Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date▼ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
01 Dec 2022
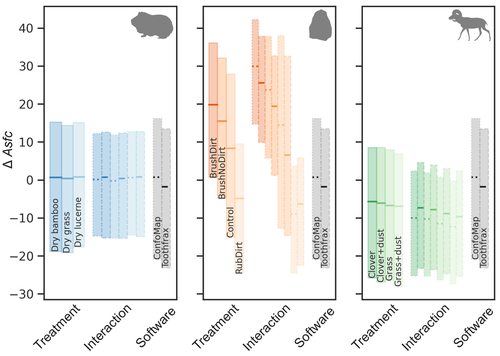
Surface texture analysis in Toothfrax and MountainsMap® SSFA module: Different software packages, different results?Ivan CALANDRA, Konstantin BOB, Gildas MERCERON, François BLATEYRON, Andreas HILDEBRANDT, Ellen SCHULZ-KORNAS, Antoine SOURON, Daniela E. WINKLER https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4671438An important comparison of software for Scale Sensitive Fractal Analysis : are ancient and new results compatible?Recommended by Alain Queffelec and Florent Rivals and Florent Rivals based on reviews by Antony Borel and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Antony Borel and 2 anonymous reviewers
The community of archaeologists, bioanthropologist and paleontologists relying on tools use-wear and dental microwear has grown in the recent years, mainly driven by the spread of confocal microscopes in the laboratories. If the diversity of microscopes is quite high, the main software used for 3D surface texture data analysis are mostly different versions of the same Mountains Map core. In addition to this software, since the beginning of 3D surface texture analysis in dental microwear, surface sensitive fractal analysis (SSFA) initially developed for industrial research (Brown & Savary, 1991) have been performed in our disciplines with the Sfrax/Toothfrax software for two decades (Ungar et al., 2003). This software being discontinued, these calculations have been integrated to the new versions of Mountains Map, with multi-core computing, full integration in the software and an update of the calculation itself. New research based on these standard parameters of surface texture analysis will be, from now on, mainly calculated with this new add-on of Mountains Map, and will be directly compared with the important literature based on the previous software. The question addressed by Calandra et al. (2022), gathering several prominent researchers in this domain including the Mountains Map developer F. Blateyron, is key for the future research: can we directly compare SSFA results from both software? Thanks to a Bayesian approach to this question, and comparing results calculated with both software on three different datasets (two on dental microwear, one on lithic raw materials), the authors show that the two software gives statistically different results for all surface texture parameters tested in the paper. Nevertheless, applying the new calculation to the datasets, they also show that the results published in original studies with these datasets would have been similar. Authors also claim that in the future, researchers will need to re-calculate the fractal parameters of previously published 3D surfaces and cannot simply integrate ancient and new data together. We also want to emphasize the openness of the work published here. All datasets have been published online and will be probably very useful for future methodological works. Authors also published their code for statistical comparison of datasets, and proposed a fully reproducible article that allowed the reviewers to check the content of the paper, which can also make this article of high interest for student training. This article is therefore a very important methodological work for the community, as noted by all three reviewers. It will certainly support the current transition between the two software packages and it is necessary that all surface texture specialists take these results and the recommendation of authors into account: calculate again data from ancient measurements, and share the 3D surface measurements on open access repositories to secure their access in the future. References Brown CA, and Savary G (1991) Describing ground surface texture using contact profilometry and fractal analysis. Wear, 141, 211–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(91)90269-Z Calandra I, Bob K, Merceron G, Blateyron F, Hildebrandt A, Schulz-Kornas E, Souron A, and Winkler DE (2022) Surface texture analysis in Toothfrax and MountainsMap® SSFA module: Different software packages, different results? Zenodo, 7219877, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7219877 Ungar PS, Brown CA, Bergstrom TS, and Walker A (2003) Quantification of dental microwear by tandem scanning confocal microscopy and scale-sensitive fractal analyses. Scanning: The Journal of Scanning Microscopies, 25, 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.4950250405 | Surface texture analysis in Toothfrax and MountainsMap® SSFA module: Different software packages, different results? | Ivan CALANDRA, Konstantin BOB, Gildas MERCERON, François BLATEYRON, Andreas HILDEBRANDT, Ellen SCHULZ-KORNAS, Antoine SOURON, Daniela E. WINKLER | <p>The scale-sensitive fractal analysis (SSFA) of dental microwear textures is traditionally performed using the software Toothfrax. SSFA has been recently integrated to the software MountainsMap® as an optional module. Meanwhile, Toothfrax suppor... |  | Computational archaeology, Palaeontology, Traceology | Alain Queffelec | Anonymous, John Charles Willman, Antony Borel | 2022-07-07 09:58:50 | View |
21 Nov 2022

Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in ArchaeologyEmma Karoune and Esther Plomp https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029Three levels of reproducible workflow remove barriers for archaeologists and increase accessibilityRecommended by Ben Marwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick based on reviews by Sam Leggett, Cyler Conrad, Cheng Liu and Lisa Lodwick
Over the last decade, a small but growing community of archaeologists, from a diversity of intellectual and demographic backgrounds, have been striving for computational reproducibility in their published research. In their survey of the accomplishments of this thriving community, Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp (2022) analyzed the wide variety of approaches researchers have taken to enhance the reproducibility of their research. A key contribution of this paper is their excellent synthesis of diverse approaches into three levels of increasing complexity. This is helpful because it provides multiple entry points for researchers new to the challenge of fortifying their research. Many researchers assume that computational reproducibility is only achievable if they have a high degree of technical skill with computers, or is only necessary if their work is very computationally intensive. Karoune and Plomp give three compelling reasons why reproducibility is important for all archaeological research, and through their three levels they demonstrate that how these levels can be accomplished with basic, non-specialized computer skills and widely used free software. They showcase exemplary work from a variety of archaeologists to show how practical and achievable reproducible research is for all archaeologists. They advocate for archaeologists to use the most widely used and supported tools and services to support their reproducible research, such as the R and Python programming languages for data analysis, and Git and GitHub for collaboration. This paper, with its extensive appendix including thoughtful responses to frequently asked questions