Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * ▲ | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
04 Oct 2023

IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A "para-description"Hagmann, Dominik; Reiner, Franziska https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/5vwg8The IUENNA project: integrating old data and documentation for future archaeologyRecommended by Ronald Visser based on reviews by Nina Richards and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Nina Richards and 3 anonymous reviewers
This recommended paper on the IUENNA project (Hagmann and Reiner 2023) is not a paper in the traditional sense, but it is a reworked version of a project proposal. It is refreshing to read about a project that has just started and see what the aims of the project are. This ties in with several open science ideas and standards (e.g. Brinkman et al. 2023). I am looking forward to see in a few years how the authors managed to reach the aims and goals of the project. The IUENNA project deals with the legacy data and old excavations on the Hemmaberg and in the Jauntal. Archaeological research in this small, but important region, has taken place for more than a century, revealing material from over 2000 years of human history. The Hemmaberg is well known for its late antique and early medieval structures, such as roads, villas and the various churches. The wider Jauntal reveals archaeological finds and features dating from the Iron Age to the recent past. The authors of the paper show the need to make sure that the documentation and data of these past archaeological studies and projects will be accessible in the future, or in their own words: "Acute action is needed to systematically transition these datasets from physical filing cabinets to a sustainable, networked virtual environment for long-term use" (Hagmann and Reiner 2023: 5). The papers clearly shows how this initiative fits within larger developments in both Digital Archaeology and the Digital Humanities. In addition, the project is well grounded within Austrian archaeology. While the project ties in with various international standards and initiatives, such as Ariadne (https://ariadne-infrastructure.eu/) and FAIR-data standards (Wilkinson et al. 2016, 2019), it would benefit from the long experience institutes as the ADS (https://archaeologydataservice.ac.uk/) and DANS (see Data Station Archaeology: https://dans.knaw.nl/en/data-stations/archaeology/) have on the storage of archaeological data. I would also like to suggest to have a look at the Dutch SIKB0102 standard (https://www.sikb.nl/datastandaarden/richtlijnen/sikb0102) for the exchange of archaeological data. The documentation is all in Dutch, but we wrote an English paper a few years back that explains the various concepts (Boasson and Visser 2017). However, these are a minor details or improvements compared to what the authors show in their project proposal. The integration of many standards in the project and the use of open software in a well-defined process is recommendable. The IUENNA project is an ambitious project, which will hopefully lead to better insights, guidelines and workflows on dealing with legacy data or documentation. These lessons will hopefully benefit archaeology as a discipline. This is important, because various (European) countries are dealing with similar problem, since many excavations of the past have never been properly published, digitalized or deposited. In the Netherlands, for example, various projects dealt with publication of legacy excavations in the Odyssee-project (https://www.nwo.nl/onderzoeksprogrammas/odyssee). This has led to the publication of various books and datasets (24) (https://easy.dans.knaw.nl/ui/datasets/id/easy-dataset:34359), but there are still many datasets (8) missing from the various projects. In addition, each project followed their own standards in creating digital data, while IUENNA will make an effort to standardize this. There are still more than 1000 Dutch legacy excavations still waiting to be published and made into a modern dataset (Kleijne 2010) and this is probably the case in many other countries. I sincerely hope that a successful end of IUENNA will be an inspiration for other regions and countries for future safekeeping of legacy data. References Boasson, W and Visser, RM. 2017 SIKB0102: Synchronizing Excavation Data for Preservation and Re-Use. Studies in Digital Heritage 1(2): 206–224. https://doi.org/10.14434/sdh.v1i2.23262 Brinkman, L, Dijk, E, Jonge, H de, Loorbach, N and Rutten, D. 2023 Open Science: A Practical Guide for Early-Career Researchers https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7716153 Hagmann, D and Reiner, F. 2023 IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A ‘para-description’. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/5vwg8 Kleijne, JP. 2010. Odysee in de breedte. Verslag van het NWO Odyssee programma, kortlopend onderzoek: ‘Odyssee, een oplossing in de breedte: de 1000 onuitgewerkte sites, die tot een substantiële kennisvermeerdering kunnen leiden, digitaal beschikbaar!’ ‐ ODYK‐09‐13. Den Haag: E‐depot Nederlandse Archeologie (EDNA). https://doi.org/10.17026/dans-z25-g4jw Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Aalbersberg, IjJ, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, ’t Hoen, PAC, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Velterop, J, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2016 The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 3(1): 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 Wilkinson, MD, Dumontier, M, Jan Aalbersberg, I, Appleton, G, Axton, M, Baak, A, Blomberg, N, Boiten, J-W, da Silva Santos, LB, Bourne, PE, Bouwman, J, Brookes, AJ, Clark, T, Crosas, M, Dillo, I, Dumon, O, Edmunds, S, Evelo, CT, Finkers, R, Gonzalez-Beltran, A, Gray, AJG, Groth, P, Goble, C, Grethe, JS, Heringa, J, Hoen, PAC ’t, Hooft, R, Kuhn, T, Kok, R, Kok, J, Lusher, SJ, Martone, ME, Mons, A, Packer, AL, Persson, B, Rocca-Serra, P, Roos, M, van Schaik, R, Sansone, S-A, Schultes, E, Sengstag, T, Slater, T, Strawn, G, Swertz, MA, Thompson, M, van der Lei, J, van Mulligen, E, Jan Velterop, Waagmeester, A, Wittenburg, P, Wolstencroft, K, Zhao, J and Mons, B. 2019 Addendum: The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 6(1): 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0009-6
| IUENNA – openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology: A "para-description" | Hagmann, Dominik; Reiner, Franziska | <p>The Go!Digital 3.0 project IUENNA – an acronym for “openIng the soUthErn jauNtal as a micro-regioN for future Archaeology” – embraces a comprehensive open science methodology. It focuses on the archaeological micro-region of the Jauntal Valley ... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Computational archaeology | Ronald Visser | 2023-04-06 13:36:16 | View | |
12 Feb 2024

3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, GermanyTharandt, Louise https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7948379Online presentation of the digital reconstruction process of a megalithic tomb : “3Duewelsteene”Recommended by Sophie C. Schmidt and James Allison based on reviews by Robert Bischoff, Ronald Visser and Scott Ure based on reviews by Robert Bischoff, Ronald Visser and Scott Ure
“3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, Germany” (Tharandt 2024) presents several 3-dimensional models of the Düwelsteene monument, along with contextual information about the grave and the process of creating the models. The website (https://3duewelsteene.github.io/) includes English and German versions, making it accessible to a wide audience. The website itself serves as the primary means of presenting the data, rather than as a supplement to a written text. This is an innovative and engaging way to present the research to a wider public. Düwelsteene (“Devil’s Stones”) is a megalithic passage grave from the Funnel Beaker culture, dating to approximately 3300 BC. to 2600 BC. that was excavated in 1932. The website displays three separate 3-dimensional models. They ares shown in the 3D viewer software 3DHOP, which enables viewers to interact with the models in several ways, Annotations on the models display further information. The first model was created by image-based modeling and shows the monument as it appears today. A second model uses historical photographs and excavation data to reconstruct the grave as it appeared prior to the 1932 archaeological excavation. Restoration work following the excavation relocated many of the stones. Pre-1932 photographs collected from residents of the nearby town of Heiden were then used to create a model showing what the tomb looked like before the restoration work. It is commendable that a “certainty view” of the model shows the certainty with which the stones can be put at the reconstructed place. Gaps in the 3D models of stones that were caused by overlap with other stones have been filled with a rough mesh and marked as such, thereby differentiating between known and unknown parts of the stones. The third model is the most imaginative and most interesting. As it shows as the grave as it might have appeared in approximately 3000 B.C., many aspects of this model are necessarily somewhat speculative. There is no direct evidence for exact size and shape of the capstones, the height of the mound, and other details. But enough is known about other similar constructions to allow these details to be inferred with some confidence. Again, care was taken to enable viewers to distinguish between the stones that are still in existence and those that were reconstructed. A video on the home page of the website adds a nice touch. It starts with the model of the Düwelsteene as it currently appears then shows, in reverse order, the changes to the grave, ending with the inferred original state. The 3D reconstructions are convincing and the methods well described. This project follows an open science approach and the FAIR principles, which is commendable and cutting edge in the field of Digital Archaeology. The preprint of the website hosted on zenodo includes all the photos, text, html files, and nine individual 3D model (.ply) files that are combined in the reconstructions exhibited on the website. A “readme.md” file includes details about building the models using CloudCompare and Blender, and modifications to the 3D viewer software (3DHOP) to get the website to improve the display of the reconstructions. We have to note that the link between the reconstructed models and the html page does not work when the files are downloaded from zenodo and opened offline. The html pages open in the browser, and the individual ply files work fine, but the 3D models do not display on the browser page when the html files are opened offline. The online version of the website is working perfectly. The 3Düwelsteene website combines the