Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors▼ | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
10 Jan 2024
Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3DFlorian Linsel, Jan Philipp Bullenkamp & Hubert Mara https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8296269A valuable contribution to automated analysis of palaeolithic artefactsRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Lutz Schubert and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Lutz Schubert and 1 anonymous reviewer
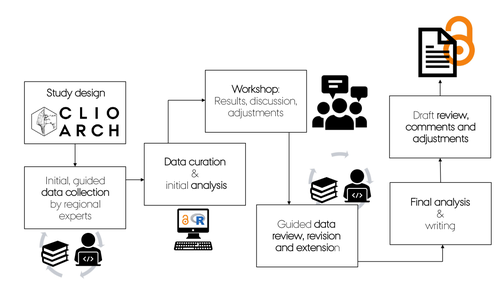
In this paper (Linsel/Bullenkamp/Mara 2024), the authors propose an automatic system for scar-ridge-pattern detection on palaeolithic artefacts based on Morse Theory. Scare-Ridge pattern recognition is a process that is usually done manually while creating a drawing of the object itself. Automatic systems to detect scars or ridges exist, but only a small amount of them is utilizing 3D data. In addition to the scar-ridges detection, the authors also experiment in automatically detecting the operational sequence, the temporal relation between scars and ridges. As a result, they can export a traditional drawing as well as graph models displaying the relationships between the scars and ridges. After an introduction to the project and the practice of documenting palaeolithic artefacts, the authors explain their procedure in automatising the analysis of scars and ridges as well as their temporal relation to each other on these artefacts. To illustrate the process, an open dataset of lithic artefacts from the Grotta di Fumane, Italy, was used and 62 artefacts selected. To establish a Ground Truth, the artefacts were first annotated manually. The authors then continue to explain in detail each step of the automated process that follows and the results obtained. In the second part of the paper, the results are presented. First the results of the segmentation process shows that the average percentage of correctly labelled vertices is over 91%, which is a remarkable result. The graph modelling however shows some more difficulties, which the authors are aware of. To enhance the process, the authors rightfully aim to include datasets of experimental archaeology in the future. They also aim to develop a way of detecting the operational sequence automatically and precisely. This paper has great potential as it showcases exactly what Digital and Computational Archaeology is about: The development of new digital methods to enhance the analysis of archaeological data. While this procedure is still in development, the authors were able to present a valuable contribution to the automatization of analytical archaeology. By creating a step towards the machine-readability of this data, they also open up the way to further steps in machine learning within Archaeology. BibliographyLinsel, F., Bullenkamp, J. P., and Mara, H. (2024). Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3D, Zenodo, 8296269, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8296269 | Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3D | Florian Linsel, Jan Philipp Bullenkamp & Hubert Mara | <p>Motivated by the concept of combining the archaeological practice of creating lithic artifact drawings with the potential of 3D mesh data, our goal in this project is not only to analyze the shape at the artifact level, but also to enable a mor... | Computational archaeology, Europe, Lithic technology, Upper Palaeolithic | Sebastian Hageneuer | 2023-09-01 23:03:59 | View | ||
11 Dec 2023
A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in EuropeFelix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus, Damian Stefański, Hans Vandendriessche, Shumon T. Hussain https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587Questioning Final Palaeolithic and early Mesolithic cultural taxonomy with a data-driven statistical approachRecommended by Anaïs Vignoles based on reviews by Dirk Leder and 2 anonymous reviewersCultural taxonomies are an essential tool for archaeologists working with prehistoric material cultures as they have historically been used to create the basic analytical units for studying cultural evolution through time (de Mortillet, 1883 ; Breuil, 1913). This approach has its limits as the taxonomic units are essentially etic constructions, i.e., they are defined in a cultural context exterior to the one that produced the material culture on which they are based (e.g., Pesesse, 2019). But to approach questions related to cultural evolution, one has to define archaeological units with clear geographic and chronological delineations in order to be compared synchronically and diachronically (e.g., Willey and Philips, 1958). In « A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolitic/Earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe », F. Riede and colleagues propose a novel and interesting approach to question the end of the Palaeolithic and beginning of the Mesolithic’s « named archaeological cultures » (NACs) analytical pertinence (Riede et al., 2023). In this particular context, NACs are indeed very numerous (n = 86) and result from complex and regional research histories. It seems thus pertinent to question the extent to which the said NACs chronological and geographic patterns result from past cultural diversity and evolution, and are not artefacts of research. To do so, the authors adopted a data-driven approach that they describe in detail in the paper. First, they gathered an European data base of lithic tool-kit composition, blade and bladelet technology and armature morphology at 350 key sites considered representative of NACs, dated between 15 and 11 ka (Hussain et al., 2023). These data were then analyzed using geometric morphometrics and a set of statisticaal tests in order to 1) test the coherence of these taxonomic units, and 2) test the chronological change in artefact shape variation. The authors conclude that the data set is partially biased by reasearch practices and histories, as their data-driven approach has only partially replicated traditional NACs for the european Late Palaeolithic/Early Mesolithic. However, their analysis of armature shape evolution has shown a tendency to diversification overtime, a pattern that was already observed in more « traditional » approaches. This study is, in my opinion, an excellent contribution for a significant step in macro-regional approaches to the archaeological record: defining discrete archaeological units that serve as a basis for subsequent analyses aimed at delineating cultural evolutionary processes. The authors propose a carefully designed and statistically grounded procedure in order to achieve these definitions in the most replicable and explicit possible manner. Taking advantage of drawings as a primary source of information is also very original despite several limitations of this approach (such as the necessary selection of most typical artefacts to be represented, the incompleteness of data publication or the difficulty to access all published work across such a large geographic area). The results of the study are convincing enough to allow the authors to discuss the pertinence of European Late Paleo/Early Mesolithic NACs, the potential epistemological and historical factors that could affect this taxonomic framework, as well as to give more weight to the traditional hypothesis of lithic cultural diversification towards the end of the Pleistocene/beginning of the Holocene in Europe. I would also like to underline the authors’ important efforts to ensure transparence and replicability of their study, as well as the accessibility of the data, thanks to extensive supplementary data and a data paper describing their data set in detail. Anaïs L. Vignoles References Breuil, H. (1913). Les subdivisions du paléolithique supérieur et leur signification. In Congrès international d’anthropologie et d’archéologie préhistoriques - compte-rendu de la XIVème session, tome 1:165‑238. Genève: Imprimerie Albert Kündig. Hussain, S. T., Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D. and Vandendriessche, H. (2023). A Pan-European Dataset Revealing Variability in Lithic Technology, Toolkits, and Artefact Shapes ~15-11 Kya. Scientific Data 10 (1): 593. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02500-9. Mortillet, G. (1883). Le Préhistorique, antiquité de l’homme. Reinwald. Paris. Pesesse, D. (2019). Analyser un silex, le façonner à nouveau ? Sur certains usages de la chaîne opératoire au Paléolithique supérieur. Techniques & culture, no 71: 74‑77. https://doi.org/10.4000/tc.11321. Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D., Vandendriessche, H. and Hussain, S. T. (2023). A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe, Zenodo, 8195587., ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587 Willey, G. R. and Phillips, P. (1958). Method and Theory in American Archaeology. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press. | A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe | Felix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus,... | <p>Archaeological systematics, together with spatial and chronological information, are commonly used to infer cultural evolutionary dynamics in the past. For the study of the Palaeolithic, and particularly the European Final Palaeolithic and earl... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Lithic technology, Mesolithic, Upper Palaeolithic | Anaïs Vignoles | 2023-07-29 16:06:17 | View | |
22 Apr 2024
The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information SystemsEric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732Exploring The Role of Archaeological Information Systems in Improving Data Management and InteroperabilityRecommended by James Stuart Taylor based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In response to the feedback provided by the reviewers, the authors have undertaken a comprehensive revision of the manuscript [1]. These revisions have specifically targeted the primary concerns raised regarding the clarity and structure of the argument concerning the transformative impact of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) on archaeological practices. In my view the revised manuscript now more clearly articulates the distinction between internal and external interoperability and emphasizes the critical importance of integrating contextual information with archaeological data. This approach directly addresses the previously identified need for enhanced traceability and usability of archaeological data, ensuring that the manuscript's contributions to the field are both clear and impactful. Moreover, the application of the proposed model at the Bibracte site is illustrated with greater clarity, serving as a concrete example of how the challenges associated with documentation and data management can be effectively addressed through the methodologies proposed in the paper. This practical demonstration enriches the manuscript, providing readers with a much clearer understanding of the model's applicability and benefits in real-world archaeological practice. The authors have also made significant efforts to refine the overall structure and coherence of the manuscript. By making complex concepts more accessible and ensuring a cohesive narrative flow throughout, the manuscript now offers a more engaging and comprehensible read. This has been achieved through careful rephrasing and restructuring of sections, particularly those relating to the T!O model's application and the conclusion, thereby enhancing reader engagement and comprehension. Alongside these structural and conceptual clarifications, explicit discussion of potential areas for future research, not only acknowledges the limitations of the current study but also highlights the significant potential for digital technologies to contribute to archaeological methodology and knowledge production. As such, the manuscript opens up new avenues for exploration and invites further scholarly engagement with the topics it addresses. I believe, these revisions address the earlier feedback quite comprehensively, presenting a robust and compelling argument for the adoption of collaborative and technologically informed approaches in the field of archaeology. The manuscript now stands as a strong example of the critical role AIS could/should play in transforming archaeological practices, offering valuable insights into how these kinds of systems might enhance the management, accessibility, and understanding of archaeological data. Through this revised submission, the authors have significantly strengthened their contribution to the ongoing discourse on digital archaeology, demonstrating the practical and theoretical implications of their work for the broader archaeological community. I am happy, therefore to recommend this paper for acceptence. Reference [1] Lacombe, E., Lukas, D. and Durost, S. (2024). The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems. Zenodo, 8309732, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8309732
| The transformation of an archaeological community and its resulting representations in the context of the co-development of open Archaeological Information Systems | Eric Lacombe, Dominik Lukas, Sébastien Durost | <p>The adoption of Archaeological Information Systems (AIS) evolves according to multiple factors, both human and technical, as well as endogenous and exogenous. In consequence the ever increasing scope of digital tools, which allow for the organi... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Protohistory, Theoretical archaeology | James Stuart Taylor | 2023-09-01 18:58:26 | View | |
02 Dec 2023
Research perspectives and their influence for typologiesEnrico Giannichedda https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7322855Complexity and Purpose – A Pragmatic Approach to the Diversity of Archaeological Classificatory Practice and TypologyRecommended by Shumon Tobias Hussain , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak based on reviews by Ulrich Veit, Martin Hinz, Artur Ribeiro and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Ulrich Veit, Martin Hinz, Artur Ribeiro and 1 anonymous reviewer
