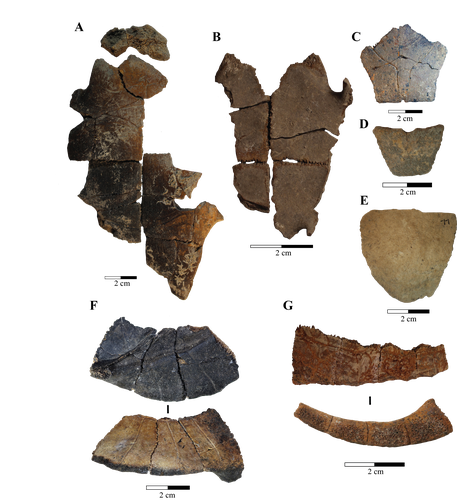

Zooarchaeological investigation of the Hoabinhian exploitation of reptiles and amphibians in Thailand and Cambodia with a focus on the Yellow-headed tortoise (Indotestudo elongata (Blyth, 1854))Corentin Bochaton, Sirikanya Chantasri, Melada Maneechote, Julien Claude, Christophe Griggo, Wilailuck Naksri, Hubert Forestier, Heng Sophady, Prasit Auertrakulvit, Jutinach Bowonsachoti, Valery Zeitoun https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.27.538552A zooarchaeological perspective on testudine bones from Hoabinhian hunter-gatherer archaeological assemblages in Southeast AsiaRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Noel Amano and Iratxe Boneta based on reviews by Noel Amano and Iratxe Boneta
The study of the evolution of the human diet has been a central theme in numerous archaeological and paleoanthropological investigations. By reconstructing diets, researchers gain deeper insights into how humans adapted to their environments. The analysis of animal bones plays a crucial role in extracting dietary information. Most studies involving ancient diets rely heavily on zooarchaeological examinations, which, due to their extensive history, have amassed a wealth of data. During the Pleistocene–Holocene periods, testudine bones have been commonly found in a multitude of sites. The use of turtles and tortoises as food sources appears to stretch back to the Early Pleistocene [1-4]. More importantly, these small animals play a more significant role within a broader debate. The exploitation of tortoises in the Mediterranean Basin has been examined through the lens of optimal foraging theory and diet breadth models (e.g. [5-10]). According to the diet breadth model, resources are incorporated into diets based on their ranking and influenced by factors such as net return, which in turn depends on caloric value and search/handling costs [11]. Within these theoretical frameworks, tortoises hold a significant position. Their small size and sluggish movement require minimal effort and relatively simple technology for procurement and processing. This aligns with optimal foraging models in which the low handling costs of slow-moving prey compensate for their small size [5-6,9]. Tortoises also offer distinct advantages. They can be easily transported and kept alive, thereby maintaining freshness for deferred consumption [12-14]. For example, historical accounts suggest that Mexican traders recognised tortoises as portable and storable sources of protein and water [15]. Furthermore, tortoises provide non-edible resources, such as shells, which can serve as containers. This possibility has been discussed in the context of Kebara Cave [16] and noted in ethnographic and historical records (e.g. [12]). However, despite these advantages, their slow growth rate might have rendered intensive long-term predation unsustainable. While tortoises are well-documented in the Southeast Asian archaeological record, zooarchaeological analyses in this region have been limited, particularly concerning prehistoric hunter-gatherer populations that may have relied extensively on inland chelonian taxa. With the present paper Bochaton et al. [17] aim to bridge this gap by conducting an exhaustive zooarchaeological analysis of turtle bone specimens from four Hoabinhian hunter-gatherer archaeological assemblages in Thailand and Cambodia. These assemblages span from the Late Pleistocene to the first half of the Holocene. The authors focus on bones attributed to the yellow-headed tortoise (Indotestudo elongata), which is the most prevalent taxon in the assemblages. The research include osteometric equations to estimate carapace size and explore population structures across various sites. The objective is to uncover human tortoise exploitation strategies in the region, and the results reveal consistent subsistence behaviours across diverse locations, even amidst varying environmental conditions. These final proposals suggest the possibility of cultural similarities across different periods and regions in continental Southeast Asia. In summary, this paper [17] represents a significant advancement in the realm of zooarchaeological investigations of small prey within prehistoric communities in the region. While certain approaches and issues may require further refinement, they serve as a comprehensive and commendable foundation for assessing human hunting adaptations.
