Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
13 Jan 2024

Dealing with post-excavation data: the Omeka S TiMMA web-databaseBastien Rueff https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7989904Managing Archaeological Data with Omeka SRecommended by Jonathan Hanna based on reviews by Electra Tsaknaki and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Electra Tsaknaki and 1 anonymous reviewer
Managing data in archaeology is a perennial problem. As the adage goes, every day in the field equates to several days in the lab (and beyond). For better or worse, past archaeologists did all their organizing and synthesis manually, by hand, but since the 1970s ways of digitizing data for long term management and analysis have gained increasing attention [1]. It is debatable whether this ever actually made things easier, particularly given the associated problem of sustainable maintenance and accessibility of the data. Many older archaeologists, for instance, still have reels and tapes full of data that now require a new form of archaeology to excavate (see [2] for an unrealized idea on how to solve this). Today, the options for managing digital archaeological data are limited only by one’s imagination. There are systems built specifically for archaeology, such as Arches [3], Ark [4], Codifi [5], Heurist [6], InTerris Registries [7], OpenAtlas [8], S-Archeo [9], and Wild Note [10], as well as those geared towards museum collections like PastPerfect [11] and CatalogIt [12], among others. There are also mainstream databases that can be adapted to archaeological needs like MS Access [13] and Claris FileMaker [14], as well as various web database apps that function in much the same way (e.g., Caspio [15], dbBee [16], Amazon's Simpledb [17], Sci-Note [18], etc.) — all with their own limitations in size, price, and utility. One could also write the code for specific database needs using pre-built frameworks like those in Ruby-On-Rails [19] or similar languages. And of course, recent advances in machine-learning and AI will undoubtedly bring new solutions in the near future. But let’s be honest — most archaeologists probably just use Excel. That's partly because, given all the options, it is hard to decide the best tool and whether its worth changing from your current system, especially given few real-world examples in the literature. Bastien Rueff’s new paper [20] is therefore a welcomed presentation on the use of Omeka S [21] to manage data collected for the Timbers in Minoan and Mycenaean Architecture (TiMMA) project. Omeka S is an open-source web-database that is based in PHP and MySQL, and although it was built with the goal of connecting digital cultural heritage collections with other resources online, it has been rarely used in archaeology. Part of the issue is that Omeka Classic was built for use on individual sites, but this has now been scaled-up in Omeka S to accommodate a plurality of sites. Some of the strengths of Omeka S include its open-source availability (accessible regardless of budget), the way it links data stored elsewhere on the web (keeping the database itself lean), its ability to import data from common file types, and its multi-lingual support. The latter feature was particularly important to the TiMAA project because it allowed members of the team (ranging from English, Greek, French, and Italian, among others) to enter data into the system in whatever language they felt most comfortable. However, there are several limitations specific to Omeka S that will limit widespread adoption. Among these, Omeka S apparently lacks the ability to export metadata, auto-fill forms, produce summations or reports, or provide basic statistical analysis. Its internal search capabilities also appear extremely limited. And that is not to mention the barriers typical of any new software, such as onerous technical training, questionable long-term sustainability, or the need for the initial digitization and formatting of data. But given the rather restricted use-case for Omeka S, it appears that this is not a comprehensive tool but one merely for data entry and storage that requires complementary software to carry out common tasks. As such, Rueff has provided a review of a program that most archaeologists will likely not want or need. But if one was considering adopting Omeka S for a project, then this paper offers critical information for how to go about that. It is a thorough overview of the software package and offers an excellent example of its use in archaeological practice.