about reproducible research in archaeology, is likely to have a wide reach and influence, beyond previous works on this topic that have largely focused on technical details. Karoune and Plomp have provided the on-ramp for a generation of archaeologists who will find their questions about reproducible research answered here. They will also find an agreeable entry point to reproducible research in one of the three levels described by the authors. Will every archaeologist embrace this way of working? Should they? The work of Leonelli (2018) can help us anticipate the answers to these questions. Leonelli asks where are the limits to reproducibility, and how do the characteristics of different ways of knowing affect the desirability of reproducibility? Leonelli's work invites us to consider that there will be archaeologists coming from different epistemic cultures for whom the motivations presented by Karoune and Plomp will not resonate. For example, archaeologists engaged in mostly hermeneutical social science and humanities research, who do little or no quantitative analysis and statistics, are unlikely to see reproducibility as meaningful or desirable for their work. We can describe these researchers as working in interpretative or constructivist epistemic cultures. In these cultures, the particulars of how an individual researcher engages with their subject are exclusive and unique, and they would argue it cannot be fully captured or shared in an meaningful way (Elman and Kapiszewski 2017). Here, knowledge is situational, emerging from a specific, once-off combination of people and circumstances. One example in archaeology is the chaîne opératoire approach of stone artefact analysis, which Monnier and Missal (2014:61) describe as "based upon the analyst's experience and intuition, and it is not replicable, nor quantifiable". To make sense of this example we can draw on Galison's (1997) concept of 'image traditions' and 'logic traditions'. An image tradition is a way of knowing that is qualitative, based on composing narratives from drawings and photographs. A logic tradition is based on the use of instruments and statistical methods to collect standardised quantitative data. Chaîne opératoire approaches fall into the image tradition, along with many other ways of working in archaeology that do not generate numbers or use them to support claims about the past. Archaeologists working in a logic tradition will find reproducible research to be more meaningful than those working in an image tradition. We should be mindful not to claim that one epistemic culture is superior to another because reproducibility is not meaningful or attainable for researchers in one culture. Such a claim would threaten the plurality that is essential for the reliability of scientific knowledge (Massimi 2022). Instead we should identify those communities in archaeology where reproducible research is both meaningful and attainable, but has not yet been widely embraced. That is the where the most beneficial effects can be expected. According to Leonelli's (2018) framework, we can recognise these communities by a few basic characteristics. For example: they are doing computationally intensive archaeology, such as using or writing software to collect, simulate, analyse or visualise data; they are doing experimental archaeology; or they are making knowledge claims that are supported by tables of numeric data and data visualisations. Archaeologists whose work shares one or more of these characteristics will find the guidance provided here by Karoune and Plomp to be highly instructive and relevant, and stand the most to benefit from it. But it is not only individual archaeological scientists that have potential to benefit from how Karoune and Plomp have lowered the barriers to reproducible research. An especially important implication of this paper is that by lowering the barriers to reproducible research, Karoune and Plomp help us all to lower barriers to participation in archaeology in general. Documenting our research transparently, and sharing our materials (such as data and code and so on) openly, can profoundly change how others can participate in archaeology. By doing this, we are enabling students and researchers elsewhere, for example in low and middle income locations, to use our materials in their teaching and learning. Other researchers and students can apply our methods to their data, and combine their data with ours to achieve syntheses beyond what a single project can do. Similarly, for archaeologists working with local, descendant or marginalized communities, the tools of reproducible research are vital for enabling community members to have full access to the archaeological process, and thus reproducibility may be considered a necessity for decolonising the discipline. Karoune and Plomp present the CARE principles (Carroll et al. 2020) to guide archaeologists in ensuring community control of data so that reproducibility can be ethically accomplished with community safety and well-being as a priority. This may have a profoundly positive impact on the demographics of archaeology, as it lowers the barriers of meaningful participation by people far beyond our immediate groups of collaborators. Making archaeology more accessible is of critical importance in stemming the negative social impacts of pseudoarchaeologists, who often claim that archaeologists actively suppress the truth of the archaeological record through secrecy, elitism, and exclusiveness. The harm in this is twofold. First, that pseudoarchaeology typically erases Indigenous heritage by claiming that their past achievements were due to an ancient, extinct advanced civilization, not Indigenous people. These claims are often adopted by white supremacists to support racist and antisemitic conspiracy theories (Turner and Turner 2021), which sometimes leads to prejudice, physical violence, radicalization and extremism. A second type of harm that can come from claims of secrecy and elitism is it drains public trust in experts, leading to science denial. Not only trust in archaeologists, but trust in many kinds of experts, including those working on urgent contemporary issues such as public health and climate change. Karoune and Plomp's work is important here because it provides a practical and affordable pathway for archaeologists to fight claims of secrecy and elitism by sharing their work in ways that make it possible for non-academics to inspect the analyses and logic in detail. Claims of secrecy and elitism can be easily countered by openness, transparently and reproducibility by archaeologists. This is not only useful for tackling pseudoarchaeologists, but also in enacting an ethic of care, framing members of the public as people that not only care about archaeology as part of humanity's shared heritage, but also care for the construction of reliable interpretations of the archaeological record to provide secure and authentic foundations for their social identities and relationships (Wylie et al 2018; de la Bellacasa 2011). By striving for reproducible research in the way described by Karoune and Plomp, we are practicing a kind of reciprocal care among ourselves as archaeologists, and between archaeologists and members of the public as two communities who care about the human past.