References [1] Hartman, G., 2004. Long-term continuity of a freshwater turtle (Mauremys caspica rivulata) population in the northern Jordan Valley and its paleoenvironmental implications. In: Goren-Inbar, N., Speth, J.D. (Eds.), Human Paleoecology in the Levantine Corridor. Oxbow Books, Oxford, pp. 61-74. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvh1dtct.11 [2] Alperson-Afil, N., Sharon, G., Kislev, M., Melamed, Y., Zohar, I., Ashkenazi, R., Biton, R., Werker, E., Hartman, G., Feibel, C., Goren-Inbar, N., 2009. Spatial organization of hominin activities at Gesher Benot Ya'aqov, Israel. Science 326, 1677-1680. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1180695 [3] Archer, W., Braun, D.R., Harris, J.W., McCoy, J.T., Richmond, B.G., 2014. Early Pleistocene aquatic resource use in the Turkana Basin. J. Hum. Evol. 77, 74-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.02.012 [4] Blasco, R., Blain, H.A., Rosell, J., Carlos, D.J., Huguet, R., Rodríguez, J., Arsuaga, J.L., Bermúdez de Castro, J.M., Carbonell, E., 2011. Earliest evidence for human consumption of tortoises in the European Early Pleistocene from Sima del Elefante, Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain. J. Hum. Evol. 11, 265-282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.06.002 [5] Stiner, M.C., Munro, N., Surovell, T.A., Tchernov, E., Bar-Yosef, O., 1999. Palaeolithic growth pulses evidenced by small animal exploitation. Science 283, 190-194. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5399.190 [6] Stiner, M.C., Munro, N.D., Surovell, T.A., 2000. The tortoise and the hare: small-game use, the Broad-Spectrum Revolution, and paleolithic demography. Curr. Anthropol. 41, 39-73. https://doi.org/10.1086/300102 [7] Stiner, M.C., 2001. Thirty years on the “Broad Spectrum Revolution” and paleolithic demography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98 (13), 6993-6996. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.121176198 [8] Stiner, M.C., 2005. The Faunas of Hayonim Cave (Israel): a 200,000-Year Record of Paleolithic Diet. Demography and Society. American School of Prehistoric Research, Bulletin 48. Peabody Museum Press, Harvard University, Cambridge. [9] Stiner, M.C., Munro, N.D., 2002. Approaches to prehistoric diet breadth, demography, and prey ranking systems in time and space. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 9, 181-214. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016530308865 [10] Blasco, R., Cochard, D., Colonese, A.C., Laroulandie, V., Meier, J., Morin, E., Rufà, A., Tassoni, L., Thompson, J.C. 2022. Small animal use by Neanderthals. In Romagnoli, F., Rivals, F., Benazzi, S. (eds.), Updating Neanderthals: Understanding Behavioral Complexity in the Late Middle Palaeolithic. Elsevier Academic Press, pp. 123-143. ISBN 978-0-12-821428-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2019-0-03240-2 [11] Winterhalder, B., Smith, E.A., 2000. Analyzing adaptive strategies: human behavioural ecology at twenty-five. Evol. Anthropol. 9, 51-72. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1520-6505(2000)9:2%3C51::aid-evan1%3E3.0.co;2-7 [12] Schneider, J.S., Everson, G.D., 1989. The Desert Tortoise (Xerobates agassizii) in the Prehistory of the Southwestern Great Basin and Adjacent areas. J. Calif. Gt. Basin Anthropol. 11, 175-202. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27825383 [13] Thompson, J.C., Henshilwood, C.S., 2014b. Nutritional values of tortoises relative to ungulates from the Middle Stone Age levels at Blombos Cave, South Africa: implications for foraging and social behaviour. J. Hum. Evol. 67, 33-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.09.010 [14] Blasco, R., Rosell, J., Smith, K.T., Maul, L.Ch., Sañudo, P., Barkai, R., Gopher, A. 2016. Tortoises as a Dietary Supplement: a view from the Middle Pleistocene site of Qesem Cave, Israel. Quat Sci Rev 133, 165-182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.12.006 [15] Pepper, C., 1963. The truth about the tortoise. Desert Mag. 26, 10-11. [16] Speth, J.D., Tchernov, E., 2002. Middle Paleolithic tortoise use at Kebara Cave (Israel). J. Archaeol. Sci. 