“Research perspectives and their influence for typologies” by E. Giannichedda (1) is a contribution to the upcoming volume on the role of typology and type-thinking in current archaeological theory and praxis edited by the recommenders. Taking a decidedly Italian perspective on classificatory practice grounded in what the author dubs the “history of material culture”, Giannichedda offers an inventory of six divergent but overall complementary modes of ordering archaeological material: i) chrono-typological and culture-historical, ii) techno-anthropological, iii) social, iv) socio-economic and v) cognitive. These various lenses broadly align with similarly labeled perspectives on the archaeological record more generally. According to the author, they lend themselves to different ways of identifying and using types in archaeological work. Importantly, Giannichedda reminds us that no ordering practice is a neutral act and typologies should not be devised for their own sake but because we have specific epistemic interests. Even though this view is certainly not shared by everyone involved in the broader debate on the purpose and goal of systematics, classification, typology or archaeological taxonomy (2–4), the paper emphatically defends the long-standing idea that ordering practices are not suitable to elucidate the structure and composition of reality but instead devise tools to answer certain questions or help investigate certain dimensions of complex past realities. This position considers typologies as conceptual prosthetics of knowing, a view that broadly resonates with what is referred to as epistemic instrumentalism in the philosophy of science (5, 6). Types and type-work should accordingly reflect well-defined means-end relationships. Based on the recognition of archaeology as part of an integrated “history of material culture” rooted in a blend of continental and Anglophone theories, Giannichedda argues that type-work should pay attention to relevant relations between various artefacts in a given historical context that help further historical understanding. Classificatory practice in archaeology – the ordering of artefactual materials according to properties – must thus proceed with the goal of multifaceted “historical reconstruction in mind”. It should serve this reconstruction, and not the other way around. By drawing on the example of a Medieval nunnery in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, Giannichedda explores how different goals of classification and typo-praxis (linked to i-v; see above) foreground different aspects, features, and relations of archaeological materials and as such allow to pinpoint and examine different constellations of archaeological objects. He argues that archaeological typo-praxis, for this reason, should almost never concern itself with isolated artefacts but should take into account broader historical assemblages of artefacts. This does not necessarily mean to pay equal attention to all available artefacts and materials, however. To the contrary, in many cases, it is necessary to recognize that some artefacts and some features are more important than others as anchors grouping materials and establishing relations with other objects. An example are so-called ‘barometer objects’ (7) or unique pieces which often have exceptional informational value but can easily be overlooked when only shared features are taken into consideration. As Giannichedda reminds us, considering all objects and properties equally is also a normative decision and does not render ordering less subjective. The archaeological analysis of types should therefore always be complemented by an examination of variants, even if some of these variants are idiosyncratic or even unique. A type, then, may be difficult to define universally. In total, “Research perspectives and their influence for typologies” emphasizes the need for “elastic” and “flexible” approaches to archaeological types and typologies in order to effectively respond to the manifold research interests cultivated by archaeologists as well as the many and complex past realities they face. Complexity is taken here to indicate that no single research perspective and associated mode of ordering can adequately capture the dimensionality and richness of these past realities and we can therefore only benefit from multiple co-existing ways of grouping and relating archaeological artefacts. Different logics of grouping may simply reveal different aspects of these realities. As such, Giannichedda’s proposal can be read as a formulation of the now classic pluralism thesis (8–11) – that only a plurality of ways of ordering and interrelating artefacts can unlock the full suite of relationships within historical assemblages archaeologists are interested in.
Bibliography 1. Giannichedda, E. (2023). Research perspectives and their influence for typologies, Zenodo, 7322855, ver. 9 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7322855 2. Dunnell, R. C. (2002). Systematics in Prehistory, Illustrated Edition (The Blackburn Press, 2002). 3. Reynolds, N. and Riede, F. (2019). House of cards: cultural taxonomy and the study of the European Upper Palaeolithic. Antiquity 93, 1350–1358. https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2019.49 4. Lyman, R. L. (2021). On the Importance of Systematics to Archaeological Research: the Covariation of Typological Diversity and Morphological Disparity. J Paleo Arch 4, 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-021-00077-6 5. Van Fraassen, B. C. (2002). The empirical stance (Yale University Press). 6. Stanford, P. K. (2006). Exceeding Our Grasp: Science, History, and the Problem of Unconceived Alternatives (Oxford University Press). https://doi.org/10.1093/0195174089.001.0001 7. Radohs, L. (2023). Urban elite culture: a methodological study of aristocracy and civic elites in sea-trading towns of the southwestern Baltic (12th-14th c.) (Böhlau). 8. Kellert, S. H., Longino, H. E. and Waters, C. K. (2006). Scientific pluralism (University of Minnesota Press). 9. Cat, J. (2012). Essay Review: Scientific Pluralism. Philosophy of Science 79, 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1086/664747 10. Chang, H. (2012). Is Water H2O?: Evidence, Realism and Pluralism (Springer Netherlands). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3932-1 11. Wylie, A. (2015). “A plurality of pluralisms: Collaborative practice in archaeology” in Objectivity in Science, (Springer), pp. 189–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14349-1_10
| Research perspectives and their influence for typologies | Enrico Giannichedda | <p>This contribution opens with a brief reflection on theoretical archaeology and practical material classification activities. Following this, the various questions that can be asked of artefacts to be classified will be briefly addressed. Questi... |  | Theoretical archaeology | Shumon Tobias Hussain | 2022-11-10 20:14:52 | View | |
28 May 2020

TIPZOO: a Touchscreen Interface for Palaeolithic Zooarchaeology. Towards making data entry and analysis easier, faster, and more reliableEmmanuel Discamps https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/aew5cA new software to improve standardization and quality of data in zooarchaeologyRecommended by Florent Rivals based on reviews by Delphine Vettese and Argant Thierry based on reviews by Delphine Vettese and Argant Thierry