References Karoune, E., and Plomp, E. (2022). Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology. Zenodo, 7320029, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7320029 de la Bellacasa, M. P. (2011). Matters of care in technoscience: Assembling neglected things. Social Studies of Science, 41(1), 85–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312710380301 Carroll, S. R., Garba, I., Figueroa-Rodríguez, O. L., Holbrook, J., Lovett, R., Materechera, S., Parsons, M., Raseroka, K., Rodriguez-Lonebear, D., Rowe, R., Sara, R., Walker, J. D., Anderson, J., and Hudson, M. (2020). The CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance. Data Science Journal, 19(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.5334/dsj-2020-043 Elman, C., and Kapiszewski, D. (2017). Benefits and Challenges of Making Qualitative Research More Transparent. Inside Higher Ed 2017, http://web.archive.org/web/20220407064134/https://www.insidehighered.com/blogs/rethinking-research/benefits-and-challenges-making-qualitative-research-more-transparent (accessed 21 Oct, 2022). Galison, P. (1997). Image and logic: a material culture of microphysics. Chicago (IL): University of Chicago Press. Leonelli, S. (2018). Re-Thinking Reproducibility as a Criterion for Research Quality [preprint]. Available online: http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/id/eprint/14352 (Accessed 21 Oct 2022). Massimi, M. (2022). Perspectival realism. Oxford University Press. Monnier, G. F., and Kele M.. "Another Mousterian debate? Bordian facies, chaîne opératoire technocomplexes, and patterns of lithic variability in the western European Middle and Upper Pleistocene." Quaternary International 350 (2014): 59-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.06.053 Turner, D. D., and Turner, M. I. (2021). “I’m Not Saying It Was Aliens”: An Archaeological and Philosophical Analysis of a Conspiracy Theory. In A. Killin and S. Allen-Hermanson (Eds.), Explorations in Archaeology and Philosophy (pp. 7–24). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61052-4_2 Wylie, C., Neeley, K., and Ferguson, S. (2018). Beyond Technological Literacy: Open Data as Active Democratic Engagement? Digital Culture & Society, 4(2), 157–182. https://doi.org/10.14361/dcs-2018-0209
| Removing Barriers to Reproducible Research in Archaeology | Emma Karoune and Esther Plomp | <p>Reproducible research is being implemented at different speeds in different disciplines, and Archaeology is at the start of this journey. Reproducibility is the practice of reanalysing data by taking the same steps and producing the same or sim... |  | Computational archaeology | Ben Marwick | 2022-06-07 10:02:46 | View | |
20 Jul 2022

Faunal remains from the Upper Paleolithic site of Nahal Rahaf 2 in the southern Judean Desert, IsraelNimrod Marom, Dariya Lokshin Gnezdilov, Roee Shafir, Omry Barzilai, Maayan Shemer https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.17.492258v4New zooarchaeological data from the Upper Palaeolithic site of Nahal Rahaf 2, IsraelRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Ana Belén Galán and Joana Gabucio based on reviews by Ana Belén Galán and Joana Gabucio
The Levantine Corridor is considered a crossing point to Eurasia and one of the main areas for detecting population flows (and their associated cultural and economic changes) during the Pleistocene. This area could have been closed during the most arid periods, giving rise to processes of population isolation between Africa and Eurasia and intermittent contact between Eurasian human communities [1,2]. Zooarchaeological studies of the early Upper Palaeolithic assemblages constitute an important source of knowledge about human subsistence, making them central to the debate on modern behaviour. The Early Upper Palaeolithic sequence in the Levant includes two cultural entities – the Early Ahmarian and the Levantine Aurignacian. This latter is dated to 39-33 ka and is considered a local adaptation of the European Aurignacian techno-complex. In this work, the authors present a zooarchaeological study of the Nahal Rahaf 2 (ca. 35 ka) archaeological site in the southern Judean Desert in Israel [3]. Zooarchaeological data from the early Upper Paleolithic desert regions of the southern Levant are not common due to preservation problems of non-lithic finds. In the case of Nahal Rahaf 2, recent excavation seasons brought to light a stratigraphical sequence composed of very well-preserved archaeological surfaces attributed to the 'Arkov-Divshon' cultural entity, which is associated with the Levantine Aurignacian. This study shows age-specific caprine (Capra cf. Capra ibex) hunting on prime adults and a generalized procurement of gazelles (Gazella cf. Gazella gazella), which seem to have been selectively transported to the site and processed for within-bone nutrients. An interesting point to note is that the proportion of goats increases along the stratigraphic sequence, which suggests to the authors a specialization in the economy over time that is inversely related to the occupational intensity of use of the site. It is also noteworthy that the materials represent a large sample compared to previous studies from the Upper Paleolithic of the Judean Desert and Negev. In summary, this manuscript contributes significantly to the study of both the palaeoenvironment and human subsistence strategies in the Upper Palaeolithic and provides another important reference point for evaluating human hunting adaptations in the arid regions of the southern Levant. References [1] Bermúdez de Castro, J.-L., Martinon-Torres, M. (2013). A new model for the evolution of the human pleistocene populations of Europe. Quaternary Int. 295, 102-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.02.036 [2] Bar-Yosef, O., Belfer-Cohen, A. (2010). The Levantine Upper Palaeolithic and Epipalaeolithic. In Garcea, E.A.A. (Ed), South-Eastern Mediterranean Peoples Between 130,000 and 10,000 Years Ago. Oxbow Books, pp. 144-167. [3] Marom, N., Gnezdilov, D. L., Shafir, R., Barzilai, O. and Shemer, M. (2022). Faunal remains from the Upper Paleolithic site of Nahal Rahaf 2 in the southern Judean Desert, Israel. BioRxiv, 2022.05.17.492258, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.17.492258v4 | Faunal remains from the Upper Paleolithic site of Nahal Rahaf 2 in the southern Judean Desert, Israel | Nimrod Marom, Dariya Lokshin Gnezdilov, Roee Shafir, Omry Barzilai, Maayan Shemer | <p>Nahal Rahaf 2 (NR2) is an Early Upper Paleolithic (ca. 35 kya) rock shelter in the southern Judean Desert in Israel. Two excavation seasons in 2019 and 2020 revealed a stratigraphical sequence composed of intact archaeological surfaces attribut... |  | Upper Palaeolithic, Zooarchaeology | Ruth Blasco | Joana Gabucio | 2022-05-19 06:16:47 | View |
26 Sep 2022