29, 471-483. https://doi.org/10.1006/jasc.2001.0740 [17] Bochaton, C., Chantasri, S., Maneechote, M., Claude, J., Griggo, C., Naksri, W., Forestier, H., Sophady, H., Auertrakulvit, P., Bowonsachoti, J. and Zeitoun, V. (2023) Zooarchaeological investigation of the Hoabinhian exploitation of reptiles and amphibians in Thailand and Cambodia with a focus on the Yellow-headed Tortoise (Indotestudo elongata (Blyth, 1854)), BioRXiv, 2023.04.27.538552 , ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.27.538552v3 | Zooarchaeological investigation of the Hoabinhian exploitation of reptiles and amphibians in Thailand and Cambodia with a focus on the Yellow-headed tortoise (*Indotestudo elongata* (Blyth, 1854)) | Corentin Bochaton, Sirikanya Chantasri, Melada Maneechote, Julien Claude, Christophe Griggo, Wilailuck Naksri, Hubert Forestier, Heng Sophady, Prasit Auertrakulvit, Jutinach Bowonsachoti, Valery Zeitoun | <p style="text-align: justify;">While non-marine turtles are almost ubiquitous in the archaeological record of Southeast Asia, their zooarchaeological examination has been inadequately pursued within this tropical region. This gap in research hind... |  | Asia, Taphonomy, Zooarchaeology | Ruth Blasco | Iratxe Boneta, Noel Amano | 2023-05-02 09:30:50 | View |
28 Aug 2023
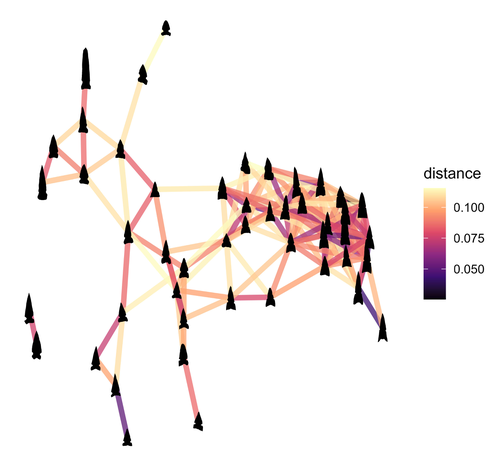
Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United StatesRobert J. Bischoff https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc2D Geometric Morphometrics of Projectile Points from the Southwestern United StatesRecommended by Adrian L. Burke based on reviews by James Conolly and 1 anonymous reviewerBischoff (2023) is a significant contribution to the growing field of geometric morphometric analysis in stone tool analysis. The subject is projectile points from the southwestern United States. Projectile point typologies or systematics remain an important part of North American archaeology, and in fact these typologies continue to be used primarily as cultural-historical markers. This article looks at projectile point types using a 2D image geometric morphometric analysis as a way of both improving on projectile point types but also testing if these types are in fact based in measurable reality. A total of 164 point outlines are analyzed using Elliptical Fourier, semilandmark and landmark analyses. The author also uses a network analysis to look at possible relationships between projectile point morphologies in space. This is a clever way of working around the predefined distributions of projectile point types, some of which are over 100 years old. Because of the dynamic nature of stone tools in terms of their use, reworking and reuse, this article can also provide solutions for studying the dynamic nature of stone tools. This article therefore also has a wide applicability to other stone tool analyses. Reference Bischoff, R. J. (2023) Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States, SocArXiv, a6wjc, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a6wjc | Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Projectile Points from the Southwest United States | Robert J. Bischoff | <p style="text-align: justify;">Traditional analyses of projectile points often use visual identification, the presence or absence of discrete characteristics, or linear measurements and angles to classify points into distinct types. Geometric mor... |  | Archaeometry, Computational archaeology, Lithic technology, North America | Adrian L. Burke | 2022-12-18 03:38:14 | View | |
14 Nov 2022
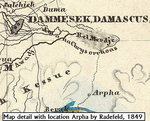
Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman CityJens Kleb https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021Cross-comparison of classical sources, explorer and scientific reports and maps in the search of an ancient city: The example of Raphana of the DecapolisRecommended by Luc Doyon based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli
Establishing the precise location of ancient cities constitutes a challenging task that requires the implementation of multi-disciplinary approaches. In his manuscript entitled “Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha: The search of an eminent Greco-Roman city”, Kleb (2022) proposes a convincing argument building on in-depth research of classical literary sources, literature review of explorer accounts and scientific publications from the 19th and 20th century as well as analysis of old and new maps, aerial photographs, and satellite images. This research report clearly emphasizes the importance of undertaking systematic interdisciplinary work on the topic to mitigate the uncertainties associated with the identification of Raphana, the Decapolis city first mentioned by Pliny the Elder. The Decapolis refers to a group of ten cities of Hellenistic traditions located on the eastern borders of the Roman Empire. This group of cities plays an important role in research that aims to contextualize the Judaean and Galilean history and to investigate urban centers in which different local and Greco-Roman influences met (Lichtenberger, 2021). While the location of most of the Decapolis cities is known and is (or was) subjected to systematic archaeological investigations (e.g., Eisenberg and Kowalewska, 2022; Makhadmeh et al., 2020; Shiyab et al., 2019), the location of others remain speculative. This is the case of Raphana for which the precise location remains difficult to establish owing in part to numerous name changes, limited information on the city structure, architecture, and size, etc. The research presented by Kleb (2022) has some merits, which is emphasized here, although the report is presented in an unusual format compared to traditional scientific articles, i.e., introduction, research background, methodology, results, and discussion. First, the extensive review of classical works allows the reader to gain a historical perspective on the change of names from Raepta/Raphana to Arpha/Arefa. The author argues these different names likely refer to a single location. Second, the author combs through an impressive literature from the 19th and 20th century and emphasize how some assumptions by explorers who visited the region were introduced in the scientific literature and remained unchallenged. Finally, the author gathers a remarkable quantity of old and new maps of the Golan, el-Ledja and Hauran regions and compare them with multiple lines of evidence to hypothesize that the location of Raphana may lie near Ar-Rafi’ah, also known as Bir Qassab, in the Ard el Fanah plain, a conclusion that now requires to be tested through fieldwork investigations. References Kleb, J. (2022) Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City. Figshare, 20550021, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021 Eisenberg, M. and Kowalewska, A. (2022). Funerary podia of Hippos of the Decapolis and the phenomenon in the Roman world. J. Roman Archaeol. 35, 107–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047759421000465 Lichtenberger, A. (2021). The Decapolis, in: A Companion to the Hellenistic and Roman Near East. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119037354.ch18 Makhadmeh, A., Al-Badarneh, M., Rawashdeh, A. and Al-Shorman, A. (2020). Evaluating the carrying capacity at the archaeological site of Jerash (Gerasa) using mathematical GIS modeling. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 23, 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.09.002 Shiyab, A., Al-Shorman, A., Turshan, N., Tarboush, M., Alawneh, F. and Rahabneh, A. (2019). Investigation of late Roman pottery from Gadara of the Decapolis, Jordan using multi-methodic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 25, 100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2019.04.003 | Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City | Jens Kleb | <p style="text-align: justify;">This research paper presents a detailed analysis of ancient literature and archaeological and geographical research until the present day for an important ancient location in the southern part of Syria. This one had... |  | Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Luc Doyon | 2021-12-30 13:54:32 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