Standardization and quality of data collection are identified as challenges for the future in zooarchaeology [1]. These issues were already identified in the early 1970s when the International Council for Archaeozoology (ICAZ) recommended to “standardize measurements and data in publications”. In the recent years, there is strong recommendations by publishers and grant to follow the FAIR Principle i.e. to “improve the findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reuse of digital assets” [2]. As zooarchaeologists, we should make our methods more clear and replicable by other researchers to produce comparable datasets. In this paper the authors make a significant step in proposing a tool to replace traditional data recording softwares. The problems related to data recording are clearly identified and discussed. All the features offered by TIPZOO allow to standardize the data, to reduce the errors when entering the data, to save time with auto-filling entries. The coding system used in TIPZOO is based on variables taken from the most used and updated literature in zooarchaeology. Its connections with various R packages allow to directly export the data and to transform the raw data to produce summary tables, graphs and basic statistics. Finally, the advantage of this tool is that it can be improved, debugged, or implemented at any time. TIPZOO provides a standardized system to compile and share large and consistent datasets that will allow comparison among assemblages at a large scale, and for this reason, I have recommended the work for PCI Archaeology. References [1] Steele, T.E. (2015). The contributions of animal bones from archaeological sites: the past and future of zooarchaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 56, 168–176. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2015.02.036 | TIPZOO: a Touchscreen Interface for Palaeolithic Zooarchaeology. Towards making data entry and analysis easier, faster, and more reliable | Emmanuel Discamps | <p>Zooarchaeological studies of fossil bone collections are often conducted using simple spreadsheet programs for data recording and analysis. After quickly summarizing the limitations of such an approach, we present a new software solution, TIPZO... |  | Spatial analysis, Taphonomy, Zooarchaeology | Florent Rivals | 2020-04-16 13:27:00 | View | |
21 Nov 2022

Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in ArchaeologyEmma Karoune and Esther Plomp https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029Three levels of reproducible workflow remove barriers for archaeologists and increase accessibilityRecommended by Ben Marwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick
Over the last decade, a small but growing community of archaeologists, from a diversity of intellectual and demographic backgrounds, have been striving for computational reproducibility in their published research. In their survey of the accomplishments of this thriving community, Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp (2022) analyzed the wide variety of approaches researchers have taken to enhance the reproducibility of their research. A key contribution of this paper is their excellent synthesis of diverse approaches into three levels of increasing complexity. This is helpful because it provides multiple entry points for researchers new to the challenge of fortifying their research. Many researchers assume that computational reproducibility is only achievable if they have a high degree of technical skill with computers, or is only necessary if their work is very computationally intensive. Karoune and Plomp give three compelling reasons why reproducibility is important for all archaeological research, and through their three levels they demonstrate that how these levels can be accomplished with basic, non-specialized computer skills and widely used free software. They showcase exemplary work from a variety of archaeologists to show how practical and achievable reproducible research is for all archaeologists. They advocate for archaeologists to use the most widely used and supported tools and services to support their reproducible research, such as the R and Python programming languages for data analysis, and Git and GitHub for collaboration. This paper, with its extensive appendix including thoughtful responses to frequently asked questions about reproducible research in archaeology, is likely to have a wide reach and influence, beyond previous works on this topic that have largely focused on technical details. Karoune and Plomp have provided the on-ramp for a generation of archaeologists who will find their questions about reproducible research answered here. They will also find an agreeable entry point to reproducible research in one of the three levels described by the authors. Will every archaeologist embrace this way of working? Should they? The work of Leonelli (2018) can help us anticipate the answers to these questions. Leonelli asks where are the limits to reproducibility, and how do the characteristics of different ways of knowing affect the desirability of reproducibility? Leonelli's work invites us to consider that there will be archaeologists coming from different epistemic cultures for whom the motivations presented by Karoune and Plomp will not resonate. For example, archaeologists engaged in mostly hermeneutical social science and humanities research, who do little or no quantitative analysis and statistics, are unlikely to see reproducibility as meaningful or desirable for their work. We can describe these researchers as working in interpretative or constructivist epistemic cultures. In these cultures, the particulars of how an individual researcher engages with their subject are exclusive and unique, and they would argue it cannot be fully captured or shared in an meaningful way (Elman and Kapiszewski 2017). Here, knowledge is situational, emerging from a specific, once-off combination of people and circumstances. One example in archaeology is the chaîne opératoire approach of stone artefact analysis, which Monnier and Missal (2014:61) describe as "based upon the analyst's experience and intuition, and it is not replicable, nor quantifiable". To make sense of this example we can draw on Galison's (1997) concept of 'image traditions' and 'logic traditions'. An image tradition is a way of knowing that is qualitative, based on composing narratives from drawings and photographs. A logic tradition is based on the use of instruments and statistical methods to collect standardised quantitative data. Chaîne opératoire approaches fall into the image tradition, along with many other ways of working in archaeology that do not generate numbers or use them to support claims about the past. Archaeologists working in a logic tradition will find reproducible research to be more meaningful than those working in an image tradition. We should be mindful not to claim that one epistemic culture is superior to another because reproducibility is not meaningful or attainable for researchers in one culture. Such a claim would threaten the plurality that is essential for the reliability of scientific