presentation of archaeological domain knowledge to a lay audience as well as in-depths information on the reconstruction process to make it an interesting contribution for researchers. By providing data and code for the website it also models an Open Science approach, which enables other researchers to re-use these materials. We congratulate the author on a successful reconstruction of the megalithic tomb, an admirable presentation of the archaeological work and the thoughtful outreach to a broad audience. Bibliography | 3Duewelsteene - A website for the 3D visualization of the megalithic passage grave Düwelsteene near Heiden in Westphalia, Germany | Tharandt, Louise | <p>The Düwelsteene near Heiden, Westphalia, is one of the most southern megalithic tombs of the Funnel Beaker culture. In 1932 the Düwelsteene were restored and the appearance of the grave was changed. Even though the megalithic tomb was excavated... |  | Computational archaeology, Mesolithic, Neolithic | Sophie C. Schmidt | 2023-05-21 17:24:22 | View | |
14 Sep 2020
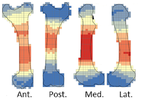
A way to break bones? The weight of intuitivenessDelphine Vettese, Trajanka Stavrova, Antony Borel, Juan Marin, Marie-Hélène Moncel, Marta Arzarello, Camille Daujeard https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/rebwtBreaking bones: Nature or Culture?Recommended by Beatrice Demarchi and Reuven Yeshurun based on reviews by Terry O'Connor, Alan Outram and 1 anonymous reviewerThe nature of breaking long bones for obtaining marrow is important in Paleolithic archaeology, due to its widespread, almost universal, character. Provided that hammer-stone percussion marks can be correctly identified using experimental datasets (e.g., [1]), the anatomical location and count of the marks may be taken to reflect recurrent “cultural” traditions in the Paleolithic [2]. Were MP humans breaking bones intuitively or did they abide by a strict “protocol”, and, if the latter, was this protocol optimized for marrow retrieval or geared towards another, less obvious goal? This paper provides a baseline for location analyses of percussion marks. Their dataset may therefore be regarded as a null hypothesis according to which the archaeological data could be tested. If Paleolithic patterns of percussion marks differ from Vettese et al.’s [3] “intuitive” patterns, then the null hypothesis is disproved and one can argue in favor of a learned pattern. The latter can be a result of ”culture”, as Vettese et al. [3] phrase it, in the sense of nonrandom action that draws on transmitted knowledge. Such comparisons bear a great potential for understanding the degree of technological behavior in the Paleolithic by factoring out the “natural” constraints of bone breakage patterns. Vettese et al. [3: fig. 14] started this discourse by comparing their experimental dataset to some Middle and Upper Paleolithic faunas; we are confident that many other studies will follow. Bibliography [1]Pickering, T.R., Egeland, C.P., 2006. Experimental patterns of hammerstone percussion damage on bones: Implications for inferences of carcass processing by humans. J. Archaeol. Sci. 33, 459–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2005.09.001 [2]Blasco, R., Rosell, J., Domínguez-Rodrigo, M., Lozano, S., Pastó, I., Riba, D., Vaquero, M., Peris, J.F., Arsuaga, J.L., de Castro, J.M.B., Carbonell, E., 2013. Learning by Heart: Cultural Patterns in the Faunal Processing Sequence during the Middle Pleistocene. PLoS One 8, e55863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055863 [3]Vettese, D., Stavrova, T., Borel, A., Marin, J., Moncel, M.-H., Arzarello, M., Daujeard, C. (2020) A way to break bones? The weight of intuitiveness. BioRxiv, 011320, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.31.011320 | A way to break bones? The weight of intuitiveness | Delphine Vettese, Trajanka Stavrova, Antony Borel, Juan Marin, Marie-Hélène Moncel, Marta Arzarello, Camille Daujeard | <p>During the Middle Paleolithic period, bone marrow extraction was an essential source of fat nutrients for hunter-gatherers especially throughout cold and dry seasons. This is attested by the recurrent findings of percussion marks in osteologica... |  | Archaeometry, Bioarchaeology, Spatial analysis, Taphonomy, Zooarchaeology | Beatrice Demarchi | 2020-04-01 11:52:05 | View | |
17 Jun 2022

Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5New method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in rock art contextsRecommended by Aitor Ruiz-Redondo based on reviews by Alain Queffelec, Laure Dayet and 1 anonymous reviewerSilica coating developed in cave art walls had an impact in the preservation of the paintings themselves. Despite it still exists a controversy about whether or not the effects contribute to the preservation of the artworks; it is evident that identifying these silica coatings would have an impact to assess the taphonomy of the walls and the paintings preserved on them. Unfortunately, current techniques -especially non-invasive ones- can hardly address amorphous silica characterisation. Thus, its presence is often detected on laboratory observations such as SEM or XRD analyses. In the paper “Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context - Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France)”, Quiers and collaborators propose a new method for the in situ detection and characterisation of amorphous silica in a rock art context based on UV laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) and UV illumination [1]. The results from both methods presented by the authors are convincing for the detection of U-silica mineralisation (U-opal in the specific case of study presented). This would allow access to a fast and cheap method to identify this kind of formations in situ in decorated caves. Beyond the relationship between opal coating and the preservation of the rock art, the detection of silica mineralisation can have further implications. First, it can help to define spot for sampling for pigment compositions, as well as reconstruct the chronology of the natural history of the caves and its relation with the human frequentation and activities. In conclusion, I am glad to recommend this original research, which offers a new approach to the identification of geological processes that affect -and can be linked with- the Palaeolithic cave art. [1] Quiers, M., Chanteraud, C., Maris-Froelich, A., Chalmin-Aljanabi, E., Jaillet, S., Noûs, C., Pairis, S., Perrette, Y., Salomon, H., Monney, J. (2022) Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France). HAL, hal-03383193, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Archaeology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03383193v5 | Light in the Cave: Opal coating detection by UV-light illumination and fluorescence in a rock art context. Methodological development and application in Points Cave (Gard, France) | Marine Quiers, Claire Chanteraud, Andréa Maris-Froelich, Émilie Chalmin-Aljanabi, Stéphane Jaillet, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Pairis, Yves Perrette, Hélène Salomon, Julien Monney | <p style="text-align: justify;">Silica coatings development on rock art walls in Points Cave questions the analytical access to pictorial matter specificities (geochemistry and petrography) and the rock art conservation state in the context of pig... |  | Archaeometry, Europe, Rock art, Taphonomy, Upper Palaeolithic | Aitor Ruiz-Redondo | 2021-10-25 11:12:48 | View | |
02 Sep 2023
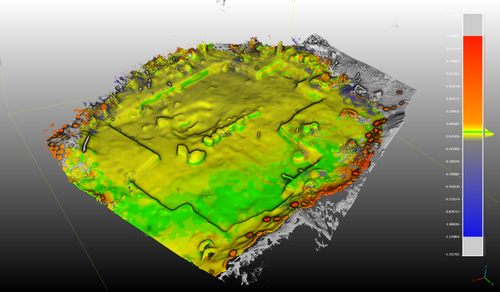
Towards a Mobile 3D Documentation Solution. Video Based Photogrammetry and iPhone 12 Pro as Fieldwork Documentation ToolsNikolai Paukkonen https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7954534The Potential of Mobile 3D Documentation using Video Based Photogrammetry and iPhone 12 ProRecommended by Ying Tung Fung based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann, Sebastian Hageneuer and 1 anonymous reviewerI am pleased to recommend the paper titled "Towards a Mobile 3D Documentation Solution. Video Based Photogrammetry and iPhone 12 Pro as Fieldwork Documentation Tools" for consideration and publication as a preprint (Paukkonen, 2023). The paper addresses a timely and relevant topic within the field of archaeology and offers valuable insights into the evolving landscape of 3D documentation methods. The advances in technology over the past decade have brought about significant changes in archaeological documentation practices. This paper makes a valuable contribution by discussing the emergence of affordable equipment suitable for 3D fieldwork documentation. Given the constraints that many archaeologists face with limited resources and tight timeframes, the comparison between photogrammetry based on a video captured by a DJI Osmo Pocket gimbal camera and iPhone 12 Pro LiDAR scans is of great significance. The research presented in the paper showcases a practical application of these new technologies in the context of a Finnish Early Modern period archaeological project. By comparing the acquisition processes and evaluating the accuracy, precision, ease of use, and time constraints associated with each method, the authors provide a comprehensive assessment of their potential for archaeological fieldwork. This practical approach is a commendable aspect of the paper, as it not only explores the technical aspects but also considers the practical implications for archaeologists on the ground. Furthermore, the paper appropriately addresses the limitations of these technologies, specifically highlighting their potential inadequacy for projects requiring a higher level of precision, such as Neolithic period excavations. This nuanced perspective adds depth to the discussion and provides a realistic portrayal of the strengths and limitations of the new documentation methods. In conclusion, the paper offers valuable insights into the future of 3D field documentation for archaeologists. The authors' thorough evaluation and practical approach make this study a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and professionals in the field. I believe that this paper would be an excellent addition to PCIArchaeology and would contribute significantly to the ongoing dialogue within the archaeological community. References Paukkonen, N. (2023) Towards a Mobile 3D Documentation Solution. Video Based Photogrammetry and iPhone 12 Pro as Fieldwork Documentation Tools, Zenodo, 8281263, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8281263 | Towards a Mobile 3D Documentation Solution. Video Based Photogrammetry and iPhone 12 Pro as Fieldwork Documentation Tools | Nikolai Paukkonen | <p>New affordable equipment suitable for 3D fieldwork documentation has appeared during the last years. Both photogrammetry and laser scanning are becoming affordable for archaeologists, who often work with limited resources and tight time constra... |  | Europe, Post-medieval, Remote sensing | Ying Tung Fung | 2023-05-21 21:32:33 | View | |