The management of symbolic raw materials in the Late Upper Paleolithic of South-Western France: a shell ornaments perspectiveSolange Rigaud, John O’Hara, Laurent Charles, Elena Man-Estier, Patrick Paillet https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/z7pqgCaching up with the study of the procurement of symbolic raw materials in the Upper PalaeolithicRecommended by Beatrice Demarchi based on reviews by Begoña Soler Mayor , Catherine Dupont and Lawrence StrausThe manuscript "The management of symbolic raw materials in the Late Upper Paleolithic of South-Western France: a shell ornaments perspective" by Solange Rigaud and colleagues (Rigaud et al. 2022) is a perfect demonstration that appropriate scientific methodologies can be used effectively in order to enhance the historical value of findings from “old” collections, despite the lack of secure stratigraphic and contextual data. The shell assemblage (n = 377) investigated here (from Rochereil, Dordogne) had been excavated during the first half of the 20th century (Jude 1960) and reported in 1993 (Taborin 1993), but only this recent analysis revealed that it was composed of largely unmodified mollusc shells, most of allochthonous origin. Rigaud et al. interpret this finding as the raw materials used to produce personal ornaments. This is especially significant, because the focus of research has been on the manufacture, use and exchange of personal ornaments in prehistory, much less so on the procurement of the raw materials. As such, the manuscript adds substantially to the growing literature on Magdalenian social networks. The authors carried out detailed taxonomic analysis based on morphological and morphometric characteristics and identified at least nine different species, including Dentalium sp., Ocenebra erinaceus, Tritia reticulata and T. gibbosula, as well as some bivalve specimens (Mytilus, Glycymeris, Spondylus, Pecten). Most of the species are commonly found in personal ornament assemblages from the Magdalenian, reflecting intentional selection (also shown by the size sorting of some of the taxa), and cultural continuity. However, microscopic examinations revealed securely-identified anthropogenic modifications on a very limited number of specimens: one Glycymeris valve (used as an ochre container), one Cardiidae valve (presence of a groove), one perforated Tritia gibbosula and two perforated Tritia reticulata bearing striations. The authors interpret this combination of anthropogenic vs natural “signals” as signifying that the assemblage represents raw material selected and stored for further processing. Assessing the provenance and age of the shells is therefore paramount: the shells found at Rochereil belong to species that can be found on both the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Assuming that molluscan taxa distribution in the past is comparable to that for the present day, this implies the exploitation of two catchment areas and long-distance transportation to the site: taking sea-level changes into account, during the Magdalenian the Mediterranean used to lie at a distance of 350 km from Rochereil, and the Atlantic was not significantly closer (~200 km). Importantly, exploitation of fossil shells cannot be discounted on the basis of the data presented here; direct dating of some of the specimens (e.g. by radiocarbon, or amino acid racemisation geochronology) would be beneficial to clarify this issue and in general to improve chronological control on the accumulation of shells. Nonetheless, the authors argue that the closest fossil deposits also lie more than 200 km away from the site, thus the material is allochthonous in origin. In synthesis, the Rochereil assemblage represents an important step towards a better understanding of the procurement chain and of the production of ornaments during the European Upper Palaeolithic. References Jude, P. E. (1960). La grotte de Rocherreil: station magdalénienne et azilienne, Masson. Rigaud, S., O'Hara, J., Charles, L., Man-Estier, E. and Paillet, P. (2022) The management of symbolic raw materials in the Late Upper Paleolithic of South-Western France: a shell ornaments perspective. SocArXiv, z7pqg, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/z7pqg Taborin, Y. (1993). La parure en coquillage au Paléolithique, CNRS éditions. | The management of symbolic raw materials in the Late Upper Paleolithic of South-Western France: a shell ornaments perspective | Solange Rigaud, John O’Hara, Laurent Charles, Elena Man-Estier, Patrick Paillet | <p>Personal ornaments manufactured on marine and fossil shell are a significant element of Upper Palaeolithic symbolic material culture, and are often found at considerable distances from Pleistocene coastlines or relevant fossil deposits. Here, w... |  | Europe, Symbolic behaviours, Upper Palaeolithic | Beatrice Demarchi | 2022-04-23 19:20:02 | View | |
30 Sep 2022
Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF dataBharath Nair, Ismael Rodríguez Palomo, Bo Markussen, Carsten Wiuf, Sarah Fiddyment and Matthew Collins https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.13.483627Assessing glutamine deamination in ancient parchment samplesRecommended by Beatrice Demarchi based on reviews by Maria Codlin and 3 anonymous reviewersData authenticity and approaches to data authentication are crucial issues in ancient protein research. The advent of modern mass spectrometry has enabled the detection of traces of ancient biomolecules contained in fossils, including protein sequences. However, detecting proteins in ancient samples does not equate to demonstrating their endogenous nature: instead, if the mechanisms that drive protein preservation and degradation are understood, then the extent of protein diagenesis can be used for evaluating preservational quality, which in turn may be related to the authenticity of the protein data. The post-mortem deamidation of asparaginyl and glutamyl residues is a key degradation reaction, which can be assessed effectively on the basis of mass spectrometry data, and which has accrued a long history of research, both in terms of describing the mechanisms governing the reactions and with regard to the best strategies for assessing and quantifying the extent of glutamine (Gln) and asparagine (Asn) deamidation in ancient samples (Pal Chowdhury et al., 2019; Ramsøe et al., 2021, 2020; Schroeter and Cleland, 2016; Simpson et al., 2016; Solazzo et al., 2014; Welker et al., 2016; Wilson et al., 2012). In their paper, Nair and colleagues (2022) build on this wealth of knowledge and present a tool for quantifying the extent of Gln deamidation in parchment. Parchment is a collagen-based material which can yield extraordinary insights into manuscript manufacturing practices in the past, as well as on the daily lives of the people who assembled and used them (“biocodicology”) (Fiddyment et al., 2021, 2019, 2015; Teasdale et al., 2017). Importantly, the extent of deamidation can be directly related to the quality of the parchment