knowledge (Massimi 2022). Instead we should identify those communities in archaeology where reproducible research is both meaningful and attainable, but has not yet been widely embraced. That is the where the most beneficial effects can be expected. According to Leonelli's (2018) framework, we can recognise these communities by a few basic characteristics. For example: they are doing computationally intensive archaeology, such as using or writing software to collect, simulate, analyse or visualise data; they are doing experimental archaeology; or they are making knowledge claims that are supported by tables of numeric data and data visualisations. Archaeologists whose work shares one or more of these characteristics will find the guidance provided here by Karoune and Plomp to be highly instructive and relevant, and stand the most to benefit from it. But it is not only individual archaeological scientists that have potential to benefit from how Karoune and Plomp have lowered the barriers to reproducible research. An especially important implication of this paper is that by lowering the barriers to reproducible research, Karoune and Plomp help us all to lower barriers to participation in archaeology in general. Documenting our research transparently, and sharing our materials (such as data and code and so on) openly, can profoundly change how others can participate in archaeology. By doing this, we are enabling students and researchers elsewhere, for example in low and middle income locations, to use our materials in their teaching and learning. Other researchers and students can apply our methods to their data, and combine their data with ours to achieve syntheses beyond what a single project can do. Similarly, for archaeologists working with local, descendant or marginalized communities, the tools of reproducible research are vital for enabling community members to have full access to the archaeological process, and thus reproducibility may be considered a necessity for decolonising the discipline. Karoune and Plomp present the CARE principles (Carroll et al. 2020) to guide archaeologists in ensuring community control of data so that reproducibility can be ethically accomplished with community safety and well-being as a priority. This may have a profoundly positive impact on the demographics of archaeology, as it lowers the barriers of meaningful participation by people far beyond our immediate groups of collaborators. Making archaeology more accessible is of critical importance in stemming the negative social impacts of pseudoarchaeologists, who often claim that archaeologists actively suppress the truth of the archaeological record through secrecy, elitism, and exclusiveness. The harm in this is twofold. First, that pseudoarchaeology typically erases Indigenous heritage by claiming that their past achievements were due to an ancient, extinct advanced civilization, not Indigenous people. These claims are often adopted by white supremacists to support racist and antisemitic conspiracy theories (Turner and Turner 2021), which sometimes leads to prejudice, physical violence, radicalization and extremism. A second type of harm that can come from claims of secrecy and elitism is it drains public trust in experts, leading to science denial. Not only trust in archaeologists, but trust in many kinds of experts, including those working on urgent contemporary issues such as public health and climate change. Karoune and Plomp's work is important here because it provides a practical and affordable pathway for archaeologists to fight claims of secrecy and elitism by sharing their work in ways that make it possible for non-academics to inspect the analyses and logic in detail. Claims of secrecy and elitism can be easily countered by openness, transparently and reproducibility by archaeologists. This is not only useful for tackling pseudoarchaeologists, but also in enacting an ethic of care, framing members of the public as people that not only care about archaeology as part of humanity's shared heritage, but also care for the construction of reliable interpretations of the archaeological record to provide secure and authentic foundations for their social identities and relationships (Wylie et al 2018; de la Bellacasa 2011). By striving for reproducible research in the way described by Karoune and Plomp, we are practicing a kind of reciprocal care among ourselves as archaeologists, and between archaeologists and members of the public as two communities who care about the human past.
References Karoune, E., and Plomp, E. (2022). Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology. Zenodo, 7320029, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029 de la Bellacasa, M. P. (2011). Matters of care in technoscience: Assembling neglected things. Social Studies of Science, 41(1), 85–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312710380301 Carroll, S. R., Garba, I., Figueroa-Rodríguez, O. L., Holbrook, J., Lovett, R., Materechera, S., Parsons, M., Raseroka, K., Rodriguez-Lonebear, D., Rowe, R., Sara, R., Walker, J. D., Anderson, J., and Hudson, M. (2020). The CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance. Data Science Journal, 19(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.5334/dsj-2020-043 Elman, C., and Kapiszewski, D. (2017). Benefits and Challenges of Making Qualitative Research More Transparent. Inside Higher Ed 2017, http://web.archive.org/web/20220407064134/https://www.insidehighered.com/blogs/rethinking-research/benefits-and-challenges-making-qualitative-research-more-transparent (accessed 21 Oct, 2022). Galison, P. (1997). Image and logic: a material culture of microphysics. Chicago (IL): University of Chicago Press. Leonelli, S. (2018). Re-Thinking Reproducibility as a Criterion for Research Quality [preprint]. Available online: http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/id/eprint/14352 (Accessed 21 Oct 2022). Massimi, M. (2022). Perspectival realism. Oxford University Press. Monnier, G. F., and Kele M.. "Another Mousterian debate? Bordian facies, chaîne opératoire technocomplexes, and patterns of lithic variability in the western European Middle and Upper Pleistocene." Quaternary International 350 (2014): 59-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.053 Turner, D. D., and Turner, M. I. (2021). “I’m Not Saying It Was Aliens”: An Archaeological and Philosophical Analysis of a Conspiracy Theory. In A. Killin and S. Allen-Hermanson (Eds.), Explorations in Archaeology and Philosophy (pp. 7–24). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61052-4_2 Wylie, C., Neeley, K., and Ferguson, S. (2018). Beyond Technological Literacy: Open Data as Active Democratic Engagement? Digital Culture & Society, 4(2), 157–182. https://doi.org/10.14361/dcs-2018-0209
| Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology | Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp | <p>Reproducible research is being implemented at different speeds in different disciplines, and Archaeology is at the start of this journey. Reproducibility is the practice of reanalysing data by taking the same steps and producing the same or sim... |  | Computational archaeology | Ben Marwick | 2022-06-07 10:02:46 | View | |