16 May 2022

Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool culturesAnnemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger https://osf.io/x8m4jOpen glossary for wood technologiesRecommended by Ruth Blasco based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé based on reviews by Paloma Vidal-Matutano, Oriol López-Bultó, Eva Francesca Martellotta and Laura Caruso Fermé
Wood is a widely available and versatile material, so it is not surprising that it has been a key resource throughout human history. However, it is more vulnerable to decomposition than other materials, and its direct use is only rarely recorded in prehistoric sites. Despite this, there are exceptions (e.g., [1-5] [6] and references therein), and indirect evidence of its use has been attested through use-wear analyses, residue analyses (e.g., [7]) and imprints on the ground (e.g., [8]). One interesting finding of note is that the technology required to make, for example, wooden spears was quite complex [9], leading some authors to propose that this type of tool production represented a cognitive leap for Pleistocene hominids [10]. Other researchers, however, have proposed that the production process for wooden tools could have been much easier than is currently thought [11]. Be that as it may, in recent years researchers have begun to approach wood remains systematically, developing analyses of natural and anthropogenic damage, often with the help of experimental reference samples. In this work, the authors elaborate a comprehensive glossary as a first step towards the understanding of the use of wood for technological purposes in different times and places, as there is still a general gap in the established nomenclature. Thus, this glossary is a synthesis and standardisation of analytical terms for early wood technologies that includes clear definitions and descriptions of traces from stone tool-using cultures, to avoid confusion in ongoing and future studies of wood tools. For this, the authors have carried out a detailed search of the current literature to select appropriate terms associated with additional readings that provide a wide, state-of-the-art description of the field of wood technology. An interesting point is that the glossary has been organised within a chaîne opératoire framework divided into categories including general terms and natural traces, and then complemented by an appendix of images. It is important to define the natural traces –understanding these as alterations caused by natural processes–because they can mask those modifications produced by other agents affecting both unmodified and modified wood before, during or after its human use. In short, the work carried out by Milks et al. [6] is an excellent and complete assessment and vital to the technological approach to wooden artifacts from archaeological contexts and establishing a common point for a standardised nomenclature. One of its particular strengths is that the glossary is a preprint that will remain open during the coming years, so that other researchers can continue to make suggestions and refinements to improve the definitions, terms and citations within it. [1] Oakley, K., Andrews, P., Keeley, L., Clark, J. (1977). A reappraisal of the Clacton spearpoint. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 43, 13-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0079497X00010343 [2] Thieme, H. (1997). Lower Palaeolithic hunting spears from Germany. Nature 385, 807-810. https://doi.org/10.1038/385807a0 [3] Schoch, W.H., Bigga, G., Böhner, U., Richter, P., Terberger, T. (2015). New insights on the wooden weapons from the Paleolithic site of Schöningen. Journal of Human Evolution 89, 214-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.08.004 [4] Aranguren, B., Revedin, A., Amico, N., Cavulli, F., Giachi, G., Grimaldi, S. et al. (2018). Wooden tools and fire technology in the early Neanderthal site of Poggetti Vecchi (Italy). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115, 2054-2059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716068115 [5] Rios-Garaizar, J., López-Bultó, O., Iriarte, E., Pérez-Garrido, C., Piqué, R., Aranburu, A., et al. (2018). A Middle Palaeolithic wooden digging stick from Aranbaltza III, Spain. PLoS ONE 13(3): e0195044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195044 [6] Milks, A. G., Lehmann, J., Böhner, U., Leder, D., Koddenberg, T., Sietz, M., Vogel, M., Terberger, T. (2022). Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures. Peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Archaeology https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/x8m4j [7] Nugent, S. (2006). Applying use-wear and residue analyses to digging sticks. Mem Qld Mus Cult Herit Ser 4, 89-105. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.890092331962439 [8] Allué, E., Cabanes, D., Solé, A., Sala, R. (2012). Hearth Functioning and Forest Resource Exploitation Based on the Archeobotanical Assemblage from Level J, in: i Roura E. (Ed.), High Resolution Archaeology and Neanderthal Behavior: Time and Space in Level J of Abric Romaní (Capellades, Spain). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3922-2_9 [9] Ennos, A.R., Chan, T.L. (2016). "Fire hardening" spear wood does slightly harden it, but makes it much weaker and more brittle. Biology Letters 12. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2016.0174 [10] Haidle, M.N. (2009). How to think a simple spear?, in: de Beaune S.A., Coolidge F.L., Wynn T. (Eds.), Cognitive Archaeology and Human Evolution. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 57-73. [11] Garofoli, D. (2015). A Radical Embodied Approach to Lower Palaeolithic Spear-making. Journal of Mind and Behavior 36, 1-26. | Wood technology: a Glossary and Code for analysis of archaeological wood from stone tool cultures | Annemieke Milks, Jens Lehmann, Utz Böhner, Dirk Leder, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Thomas Terberger | <p>The analysis of wood technologies created by stone tool-using cultures remains underdeveloped relative to the study of lithic and bone technologies. In recent years archaeologists have begun to approach wood assemblages systematically, developi... |  | Ancient Palaeolithic, Archaeobotany, Mesolithic, Middle Palaeolithic, Neolithic, Raw materials, Taphonomy, Traceology, Upper Palaeolithic | Ruth Blasco | 2021-12-01 12:18:53 | View | |
02 Feb 2024

Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley CollectionRaykovska Miglena, Jones Kristen, Klecherova Hristina, Alexandrov Stefan, Petkov Nikolay, Hristova Tanya, Ivanov Georgi https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8027548Out of the storeroom and into the virtualRecommended by Jitte Waagen based on reviews by Alicia Walsh and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Alicia Walsh and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Raykovska et al. 2023) discusses the digital documentation techniques and development of a virtual exhibition for artefacts retrieved from the necropolis of Baley, Bulgaria. The principal aim of this particular project is a solid one, trying to provide a solution to display artefacts that would otherwise remain hidden in museum storerooms. The paper describes how through a combination of 3D scanning and photogrammetry high quality 3D models have been produced, and provide content for an online virtual exhibition for the scientific community but also the larger public. It is a well-written and concise paper, in which the information on developed methods and techniques are transparently described, and various important aspects of digitization workflows, such as the importance of storing raw data, are addressed. The paper is a timely discussion on this subject, as strategies to develop digital artefact collections and what to do with those are increasingly being researched. Specifically, it discusses a workflow and its results, both in great detail. Although critical reflection on the process, goals and results from various perspectives would have been a valuable addition to the paper (cf., Jeffra 2020, Paardekoper 2019), it nonetheless provides a good practice example of how to approach the creation of a virtual museum. Those who consider projects concerning digital documentation of archaeological artefacts as well as the creation of virtual spaces to use those in for research, education or valorisation purposes would do well to read this paper carefully. References Jeffra, C., Hilditch, J., Waagen, J., Lanjouw, T., Stoffer, M., de Gelder, L., and Kim, M. J. (2020). Blending the Material and the Digital: A Project at the Intersection of Museum Interpretation, Academic Research, and Experimental Archaeology. The EXARC Journal, 2020(4). https://exarc.net/ark:/88735/10541 Paardekooper, R.P. (2019). Everybody else is doing it, so why can’t we? Low-tech and High-tech approaches in archaeological Open-Air Museums. The EXARC Journal, 2019(4). https://exarc.net/ark:/88735/10457/ Raykovska, M., Jones, K., Klecherova, H., Alexandrov, S., Petkov, N., Hristova, T., and Ivanov, G. (2023). Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley Collection. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10091870 | Implementing Digital Documentation Techniques for Archaeological Artifacts to Develop a Virtual Exhibition: the Necropolis of Baley Collection | Raykovska Miglena, Jones Kristen, Klecherova Hristina, Alexandrov Stefan, Petkov Nikolay, Hristova Tanya, Ivanov Georgi | <p>Over the past decade, virtual reality has been quickly growing in popularity across disciplines including the field of archaeology and cultural heritage. Despite numerous artifacts being uncovered each year by archaeological excavations around ... |  | Ceramics, Computational archaeology, Conservation/Museum studies | Jitte Waagen | 2023-06-12 14:02:44 | View | |
14 Nov 2023
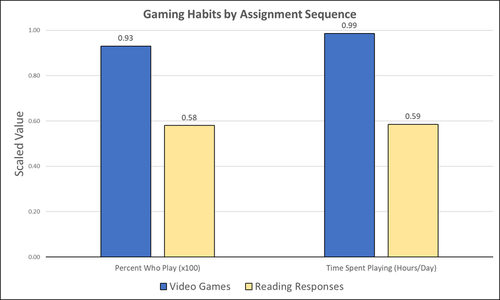
Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics ClassroomStephan, Robert https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286Learning with Archaeogaming? A study based on student feedbackRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Stephan 2023) is about the use of video games as a pedagogical tool in class. Instead of taking the perspective of a lecturer, the author seeks the student’s perspectives to evaluate the success of an interactive teaching method at the crossroads of history, archaeology, and classics. The paper starts with a literature review, that highlights the intensive use of video games among college students and high schoolers as well as the impact video games can have on learning about the past. The case study this paper is based on is made with the game Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey, which is introduced in the next part of the paper as well as