produced: rapid direct deamidation of Gln is induced by the liming process, therefore high extents of deamidation are linked to prolonged exposure to the high pH conditions which are typical of liming, thus implying lower-quality parchment. Nair et al.’s approach focuses on collagen peptides which are typically detected during MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analyses of parchment and build a simple three-step workflow able to yield an overall index of deamidation for a sample (the parchment glutamine index - PQI) 一 taking into account that different Gln residues degrade at different rates according to their micro-chemical environment. The first step involves pre-processing the MALDI spectra, since Nair et al. are specifically interested in maximising information which can be obtained by low-quality data. The second step builds on well-established methods for quantifying Q → E from MALDI-TOF data by modelling the convoluted isotope distributions (Wilson et al., 2012). Once relative rates of deamidation in selected peptides within a given sample are calculated, the third step uses a mixed effects model to combine the individual deamidation estimates and to obtain an overall estimate of the deamidation for a parchment sample (PQI). The PQI can be used effectively for assessing parchment quality, as the authors show for the dataset from Orval Abbey. However, PQI could also have wider applications to the study of processed collagen, which is widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In general, the study by Nair et al. is a welcome addition to a growing body of research on protein diagenesis, which will ultimately improve models for the assessment of the authenticity of biomolecular data in archaeology. References Chowdhury, P.M., Wogelius, R., Manning, P.L., Metz, L., Slimak, L., and Buckley, M. 2019. Collagen deamidation in archaeological bone as an assessment for relative decay rates. Archaeometry 61:1382–1398. https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.12492 Fiddyment, S., Goodison, N.J., Brenner, E., Signorello, S., Price, K., and Collins, M.J.. 2021. Girding the loins? Direct evidence of the use of a medieval parchment birthing girdle from biomolecular analysis. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.202055 Fiddyment,S., Holsinger, B., Ruzzier, C., Devine, A., Binois, A., Albarella, U., Fischer, R., Nichols, E., Curtis, A., Cheese, E., Teasdale, M.D., Checkley-Scott, C., Milner, S.J., Rudy, K.M., Johnson, E.J., Vnouček, J., Garrison, M., McGrory, S., Bradley, D.G., and Collins, M.J. 2015. Animal origin of 13th-century uterine vellum revealed using noninvasive peptide fingerprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15066–15071. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512264112 Fiddyment, S., Teasdale, M.D., Vnouček, J., Lévêque, É., Binois, A., and Collins, M.J. 2019. So you want to do biocodicology? A field guide to the biological analysis of parchment. Heritage Science 7:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-019-0278-6 Nair, B., Rodríguez Palomo, I., Markussen, B., Wiuf, C., Fiddyment, S., and Collins, M. Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF data. BiorRxiv, 2022.03.13.483627, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.13.483627 Ramsøe, A., Crispin, M., Mackie, M., McGrath, K., Fischer, R., Demarchi, B., Collins, M.J., Hendy, J., and Speller, C. 2021. Assessing the degradation of ancient milk proteins through site-specific deamidation patterns. Sci Rep 11:7795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87125-x Ramsøe, A., van Heekeren, V., Ponce, P., Fischer, R., Barnes, I., Speller, C., and Collins, M.J. 2020. DeamiDATE 1.0: Site-specific deamidation as a tool to assess authenticity of members of ancient proteomes. J Archaeol Sci 115:105080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2020.105080 Schroeter, E.R., and Cleland, T.P. 2016. Glutamine deamidation: an indicator of antiquity, or preservational quality? Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 30:251–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.7445 Simpson, J.P., Penkman, K.E.H., and Demarchi, B. 2016. The effects of demineralisation and sampling point variability on the measurement of glutamine deamidation in type I collagen extracted from bone. J Archaeol Sci 69: 29-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2016.02.002 Solazzo, C., Wilson, J., Dyer, J.M., Clerens, S., Plowman, J.E., von Holstein, I., Walton Rogers, P., Peacock, E.E., and Collins, M.J. 2014. Modeling deamidation in sheep α-keratin peptides and application to archeological wool textiles. Anal Chem 86:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4026362 Teasdale, M.D., Fiddyment, S., Vnouček, J., Mattiangeli, V., Speller, C., Binois, A., Carver, M., Dand, C., Newfield, T.P., Webb, C.C., Bradley, D.G., and Collins M.J. 2017. The York Gospels: a 1000-year biological palimpsest. R Soc Open Sci 4:170988. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.170988 Welker, F., Soressi, M.A., Roussel, M., van Riemsdijk, I., Hublin, J.-J., and Collins, M.J. 2016. Variations in glutamine deamidation for a Châtelperronian bone assemblage as measured by peptide mass fingerprinting of collagen. STAR: Science & Technology of Archaeological Research 3:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/20548923.2016.1258825 Wilson, J., van Doorn, N.L., and Collins, M.J. 2012. Assessing the extent of bone degradation using glutamine deamidation in collagen. Anal Chem 84:9041–9048. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301333t | Parchment Glutamine Index (PQI): A novel method to estimate glutamine deamidation levels in parchment collagen obtained from low-quality MALDI-TOF data | Bharath Nair, Ismael Rodríguez Palomo, Bo Markussen, Carsten Wiuf, Sarah Fiddyment and Matthew Collins | <p style="text-align: justify;">Parchment was used as a writing material in the Middle Ages and was made using animal skins by liming them with Ca(OH)<span class="math-tex">\( _2 \)</span>. During liming, collagen peptides containing Glutamine (Q)... | Bioarchaeology, Europe, Medieval, Zooarchaeology | Beatrice Demarchi | 2022-03-22 12:54:10 | View | ||
26 Apr 2022
Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a reviewAllowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/skeu5Archaeophenomics: an up-and-coming field in bioarchaeologyRecommended by Anneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewerAnneke H. van Heteren based on reviews by Stefan Schlager and 1 anonymous reviewer Phenomics is the analysis of high-dimensional phenotypic data [1]. Phenomics research strategies are capable of linking genetic variation to phenotypic variation [2], but a genetic component is not absolutely necessary. The paper “Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics: a review” by Evin and colleagues [3] examines the use of geometric morphometrics in bioarchaeology and coins the term archaeophenomics. Archaeophenomics can be described as the large-scale phenotyping of ancient remains, and both addresses taxonomic identification, as well as infers spatio-temporal agrobiodiversity dynamics. It is a relatively new field in bioarchaeology with the first paper using this approach stemming from 2004. This study by Evin et al. [3] presents an excellent review and unquestionably demonstrates the potential of archaeophenomics. The authors provide an exhaustive review specifically of bioarchaeological studies in international journals using geometric morphometrics to study archaeological remains of domestic species. Although geometric morphometrics lends itself well for archaeophenomics, readers should keep in mind that this is not the only method and other approaches might equally fall under archaeophenomics as long as high-dimensional phenotypic archaeological data are involved. Distinguishing archaeophenomics from phenomics is important because of a critical difference. Archaeological remains are often altered by taphonomical processes. As such data may not be as complete as when working with modern specimens. Although this poses difficulties, morphometric analyses can usually still be performed as long as the structures presenting the relevant geometrical features are present. Even fragmented remains can be studied with a restricted version of the original landmarking/measurement protocol. Evin et al. [3] define archaeophenomics as “phenomics of the past”. This is only partly correct. It can be deduced from their review that they really mean phenomics of our (human) past. This leaves a gap for phenomics of the non-human past, for which I suggest the term palaeophenomics. [1] Jin, L. (2021). Welcome to the Phenomics Journal. Phenomics, 1, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-020-00009-4.
| Archaeophenomics of ancient domestic plants and animals using geometric morphometrics : a review | Allowen Evin, Laurent Bouby, Vincent Bonhomme, Angèle Jeanty, Marine Jeanjean, Jean-Frédéric Terral | <p>Geometric morphometrics revolutionized domestication studies through the precise quantification of the phenotype of ancient plant and animal remains. Geometric morphometrics allow for an increasingly detailed understanding of the past agrobiodi... |  | Archaeobotany, Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Zooarchaeology | Anneke H. van Heteren | 2022-02-17 09:50:39 | View | |
14 Nov 2022
Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman CityJens Kleb https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021Cross-comparison of classical sources, explorer and scientific reports and maps in the search of an ancient city: The example of Raphana of the DecapolisRecommended by Luc Doyon based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli based on reviews by Rocco Palermo and Francesca Mazzilli
Establishing the precise location of ancient cities constitutes a challenging task that requires the implementation of multi-disciplinary approaches. In his manuscript entitled “Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha: The search of an eminent Greco-Roman city”, Kleb (2022) proposes a convincing argument building on in-depth research of classical literary sources, literature review of explorer accounts and scientific publications from the 19th and 20th century as well as analysis of old and new maps, aerial photographs, and satellite images. This research report clearly emphasizes the importance of undertaking systematic interdisciplinary work on the topic to mitigate the uncertainties associated with the identification of Raphana, the Decapolis city first mentioned by Pliny the Elder. The Decapolis refers to a group of ten cities of Hellenistic traditions located on the eastern borders of the Roman Empire. This group of cities plays an important role in research that aims to contextualize the Judaean and Galilean history and to investigate urban centers in which different local and Greco-Roman influences met (Lichtenberger, 2021). While the location of most of the Decapolis cities is known and is (or was) subjected to systematic archaeological investigations (e.g., Eisenberg and Kowalewska, 2022; Makhadmeh et al., 2020; Shiyab et al., 2019), the location of others remain speculative. This is the case of Raphana for which the precise location remains difficult to establish owing in part to numerous name changes, limited information on the city structure, architecture, and size, etc. The research presented by Kleb (2022) has some merits, which is emphasized here, although the report is presented in an unusual format compared to traditional scientific articles, i.e., introduction, research background, methodology, results, and discussion. First, the extensive review of classical works allows the reader to gain a historical perspective on the change of names from Raepta/Raphana to Arpha/Arefa. The author argues these different names likely refer to a single location. Second, the author combs through an impressive literature from the 19th and 20th century and emphasize how some assumptions by explorers who visited the region were introduced in the scientific literature and remained unchallenged. Finally, the author gathers a remarkable quantity of old and new maps of the Golan, el-Ledja and Hauran regions and compare them with multiple lines of evidence to hypothesize that the location of Raphana may lie near Ar-Rafi’ah, also known as Bir Qassab, in the Ard el Fanah plain, a conclusion that now requires to be tested through fieldwork investigations. References Kleb, J. (2022) Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City. Figshare, 20550021, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20550021 Eisenberg, M. and Kowalewska, A. (2022). Funerary podia of Hippos of the Decapolis and the phenomenon in the Roman world. J. Roman Archaeol. 35, 107–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047759421000465 Lichtenberger, A. (2021). The Decapolis, in: A Companion to the Hellenistic and Roman Near East. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119037354.ch18 Makhadmeh, A., Al-Badarneh, M., Rawashdeh, A. and Al-Shorman, A. (2020). Evaluating the carrying capacity at the archaeological site of Jerash (Gerasa) using mathematical GIS modeling. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 23, 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.09.002 Shiyab, A., Al-Shorman, A., Turshan, N., Tarboush, M., Alawneh, F. and Rahabneh, A. (2019). Investigation of late Roman pottery from Gadara of the Decapolis, Jordan using multi-methodic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 25, 100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2019.04.003 | Raphana of the Decapolis and its successor Arpha - The search for an eminent Greco-Roman City | Jens Kleb | <p style="text-align: justify;">This research paper presents a detailed analysis of ancient literature and archaeological and geographical research until the present day for an important ancient location in the southern part of Syria. This one had... |  | Landscape archaeology, Mediterranean, Spatial analysis, Theoretical archaeology | Luc Doyon | 2021-12-30 13:54:32 | View | |