12 Apr 2024
Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective SurveysE. B. Banning, Steven Edwards, and Isaac Ullah https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8072178A new tool to increase the robustness of archaeological field surveyRecommended by Jitte Waagen based on reviews by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas based on reviews by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas
This well-written and interesting paper ‘Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys’ deals with the development of a ‘modular, accessible, and simple web-based platform for survey planning and quality assurance’ in the area of pedestrian field survey methods (Banning et al. 2024). Although there have been excellent treatments of statistics in archaeological field survey (among which various by the first author: Banning 2020, 2021), and there is continuous methodological debate on platforms such as the International Mediterranean Survey Workshop (IMSW), in papers dealing with the current development and state of the field (Knodell et al. 2023), good practices (Attema et al. 2020) or the merits of a quantifying approach to archaeological densities (cf. de Haas et al. 2023), this paper rightfully addresses the lack of rigorous statistical approaches in archaeological field survey. As argued by several scholars such as Orton (2000), this mainly appears the result of lack of knowledge/familiarity/resources to bring in the required expertise etc. with the application of seemingly intricate statistics (cf. Waagen 2022). In this context this paper presents a welcome contribution to the feasibility of a robust archaeological field survey design. The SPACE application, under development by the authors, is introduced in this paper. It is a software tool that aims to provide different modules to assist archaeologists to make calculations for sample size, coverage, stratification, etc. under the conditions of survey goals and available resources. In the end, the goal is to ensure archaeological field surveys will attain their objectives effectively and permit more confidence in the eventual outcomes. The module concerning Sweep Widths, an issue introduced by the main author in 2006 (Banning 2006) is finished; the sweep width assessment is a methodology to calibrate one’s survey project for artefact types, landscape, visibility and person-bound performance, eventually increasing the quality (comparability) of the collected samples. This is by now a well-known calibration technique, yet little used, so this effort to make that more accessible is certainly laudable. An excellent idea, and another aim of this project, is indeed to build up a database with calibration data, so applying sweep-width corrections will become easier accessible to practitioners who lack time to set up calibration exercises. It will be very interesting to have a closer look at the eventual platform and to see if, and how, it will be adapted by the larger archaeological field survey community, both from an academic research perspective as from a heritage management point of view. I happily recommend this paper and all debate relating to it, including the excellent peer reviews of the manuscript by Philip Verhagen and Tymon de Haas (available as part of this PCI recommendation procedure), to any practitioner of archaeological field survey. References Attema, P., Bintliff, J., Van Leusen, P.M., Bes, P., de Haas, T., Donev, D., Jongman, W., Kaptijn, E., Mayoral, V., Menchelli, S., Pasquinucci, M., Rosen, S., García Sánchez, J., Luis Gutierrez Soler, L., Stone, D., Tol, G., Vermeulen, F., and Vionis. A. 2020. “A guide to good practice in Mediterranean surface survey projects”, Journal of Greek Archaeology 5, 1–62. https://doi.org/10.32028/9781789697926-2 Banning, E.B., Alicia L. Hawkins, S.T. Stewart, Sweep widths and the detection of artifacts in archaeological survey, Journal of Archaeological Science, Volume 38, Issue 12, 2011, Pages 3447-3458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2011.08.007 Banning, E.B. 2020. Spatial Sampling. In: Gillings, M., Hacıgüzeller, P., Lock, G. (eds.) Archaeological Spatial Analysis. A Methodological Guide. Routledge. Banning, E.B. 2021. Sampled to Death? The Rise and Fall of Probability Sampling in Archaeology. American Antiquity, 86(1), 43-60. https://doi.org/10.1017/aaq.2020.39 Banning, E. B. Steven Edwards, & Isaac Ullah. (2024). Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys. Zenodo, 8072178, ver. 9 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8072178 Knodell, A.R., Wilkinson, T.C., Leppard, T.P. et al. 2023. Survey Archaeology in the Mediterranean World: Regional Traditions and Contributions to Long-Term History. J Archaeol Res 31, 263–329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10814-022-09175-7 Orton, C. 2000. Sampling in Archaeology. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139163996 Waagen, J. 2022. Sampling past landscapes. Methodological inquiries into the bias problems of recording archaeological surface assemblages. PhD-Thesis. https://hdl.handle.net/11245.1/e9cb922c-c7e4-40a1-b648-7b8065c46880 de Haas, T., Leppard, T. P., Waagen, J., & Wilkinson, T. (2023). Myopic Misunderstandings? A Reply to Meyer (JMA 35(2), 2022). Journal of Mediterranean Archaeology, 36(1), 127-137. https://doi.org/10.1558/jma.27148 | Survey Planning, Allocation, Costing and Evaluation (SPACE) Project: Developing a Tool to Help Archaeologists Conduct More Effective Surveys | E. B. Banning, Steven Edwards, and Isaac Ullah | <p>Designing an effective archaeological survey can be complicated and confidence that it was effective requires post-survey evaluation. The goal of SPACE is to develop software to facilitate survey designers’ decisions and partially automate tool... |  | Computational archaeology, Landscape archaeology | Jitte Waagen | 2023-06-28 13:42:28 | View | |
02 Sep 2023

Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA ISDudek Iwona, Blaise Jean-Yves https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8311129Using information visualisation to improve traceability, transmissibility and verifiability in research workflowsRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by Adéla Sobotkova and 2 anonymous reviewersThe paper “Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS” (Dudek & Blaise, 2023) describes a prototype of an information system developed to improve the traceability, transmissibility and verifiability of archaeological research workflows. A key aspect of the work with MEMORIA is to make research documentation and the workflows underpinning the conducted research more approachable and understandable using a series of visual interfaces that allow users of the system to explore archaeological documentation, including metadata describing the data and paradata that describes its underlying processes. The work of Dudek and Blaise address one of the central barriers to reproducibility and transparency of research data and propose a set of both theoretically and practically well-founded tools and methods to solve this major problem. From the reported work on MEMORIA IS, information