previous works on the same game. The author then explains his method, which entailed the tasks students had to complete for a class in classics. They could either choose to play a video game or more classically read some texts. After the tasks were done, students filled out a 14-question-survey to collect data about prior gaming experience, assignment enjoyment, and other questions specific to the assignments. The results were based on only a fraction of the course participants (n=266) that completed the survey (n=26), which is a low number for doing statistical analysis. Besides some quantitative questions, students had also the possibility to freely give feedback on the assignments. Both survey types (quantitative answers and qualitative feedback) solely relied on the self-assessment of the students and one might wonder how representative a self-assessment is for evaluating learning outcomes. Both problems (size of the survey and actual achievements of learning outcomes) are getting discussed at the end of the paper, that rightly refers to its results as preliminary. I nevertheless think that this survey can help to better understand the role that video games can play in class. As the author rightly claims, this survey needs to be enhanced with a higher number of participants and a better way of determining the learning outcomes objectively. This paper can serve as a start into how we can determine the senseful use of video games in classrooms and what students think about doing so. References
Stephan, R. (2023). Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom, Zenodo, 8221286, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286
| Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom | Stephan, Robert | <p>This study assesses student feedback from the implementation of Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey as a teaching tool in a lower level, general education Classics course (CLAS 160B1 - Meet the Ancients: Gateway to Greece and Rome). In this course, which... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Mediterranean | Sebastian Hageneuer | Anonymous, Jeremiah McCall | 2023-08-07 16:45:31 | View |
14 Mar 2024
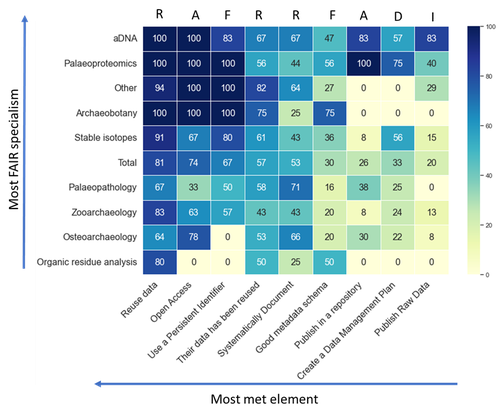
How FAIR is Bioarchaeological Data: with a particular emphasis on making archaeological science data ReusableLien-Talks, Alphaeus https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8139910FAIR data in bioarchaeology - where are we at?Recommended by Claudia Speciale based on reviews by Emma Karoune, Jan Kolar and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Emma Karoune, Jan Kolar and 2 anonymous reviewers
The increasing reliance on digital and big data in archaeology is pushing the scientific community more and more to reconsider their storing and use [1, 2]. Furthermore, the openness and findability in the way these data are shared represent a key matter for the growth of the discipline, especially in the case of bioarchaeology and archaeological sciences [3]. In this paper, [4] the author presents the result of a survey targeted on UK bioarchaeologists and then extended worldwide. The paper maintains the structure of a report as it was intended for the conference it was part of (CAA 2023, Amsterdam) but it represents the first public outcome of an inquiry on the bioarchaeological scientific community. A reflection on ourselves and our own practices. Are all the disciplines adhering to the same policies? Do any bioarchaeologist use the same protocols and formats? Are there any differences in between the domains? Is the Needs Analysis fulfilling the questions? The results, obtained through an accurate screening to avoid distortions, are creating an intriguing picture on the current state of "fairness" and highlighting how Institutions' rules and policies can and should indicate the correct workflow to follow. In the end, the wide application of the FAIR principles will contribute significantly to the growth of the disciplines and to create an environment where the users are not just contributors, but primary beneficiaries of the system. [1] Huggett j. (2020). Is Big Digital Data Different? Towards a New Archaeological Paradigm, Journal of Field Archaeology, 45:sup1, S8-S17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00934690.2020.1713281 [2] Nicholson C., Kansa S., Gupta N. and Fernandez R. (2023). Will It Ever Be FAIR?: Making Archaeological Data Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. Advances in Archaeological Practice 11 (1): 63-75. https://doi.org/10.1017/aap.2022.40 [3] Plomp E., Stantis C., James H.F., Cheung C., Snoeck C., Kootker L., Kharobi A., Borges C., Reynaga D.K.M., Pospieszny Ł., Fulminante, F., Stevens, R., Alaica, A. K., Becker, A., de Rochefort, X. and Salesse, K. (2022). The IsoArcH initiative: Working towards an open and collaborative isotope data culture in bioarchaeology. Data in brief, 45, p.108595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2022.108595 [4] Lien-Talks, A. (2024). How FAIR is Bioarchaeological Data: with a particular emphasis on making archaeological science data Reusable. Zenodo, 8139910, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8139910 | How FAIR is Bioarchaeological Data: with a particular emphasis on making archaeological science data Reusable | Lien-Talks, Alphaeus | <p>Bioarchaeology, which encompasses the study of ancient DNA, osteoarchaeology, paleopathology, palaeoproteomics, stable isotopes, and zooarchaeology, is generating an ever-increasing volume of data as a result of advancements in molecular biolog... |  | Bioarchaeology, Computational archaeology, Zooarchaeology | Claudia Speciale | 2023-07-12 19:12:44 | View | |