16 May 2022

Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool culturesAnnemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger https://osf.io/x8m4jOpen glossary for wood technologiesRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé
Wood is a widely available and versatile material, so it is not surprising that it has been a key resource throughout human history. However, it is more vulnerable to decomposition than other materials, and its direct use is only rarely recorded in prehistoric sites. Despite this, there are exceptions (e.g., [1-5] [6] and references therein), and indirect evidence of its use has been attested through use-wear analyses, residue analyses (e.g., [7]) and imprints on the ground (e.g., [8]). One interesting finding of note is that the technology required to make, for example, wooden spears was quite complex [9], leading some authors to propose that this type of tool production represented a cognitive leap for Pleistocene hominids [10]. Other researchers, however, have proposed that the production process for wooden tools could have been much easier than is currently thought [11]. Be that as it may, in recent years researchers have begun to approach wood remains systematically, developing analyses of natural and anthropogenic damage, often with the help of experimental reference samples. In this work, the authors elaborate a comprehensive glossary as a first step towards the understanding of the use of wood for technological purposes in different times and places, as there is still a general gap in the established nomenclature. Thus, this glossary is a synthesis and standardisation of analytical terms for early wood technologies that includes clear definitions and descriptions of traces from stone tool-using cultures, to avoid confusion in ongoing and future studies of wood tools. For this, the authors have carried out a detailed search of the current literature to select appropriate terms associated with additional readings that provide a wide, state-of-the-art description of the field of wood technology. An interesting point is that the glossary has been organised within a chaîne opératoire framework divided into categories including general terms and natural traces, and then complemented by an appendix of images. It is important to define the natural traces –understanding these as alterations caused by natural processes–because they can mask those modifications produced by other agents affecting both unmodified and modified wood before, during or after its human use. In short, the work carried out by Milks et al. [6] is an excellent and complete assessment and vital to the technological approach to wooden artifacts from archaeological contexts and establishing a common point for a standardised nomenclature. One of its particular strengths is that the glossary is a preprint that will remain open during the coming years, so that other researchers can continue to make suggestions and refinements to improve the definitions, terms and citations within it. [1] Oakley, K., Andrews, P., Keeley, L., Clark, J. (1977). A reappraisal of the Clacton spearpoint. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 43, 13-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0079497X00010343 [2] Thieme, H. (1997). Lower Palaeolithic hunting spears from Germany. Nature 385, 807-810. https://doi.org/10.1038/385807a0 [3] Schoch, W.H., Bigga, G., Böhner, U., Richter, P., Terberger, T. (2015). New insights on the wooden weapons from the Paleolithic site of Schöningen. Journal of Human Evolution 89, 214-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.08.004 [4] Aranguren, B., Revedin, A., Amico, N., Cavulli, F., Giachi, G., Grimaldi, S. et al. (2018). Wooden tools and fire technology in the early Neanderthal site of Poggetti Vecchi (Italy). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115, 2054-2059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716068115 [5] Rios-Garaizar, J., López-Bultó, O., Iriarte, E., Pérez-Garrido, C., Piqué, R., Aranburu, A., et al. (2018). A Middle Palaeolithic wooden digging stick from Aranbaltza III, Spain. PLoS ONE 13(3): e0195044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195044 [6] Milks, A. G., Lehmann, J., Böhner, U., Leder, D., Koddenberg, T., Sietz, M., Vogel, M., Terberger, T. (2022). Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures. Peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/x8m4j [7] Nugent, S. (2006). Applying use-wear and residue analyses to digging sticks. Mem Qld Mus Cult Herit Ser 4, 89-105. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.890092331962439 [8] Allué, E., Cabanes, D., Solé, A., Sala, R. (2012). Hearth Functioning and Forest Resource Exploitation Based on the Archeobotanical Assemblage from Level J, in: i Roura E. (Ed.), High Resolution Archaeology and Neanderthal Behavior: Time and Space in Level J of Abric Romaní (Capellades, Spain). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3922-2_9 [9] Ennos, A.R., Chan, T.L. (2016). "Fire hardening" spear wood does slightly harden it, but makes it much weaker and more brittle. Biology Letters 12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2016.0174 [10] Haidle, M.N. (2009). How to think a simple spear?, in: de Beaune S.A., Coolidge F.L., Wynn T. (Eds.), Cognitive Archaeology and Human Evolution. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 57-73. [11] Garofoli, D. (2015). A Radical Embodied Approach to Lower Palaeolithic Spear-making. Journal of Mind and Behavior 36, 1-26. | Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures | Annemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger | <p>The analysis of wood technologies created by stone tool-using cultures remains underdeveloped relative to the study of lithic and bone technologies. In recent years archaeologists have begun to approach wood assemblages systematically, developi... |  | Ancient Palaeolithic, Archaeobotany, Mesolithic, Middle Palaeolithic, Neolithic, Raw materials, Taphonomy, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Ruth Blasco | 2021-12-01 12:18:53 | View | |
17 Jun 2022

Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5New method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in rock art contextsRecommended by Aitor Ruiz-Redondo based on reviews by Alain Queffelec, Laure Dayet and 1 anonymous reviewerSilica coating developed in cave art walls had an impact in the preservation of the paintings themselves. Despite it still exists a controversy about whether or not the effects contribute to the preservation of the artworks; it is evident that identifying these silica coatings would have an impact to assess the taphonomy of the walls and the paintings preserved on them. Unfortunately, current techniques -especially non-invasive ones- can hardly address amorphous silica characterisation. Thus, its presence is often detected on laboratory observations such as SEM or XRD analyses. In the paper “Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context - Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)”, Quiers and collaborators propose a new method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in a rock art context based on UV laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) and UV illumination [1]. The results from both methods presented by the authors are convincing for the detection of U-silica mineralisation (U-opal in the specific case of study presented). This would allow access to a fast and cheap method to identify this kind of formations in situ in decorated caves. Beyond the relationship between opal coating and the preservation of the rock art, the detection of silica mineralisation can have further implications. First, it can help to define spot for sampling for pigment compositions, as well as reconstruct the chronology of the natural history of the caves and its relation with the human frequentation and activities. In conclusion, I am glad to recommend this original research, which offers a new approach to the identification of geological processes that affect -and can be linked with- the Palaeolithic cave art. [1] Quiers, M., Chanteraud, C., Maris-Froelich, A., Chalmin-Aljanabi, E., Jaillet, S., Noûs, C., Pairis, S., Perrette, Y., Salomon, H., Monney, J. (2022) Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France). HAL, hal-03383193, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5 | Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France) | Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney | <p style="text-align: justify;">Silica coatings development on rock art walls in Points Cave questions the analytical access to pictorial matter specificities (geochemistry and petrography) and the rock art conservation state in the context of pig... |  | Archaeometry, Europe, Rock art, Taphonomy, Upper Palaeolithic | Aitor Ruiz-Redondo | 2021-10-25 11:12:48 | View | |
01 Dec 2021
A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-MaatheideSonja Tomasso, Dries Cnuts, Justin Coppe, Marijn Van Gils, Ferdi Geerts, Marc De Bie, Veerle Rots https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pf3smPotential of a large-scale functional analysis to reconstructing past human activities at the Final Palaeolithic site of Lommel-MaatheideRecommended by Marta Arzarello and Alice Leplongeon based on reviews by Gabriele Luigi Francesco Berruti and Ana Abrunhosa and Alice Leplongeon based on reviews by Gabriele Luigi Francesco Berruti and Ana Abrunhosa
The paper “A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide” [1] focuses on the final Palaeolithic (Federmesser) site of Lommel-Maatheide. Federmesser sites from northern Belgium such as Lommel-Maatheide, Meer and Rekem, show evidence for dense human occupation of specific areas located on top of Tardiglacial dunes nearby water bodies [2]. Preserved spatial distribution of finds at the sites suggest different activity areas and the presence of habitat structures [2]. However, because of the low organic preservation at the sites, functional analyses of lithic assemblages have the potential to significantly contribute to the spatial organisation of activities at these sites. This study by Tomasso et al. [1], represents an excellent example of a large-scale integrated approach to the study of lithic industries. The article undoubtedly demonstrates the potential of the proposed methodology and the reliability of the results obtained. The article explores two different aspects (linked and excellently interconnected here): the possibility to apply use wear, residue and fracture analyses, on lithic assemblages affected by taphonomical alterations and to study lithic assemblages from dune landscapes. The study allows to answer differentiated questions: what is the influence of taphonomical alterations on use wear analysis? How do excavation methods impact the formation of use wear and the preservation of residues? Can we recognize distinct domestic activities? The article also provides an interesting hypothesis about hunting activities and propulsion methods. The applied methodology is effectively interdisciplinary and innovative. It demonstrates how a truly integrated and articulated approach can represent the turning point for going beyond a mainly descriptive dimension to move towards a real understanding of the sites. Studies dedicated to the analysis of the propulsion mode are not very frequent, but they are surely very important to better understand human behaviour [3]. Here, the methodology developed for the evaluation of the propulsion mode represent an important starting point for the definition of a new approach. Morphological and morphometrical analysis are integrated to the evaluation of the mechanical stress, to fracture delineations and to the hafting system (the latter defined on experimental basis). This article therefore underlines the potential of combining different approaches to functional analysis associated with a ‘tailored’ reference collection and applying them to a high number of artefacts for reconstructing past human activities involving materials that are otherwise not preserved in these contexts. [1] Tomasso, S., Cnuts, D., Coppe, J., Geerts, F., Gils, M.V., Bie, M.D., Rots, V. (2021). A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pf3sm, ver 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology. [2] De Bie, M., Van Gils, M. (2006). Les habitats des groupes à Federmesser (aziliens) dans le Nord de la Belgique. Bulletin de la Société préhistorique française, 103, 781–790. [3] Coppe, J., Lepers, C., Clarenne, V., Delaunois, E., Pirlot, M. and Rots V. (2019). Ballistic Study Tackles Kinetic Energy Values of Palaeolithic Weaponry. Archaeometry, (61)4, 933-956. https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.12452 | A closer look at an eroded dune landscape: first functional insights into the Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide | Sonja Tomasso, Dries Cnuts, Justin Coppe, Marijn Van Gils, Ferdi Geerts, Marc De Bie, Veerle Rots | <p>The vast Federmessergruppen site of Lommel-Maatheide, which is located in the Campine region (Northern Belgium), revealed the presence of numerous Final Palaeolithic concentrations situated on a large Late Glacial sand ridge on the northern edg... | Environmental archaeology, Landscape archaeology, Lithic technology, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Marta Arzarello | 2021-09-14 17:04:38 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