visualisation and the proposed tools emerge as an interesting and potentially powerful approach for a major push in improving the traceability, transmissibility and verifiability of research data through making research workflows easier to approach and understand. In comparison to technical work relating to archaeological data management, this paper starts commendably with a careful explication of the conceptual and epistemic underpinnings of the MEMORIA IS both in documentation research, knowledge organisation and information visualisation literature. Rather than being developed on the basis of a set of opaque assumptions, the meticulous description of the MEMORIA IS and its theoretical and technical premises is exemplary in its transparence and richness and has potential for a long-term impact as a part of the body of literature relating to the development of archaeological documentation and documentation tools. While the text is sometimes fairly densely written, it is worth taking the effort to read it through. Another major strength of the paper is that it provides a rich set of examples of the workings of the prototype system that makes it possible to develop a comprehensive understanding of the proposed approaches and assess their validity. As a whole, this paper and the reported work on MEMORIA IS forms a worthy addition to the literature on and practical work for developing critical infrastructures for data documentation, management and access in archaeology. Beyond archaeology and the specific context of the discussed work discussed this paper has obvious relevance to comparable work in other fields. ReferencesDudek, I. and Blaise, J.-Y. (2023) Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS, Zenodo, 8252923, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8252923
| Research workflows, paradata, and information visualisation: feedback on an exploratory integration of issues and practices - MEMORIA IS | Dudek Iwona, Blaise Jean-Yves | <p>The paper presents an exploratory web information system developed as a reaction to practical and epistemological questions, in the context of a scientific unit studying the architectural heritage (from both historical sciences perspective, and... |  | Computational archaeology | Isto Huvila | 2023-05-02 12:50:39 | View | |
29 Apr 2024

Study and enhancement of the heritage value of a fortified settlement along the Limes Arabicus. Umm ar-Rasas (Amman, Jordan) between remote sensing analysis, photogrammetry and laser scanner surveys.Di Palma Francesca, Gabrielli Roberto, Merola Pasquale, Miccoli Ilaria, Scardozzi Giuseppe https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8306381Integrating remote sensing and photogrammetric approaches to studying a fortified settlement along the Limes Arabicus: Umm ar‐Rasas (Amman, Jordan).Recommended by Alessia Brucato based on reviews by Francesc C. Conesa, Giuseppe Ceraudo and 1 anonymous reviewerDi Palma et alii manuscript delves into applying remote sensing and photogrammetry methods to document and analyze the castrum at the Umm er-Rasas site in Jordan. This research aimed to map all the known archaeological evidence, detect new historical structures, and create a digital archive of the site's features for study and education purposes [1]. Their research has been organized into two phases. The first one consisted of a remote sensing survey and involved collecting historical and modern aerial and satellite imagery, such as: aerial photographs by Sir Marc Aurel Stein from 1939; panchromatic spy satellite images from the Cold War period (Corona KH-4B and Hexagon KH-9); high and very high resolution (HR and VHR) modern multispectral satellite images (Pléiades-1A and Pléiades Neo-4) [1]. This dataset was processed using the ENVI 4.4 software and applying multiple image-enhancing techniques (Pansharpening, RGB composite, data fusion, and Principal Component Analysis). Then, the resulting images were integrated into a QGIS project, allowing for visual analyses of the site's features and terrain. These investigations provided: · a broad overview of the site, · the discovery of a previously unknown archaeological feature (the northeastern dam), · a stage for targeted ground-level investigations [1]. The project's second phase was dedicated to intensive fieldwork operations, including pedestrian surveys, stratigraphic excavations, and photogrammetric recordings, such as: photographic reconstructions via Structure from Motion (SfM) and laser scanner sessions (using two FARO X330 HDR). In particular, the laser scanner data were processed with Reconstructor 4.4, which provided highly detailed 3D models for the QGIS database. These results were crucial in validating the information acquired during the first phase. Overall, the paper is well written, with clear objectives and a systematic presentation of the site [2,3,10,11], the research materials, and the study phases. The dataset was described in meticulous detail (especially the remote sensing sources and the laser scanner recordings). The methods implemented in this study are rigorously described [4,5,6,7,8,9] and show a high level of integration between aerial and field techniques. The results are neatly illustrated and fit into the current debates about the efficacy of remote sensing detection and multiscale approaches in archaeological research. In conclusion, this manuscript significantly contributes to archaeological research, unveiling new and exciting findings about the site of Umm er-Rasas. Its findings and methodologies warrant publication and further exploration. References: 1. Di Palma, F., Gabrielli, R., Merola, P., Miccoli, I. and Scardozzi, G. (2024). Study and enhancement of the heritage value of a fortified settlement along the Limes Arabicus. Umm ar-Rasas (Amman, Jordan) between remote sensing analysis, photogrammetry and laser scanner surveys. Zenodo, 8306381, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8306381 2. Abela J. and Acconci A. (1997), Umm al‐Rasas Kastron Mefa’a. Excavation Campaign 1997. Church of St. Paul: northern and southern flanks. Liber Annus, 47, 484‐488. 3. Bujard J. (2008), Kastron Mefaa, un bourg à l'époque byzantine: Travaux de la Mission archéologique de la Fondation Max van Berchem à Umm al‐Rasas, Jordanie (1988‐1997), PhD diss., University of Fribourg 2008. 4. Cozzolino M., Gabrielli R., Galatà P., Gentile V., Greco G., Scopinaro E. (2019), Combined use of 3D metric surveys and non‐invasive geophysical surveys at the stylite tower (Umm ar‐Rasas, Jordan), Annals of geophysics, 62, 3, 1‐9. http://dx.doi.org/10.4401/ag‐8060 5. Gabrielli R., Salvatori A., Lazzari A., Portarena D. (2016), Il sito di Umm ar‐Rasas – Kastron Mefaa – Giordania. Scavare documentare conservare, viaggio nella ricerca archeologica del CNR. Roma 2016, 236‐240. 6. Gabrielli R., Portarena D., Franceschinis M. (2017), Tecniche di documentazione dei tappeti musivi del sito archeologico di Umm al‐Rasas Kastron Mefaa (Giordania). Archeologia e calcolatori, 28 (1), 201‐218. https://doi.org/10.19282/AC.28.1.2017.12 7. Lasaponara R., Masini N. (2012 ed.), Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology, New York 2012. 