[1] Doran, J. E., and F. R. Hodson (1975) Mathematics and Computers in Archaeology. Harvard University Press. [2] Snow, Dean R., Mark Gahegan, C. Lee Giles, Kenneth G. Hirth, George R. Milner, Prasenjit Mitra, and James Z. Wang (2006) Cybertools and Archaeology. Science 311(5763):958–959. [3] https://www.archesproject.org/ [4] https://ark.lparchaeology.com/ [5] https://codifi.com/ [6] https://heuristnetwork.org/ [7] https://www.interrisreg.org/ [8] https://openatlas.eu/ [9] https://www.skinsoft-lab.com/software/archaelogy-collection-management [10] https://wildnoteapp.com/ [11] https://museumsoftware.com/ [12] https://www.catalogit.app/ [13] https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/access [14] https://www.claris.com/filemaker/ [15] https://www.caspio.com/ [16] https://www.dbbee.com/ [17] https://aws.amazon.com/simpledb/ [18] https://www.scinote.net/ [19] https://rubyonrails.org/ [20] Rueff, Bastien (2023) Dealing with Post-Excavation Data: The Omeka S TiMMA Web-Database. peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://zenodo.org/records/7989905 [21] https://omeka.org/
| Dealing with post-excavation data: the Omeka S TiMMA web-database | Bastien Rueff | <p>This paper reports on the creation and use of a web database designed as part of the TiMMA project with the Content Management System Omeka S. Rather than resulting in a technical manual, its goal is to analyze the relevance of using Omeka S in... |  | Buildings archaeology, Computational archaeology | Jonathan Hanna | 2023-05-31 12:16:25 | View | |
10 Jan 2024
Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3DFlorian Linsel, Jan Philipp Bullenkamp & Hubert Mara https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8296269A valuable contribution to automated analysis of palaeolithic artefactsRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Lutz Schubert and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Lutz Schubert and 1 anonymous reviewer
In this paper (Linsel/Bullenkamp/Mara 2024), the authors propose an automatic system for scar-ridge-pattern detection on palaeolithic artefacts based on Morse Theory. Scare-Ridge pattern recognition is a process that is usually done manually while creating a drawing of the object itself. Automatic systems to detect scars or ridges exist, but only a small amount of them is utilizing 3D data. In addition to the scar-ridges detection, the authors also experiment in automatically detecting the operational sequence, the temporal relation between scars and ridges. As a result, they can export a traditional drawing as well as graph models displaying the relationships between the scars and ridges. After an introduction to the project and the practice of documenting palaeolithic artefacts, the authors explain their procedure in automatising the analysis of scars and ridges as well as their temporal relation to each other on these artefacts. To illustrate the process, an open dataset of lithic artefacts from the Grotta di Fumane, Italy, was used and 62 artefacts selected. To establish a Ground Truth, the artefacts were first annotated manually. The authors then continue to explain in detail each step of the automated process that follows and the results obtained. In the second part of the paper, the results are presented. First the results of the segmentation process shows that the average percentage of correctly labelled vertices is over 91%, which is a remarkable result. The graph modelling however shows some more difficulties, which the authors are aware of. To enhance the process, the authors rightfully aim to include datasets of experimental archaeology in the future. They also aim to develop a way of detecting the operational sequence automatically and precisely. This paper has great potential as it showcases exactly what Digital and Computational Archaeology is about: The development of new digital methods to enhance the analysis of archaeological data. While this procedure is still in development, the authors were able to present a valuable contribution to the automatization of analytical archaeology. By creating a step towards the machine-readability of this data, they also open up the way to further steps in machine learning within Archaeology. BibliographyLinsel, F., Bullenkamp, J. P., and Mara, H. (2024). Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3D, Zenodo, 8296269, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8296269 | Linking Scars: Topology-based Scar Detection and Graph Modeling of Paleolithic Artifacts in 3D | Florian Linsel, Jan Philipp Bullenkamp & Hubert Mara | <p>Motivated by the concept of combining the archaeological practice of creating lithic artifact drawings with the potential of 3D mesh data, our goal in this project is not only to analyze the shape at the artifact level, but also to enable a mor... | Computational archaeology, Europe, Lithic technology, Upper Palaeolithic | Sebastian Hageneuer | 2023-09-01 23:03:59 | View | ||
08 Jan 2024

Comparing summed probability distributions of shoreline and radiocarbon dates from the Mesolithic Skagerrak coast of NorwayIsak Roalkvam, Steinar Solheim https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/2f8phTaking the Reverend Bayes to the seaside: Improving Norwegian Mesolithic shoreline dating with advanced statistical approachesRecommended by Felix Riede based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe paper entitled “Comparing summed probability distributions of shoreline and radiocarbon dates from the Mesolithic Skagerrak coast of Norway” by Isak Roalkvam and Steinar Solheim (2024) sheds new light on the degree to which shoreline dating may be used as a reliable chronological and palaeodemographic proxy in the Mesolthic of southern Norway. Based on geologically motivated investigations of eustatic and isostatic sea-level changes, shoreline dating has long been used as a method to date archaeological sites in Scandinavia, not least in Norway (e.g., Bjerck 2008; Astrup 2018). Establishing reliable sea-level curves requires much effort and variations across regions may be substantial. While this topic has seen a great deal of attention in Norway specifically, many purely geological questions remain. In addition, dating archaeological sites by linking their elevation to previously