31 Jan 2024
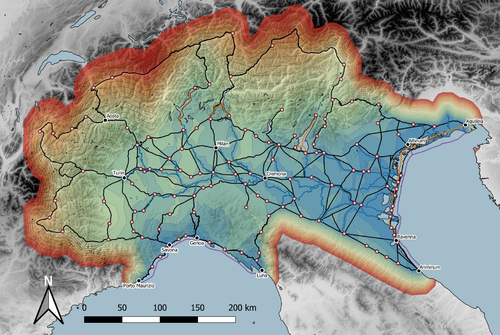
Rivers vs. Roads? A route network model of transport infrastructure in Northern Italy during the Roman periodJames Page https://zenodo.org/records/7971399Modelling Roman Transport Infrastructure in Northern ItalyRecommended by Andrew McLean based on reviews by Pau de Soto and Adam PažoutStudies of the economy of the Roman Empire have become increasingly interdisciplinary and nuanced in recent years, allowing the discipline to make great strides in data collection and importantly in the methods through which this increasing volume of data can be effectively and meaningfully analysed [see for example 1 and 2]. One of the key aspects of modelling the ancient economy is understanding movement and transport costs, and how these facilitated trade, communication and economic development. With archaeologists adopting more computational techniques and utilising GIS analysis beyond simply creating maps for simple visualisation, understanding and modelling the costs of traversing archaeological landscapes has become a much more fruitful avenue of research. Classical archaeologists are often slower to adopt these new computational techniques than others in the discipline. This is despite (or perhaps due to) the huge wealth of data available and the long period of time over which the Roman economy developed, thrived and evolved. This all means that the Roman Empire is a particularly useful proving ground for testing and perfecting new methodological developments, as well as being a particularly informative period of study for understanding ancient human behaviour more broadly. This paper by Page [3] then, is well placed and part of a much needed and growing trend of Roman archaeologists adopting these computational approaches in their research. Page’s methodology builds upon De Soto’s earlier modelling of transport costs [4] and applies it in a new setting. This reflects an important practice which should be more widely adopted in archaeology. That of using existing, well documented methodologies in new contexts to offer wider comparisons. This allows existing methodologies to be perfected and tested more robustly without reinventing the wheel. Page does all this well, and not only builds upon De Soto’s work, but does so using a case study that is particularly interesting with convincing and significant results. As Page highlights, Northern Italy is often thought of as relatively isolated in terms of economic exchange and transport, largely due to the distance from the sea and the barriers posed by the Alps and Apennines. However, in analysing this region, and not taking such presumptions for granted, Page quite convincingly shows that the waterways of the region played an important role in bringing down the cost of transport and allowed the region to be far more interconnected with the wider Roman world than previous studies have assumed. This article is clearly a valuable and important contribution to our understanding of computational methods in archaeology as well as the economy and transport network of the Roman Empire. The article utilises innovative techniques to model transport in an area of the Roman Empire that is often overlooked, with the economic isolation of the area taken for granted. Having high quality research such as this specifically analysing the region using the most current methodologies is of great importance. Furthermore, developing and improving methodologies like this allow for different regions and case studies to be analysed and directly compared, in a way that more traditional analyses simply cannot do. As such, Page has demonstrated the importance of reanalysing traditional assumptions using the new data and analyses now available to archaeologists. References [1] Brughmans, T. and Wilson, A. (eds.) (2022). Simulating Roman Economies: Theories, Methods, and Computational Models. Oxford. [2] Dodd, E.K. and Van Limbergen, D. (eds.) (2024). Methods in Ancient Wine Archaeology: Scientific Approaches in Roman Contexts. London ; New York. [3] Page, J. (2024). Rivers vs. Roads? A route network model of transport infrastructure in Northern Italy during the Roman period, Zenodo, 7971399, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7971399 [4] De Soto P (2019). Network Analysis to Model and Analyse Roman Transport and Mobility. In: Finding the Limits of the Limes. Modelling Demography, Economy and Transport on the Edge of the Roman Empire. Ed. by Verhagen P, Joyce J, and Groenhuijzen M. Springer Open Access, pp. 271–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04576-0_13 | Rivers vs. Roads? A route network model of transport infrastructure in Northern Italy during the Roman period | James Page | <p>Northern Italy has often been characterised as an isolated and marginal area during the Roman period, a region constricted by mountain ranges and its distance from major shipping lanes. Historians have frequently cited these obstacles, alongsid... |  | Classic, Computational archaeology | Andrew McLean | 2023-05-28 15:11:31 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Alain Queffelec
Marta Arzarello
Ruth Blasco
Otis Crandell
Luc Doyon
Sian Halcrow
Emma Karoune
Aitor Ruiz-Redondo
Philip Van Peer