8. Lasaponara R., Masini N. and Scardozzi G. (2007), Immagini satellitari ad alta risoluzione e ricerca archeologica: applicazioni e casi di studio con riprese pancromatiche e multispettrali di QuickBird. Archeologia e Calcolatori, 18 (2), 187‐227. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/33150351.pdf 9. Lasaponara R., Masini N., Scardozzi G. (2010), Elaborazioni di immagini satellitari ad alta risoluzione e ricognizione archeologica per la conoscenza degli insediamenti rurali del territorio di Hierapolis di Frigia (Turchia). Il dialogo dei Saperi – Metodologie integrate per i Beni Culturali, Edizioni scientifiche italiane, 479‐494. 10. Piccirillo M., Abela J. and Pappalardo C. (2007), Umm al‐Rasas ‐ campagna 2007. Rapporto di scavo. Liber Annus, 57, 660‐668. 11. Poidebard A. (1934), La trace de Rome dans le désert de Syrie : le limes de Trajan à la conquête arabe ; recherches aériennes 1925 – 1932. Paris : Geuthner. | Study and enhancement of the heritage value of a fortified settlement along the Limes Arabicus. Umm ar-Rasas (Amman, Jordan) between remote sensing analysis, photogrammetry and laser scanner surveys. | Di Palma Francesca, Gabrielli Roberto, Merola Pasquale, Miccoli Ilaria, Scardozzi Giuseppe | <p>The Limes Arabicus is an excellent laboratory for experimenting with the huge potential of historical remote sensing data for identifying and mapping fortified centres along this sector of the eastern frontier of the Roman Empire and then the B... |  | Antiquity, Asia, Classic, Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Remote sensing, Spatial analysis | Alessia Brucato | 2023-08-31 23:34:16 | View | |
02 Jan 2024
Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenariosDiamanti, Eleni; Yip, Mauhing; Stahl, Annette; Ødegård, Øyvind https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305098Beyond Deep Blue: Underwater robotics, simulations and archaeologyRecommended by Daniel Carvalho based on reviews by Marco Moderato and 1 anonymous reviewerDiamanti et al. (2024) is a significant contribution to the field of underwater robotics and their use in archaeology, with an innovative approach to some major problems in the deployment of said technologies. It identifies issues when it comes to approaching Underwater Cultural Heritage (UCH) sites and does so through an interest in the combination of data, maneuverability, and the interpretation provided by the instruments that archaeologists operate. The article's motives are clear: it is not enough to find the means to reach these sites, but rather is fundamental to take a step forward in methodology and how we can safeguard certain aspects of data recovery with robust mission planning. To this end, the article does not fail to highlight previous contributions, in an intertwined web of references that demonstrate the marked evolution of the use of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Autonomous Surface Vehicles (ASVs), which are growing exponentially in use (see Kapetanović et al. 2020). It should be emphasized that the notion of ‘aquatic environment’ used here is quite broad and is not limited to oceanic or maritime environments, which allows for a larger perspective on distinct technologies that proliferate in underwater archaeology. There is also a relevant discussion on the typologies of sensors and how these autonomous vehicles obtain their data, where are debated Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and LiDAR systems. Thus, the authors of this article propose the creation of a model that acquires data through simulations, which allows for a better understanding of what a real mission presupposes in the field. Their tripartite method - pre-mission planning; mission plan and post-mission plan - offers a performing algorithm that simplifies and provides reliability to all the parts of the intervention. The use of real cases to create simulation models allows for a substantial approximation to common practice in underwater environments. And yet, the article is at its most innovative status when it combines all the elements it sets out to explore. It could simply focus on the methodological or planning component, on obtaining data, or on theoretical problems. But it goes further, which makes this approach more complete and of interest to the archaeological community. By not taking any part as isolated, the problems and possible solutions arising from the course of the mission are carried over from one parameter to another, where details are worked upon and efficiency goals are set. One of the most significant cases is the tuning of ocean optics in aquatic environments according to the idiosyncracies of real cases (Diamanti et al. 2024: 8), a complex endeavor but absolutely necessary in order to increase the informative potential of the simulation. The exploration of various data capture models is also welcome, for the purposes of comparison and adaptation on a case-by-case basis. The brief theoretical reflection offered at the end of the article dwells in all these points and problematizes the difference between terrestrial and aquatic archaeology. In fact, the distinction does not only exist in the technical component, as although it draws in theoretical elements from archaeology that is carried out on land (see Krieger 2012 for this matter), the problems and interpretations are shaped by different factors and therefore become unique (Diamanti et al 2024: 15). The future, according to the authors, lies in increasing the autonomy of these vehicles so that the human element does not have to make decisions in a systematic way. It is in that note, and in order for that path to become closer to reality, that we strongly recommend this article for publication, in conjunction with the comments of the reviewers. We hope that its integrated approach, which brings together methods, theories and reflections, can become a broader modus operandi within the field of underwater robotics applied to archaeology. References: Diamanti, E., Yip, M., Stahl, A. and Ødegård, Ø. (2024). Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenarios, Zenodo, 8305098, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305098 Kapetanović, N., Vasilijević, A., Nađ, Đ., Zubčić, K., and Mišković, N. (2020). Marine Robots Mapping the Present and the Past: Unraveling the Secrets of the Deep. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3902. MDPI AG. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/rs12233902 Krieger, W. H. (2012). Theory, Locality, and Methodology in Archaeology: Just Add Water? HOPOS: The Journal of the International Society for the History of Philosophy of Science, 2(2), 243–257. https://doi.org/10.1086/666956
| Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenarios | Diamanti, Eleni; Yip, Mauhing; Stahl, Annette; Ødegård, Øyvind | <p>This paper presents a novel method for visual-based 3D mapping of underwater cultural heritage sites through marine robotic operations. The proposed methodology addresses the three main stages of an underwater robotic mission, specifically the ... | Computational archaeology, Remote sensing | Daniel Carvalho | 2023-08-31 16:03:10 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