established seal-level curves relies strongly on the foundational assumption that such sites were in fact shore-bound. Given the strong contrast between terrestrial and marine productivity in high-latitude regions such as Norway, this assumption per se is not unreasonable. It is very likely that the sea has played a decisive role in the lives of Stone Age peoples throughout (Persson et al. 2017), just as it has in later periods here. However, many confounding factors relating to both taphonomy and human behaviour are also likely to have loosened the shore/site relationship. Systematic variations driven by cultural norms about settlement location, mobility, as well as factors such as shelter construction, fuel use and a range of other possible factors could variously have impacted the validity or at least the precision of shoreline dating. By developing a new methodology for handling and assessing a large number of shoreline dated sites, Roalkvam and Solheim use state-of-the-art Bayesian statistical methods to compare shoreline and radiocarbon dates as proxies for population activity. The probabilistic treatment of shoreline dates in this way is novel, and the divergences between the two data sets are interpreted by the authors in light of specific behavioural, cultural, and demographic changes. Many of the peaks and troughs observed in these time-series may be interpreted in light of long-observed cultural transitions while others may relate to population dynamics now also visible in palaeogenomic analyses (Günther et al. 2018; Manninen et al. 2021). Overall, this paper makes an innovative and fresh contribution to the use of shoreline dating in Norwegian archaeology, specifically by articulating it with recent developments in Open Science and data-driven approaches to archaeological questions (Marwick et al. 2017). References Astrup, P. M. 2018. Sea-Level Change in Mesolithic Southern Scandinavia : Long- and Short-Term Effects on Society and the Environment. Aarhus: Aarhus University Press. Bjerck, H. B. 2008. Norwegian Mesolithic Trends: A Review. In Mesolithic Europe, edited by Geoff Bailey and Penny Spikins, 60–106. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Günther, T., Malmström, H., Svensson, E. M., Omrak, A., Sánchez-Quinto, F., Kılınç, G. M., Krzewińska, M. et al. 2018. Population Genomics of Mesolithic Scandinavia: Investigating Early Postglacial Migration Routes and High-Latitude Adaptation. PLOS Biology 16 (1): e2003703. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2003703 Manninen, M. A., Damlien, H., Kleppe, J. I., Knutsson, K., Murashkin, A., Niemi, A. R., Rosenvinge, C. S. and Persson, P. 2021. First Encounters in the North: Cultural Diversity and Gene Flow in Early Mesolithic Scandinavia. Antiquity 95 (380): 310–28. https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2020.252 Marwick, B., d’Alpoim Guedes, J. A., Barton, C. M., Bates, L. A., Baxter, M., Bevan, A., Bollwerk, E. A. et al. 2017. Open Science in Archaeology. The SAA Archaeological Record 17 (4): 8–14. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/72n8g Persson, P., Riede, F., Skar, B., Breivik, H. M. and Jonsson, L. 2017. The Ecology of Early Settlement in Northern Europe: Conditions for Subsistence and Survival. Sheffield: Equinox. Roalkvam, I. and Solheim, S. (2024). Comparing summed probability distributions of shoreline and radiocarbon dates from the Mesolithic Skagerrak coast of Norway, SocArXiv, 2f8ph, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/2f8ph | Comparing summed probability distributions of shoreline and radiocarbon dates from the Mesolithic Skagerrak coast of Norway | Isak Roalkvam, Steinar Solheim | <p>By developing a new methodology for handling and assessing a large number of shoreline dated sites, this paper compares the summed probability distribution of radiocarbon dates and shoreline dates along the Skagerrak coast of south-eastern Norw... |  | Computational archaeology, Dating, Europe, Mesolithic, Paleoenvironment | Felix Riede | 2023-09-26 16:43:29 | View | |
05 Jan 2024
The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A Website Approach to Archaeological Typology.Giorgio Buccellati and Marilyn Kelly-Buccellati https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7743834Roster and Lexicon – A Radical Digital-Dialogical Approach to Questions of Typology and Categorization in ArchaeologyRecommended by Shumon Tobias Hussain , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Dominik Hagmann and 2 anonymous reviewers
“The density of types and the dignity of the fragment. A website approach to archaeological typology” by G. Buccellati and M. Kelly-Buccellati (1) is a contribution to the rapidly growing literature on digital approaches to archaeological data management, expertly showcasing the significant theoretical and epistemological impetus of such work. The authors offer a conceptually lucid discussion of key concepts in archaeological ordering practices surrounding the longstanding tension between so-called ‘etic’ and ‘emic’ approaches, thereby providing a thorough systematic of how to think through sameness and difference in the context of voluminous digital archaeological data. As a point of departure, the authors reconsider the relationship between archaeological fragments – spatiotemporally bounded artefacts and features – and their larger meaning-giving totality as the primary locus of archaeological knowledge. Typology can then be said to serve this overriding quest to resolve the conflict between parts and wholes, as the parts themselves are never sufficient to render the whole but the whole remains elusive without reference to the parts. Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati here make an interesting point about the importance to register the globality of the archaeological record – that is, literally everything encountered in the soil – without making any prior choices as to what supposedly matters and what not. The distinctiveness of the archaeological enterprise, according to them, indeed consists of the circumstance that merely disconnected fragments come to the attention of archaeologists and the only objective data that can be attained, because of this, are about the situated location of fragments in the ground and their relation to other fragments – what they call ‘emplacement’. This, we would add, includes the relationship of fragments with human observers and the employed methods of excavation as observation. As the authors say: “[i]t is in this sense that the fragments are natively digital: they are atoms that do not cohere into a typological whole”. The systematic exploration of how the so recovered fragments may be re-articulated is then essentially the goal of archaeological categorization and typology but these practices can only ever be successful if the whole context of original ‘emplacement’ is carefully taken into consideration. This reconstruction of the fundamental epistemological situation archaeology finds itself in leads the authors to a general rejection of ‘more’ vs. ‘less’ objective or even subjective ordering practices as such qualifications tend to miss the point. What matters is to enable the flexible and scalable confrontation of isolated archaeological fragments, to do experiment with and test different part-whole relations and their possible knowledge contributions. It is no coincidence that the authors insist on a dynamical approach to ordering practices and type-thinking in archaeology here, which in many ways comes often very close to the general conceptual orientation philosopher Stephen C. Pepper (2) has called ‘organicism’ – a preoccupation of resolving the tension between heterogeneous fragments and coherent wholes without losing sight of the specificity of each single fragment. In the view of organicist thinkers, and the authors seem to share this recognition, to take complexity seriously means to centre the dialectics between fragments and wholes in their entirety. This notion is directly reflected in the authors’ interesting definition of ‘big data’ in archaeology as a multi-layered and multi-referential system of organizing the totality of observations of emplacement (the Global record). Based on this broader exposition, Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati make some perceptive and noteworthy observations vis-à-vis the aforementioned emic-etic distinction that has caused so much archaeological confusion and debate (3–6). To begin with, emic and etic designate different systemic logics of organizing observable sameness and difference. Emic systems are closed and foreground the idea of the roster, they recognize only a limited set of types whose identity depends on relative differences. Etic systems, on the other hand, are in principle open (and even open-ended) and rely on the notion of the lexicon; they enlist a principally endless repertoire of traits, types and sub-types (classes and sub-classes may be added to this list of course). Difference in etic systems is moreover defined according to some general standards that appear to eclipse the standards of the system itself. Etic systems therefore tend to advocate supposedly universal principles of how to establish similarity vs. difference, although, in reality, there is substantial debate as to what these principles may be or whether such endeavour is a useful undertaking. In the wild, both etic and emic systems of ordering and categorization are of course encountered in the plural but etic systems deploy external standards of order while emic systems operate via internal standards. An interesting observation by the authors in this context is that archaeological reasoning in relation to sameness and difference is almost never either exclusively etic or exclusively emic. The simple reason is that any grouping of fragments according to technological (means/modes of production) or functional considerations (use-wear, tool design, relation between form and function) based on empirical evidence is typically already infused by emic standards. The classic example from the analysis of archaeological pottery is ware groups, which reference the nexus of technological know-how and concrete practices, and which rely, in a given context, on internal, relative differentiations between the respective observed practices. Yet ignoring these distinctions would sideline significant knowledge on the past. These discussions are refreshing as they may indicate that ordering practices – when considered as an end in themselves – misconstrue the archaeological process as static and so advocate for categories, classes, and types to be carved out before any serious analysis can begin. It could in fact be argued that in doing so, they merely construct a new closed system, then emic by definition. Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati propose an alternative without discarding the intuition that ordering archaeological materials is conditional to the inferential and knowledge-production process: they propose that typologies should be treated as arguments. Moreover, the sort of argument they have in mind is to a lesser extent ‘formal-logical’ but instead emphatically ‘dialogical’ in nature, as such argumentative form helps to combat the inherent static-ness of ordering practices the authors criticize, and so discloses a radically dynamic approach to the undertaking of fragment-whole matching. The organicist inclination to preserve ‘the dignity of fragments’ while working towards their resolution in attendant wholes and sub-wholes further gives rise to the idea that such ‘native digital fragments’ must be brought into systematic conversation with one another, acknowledging the involved complexity. To this end, the authors frame ordering work and typo-praxis as a ‘digital discourse’ and ask what the conditions and possibilities for such discourse are and how it can be facilitated. It is here that they put forward the idea that the webpage may provide an ideal epistemic model system to promote the preservation of emplaced archaeological fragments while simultaneously promoting multistranded and multi-context explorations of fragment coherence and articulation. The website enables unique forms of exploration and engagement with data and new arguments escaping the fixity of the analogue-printed which dominates current archaeological practice. Similar experiences were for example made in the context of Gardin’s ‘logicism’, leading to broadly comparable attempts to overcome the analogue with more dynamic, HTML/web-based forms of data presentation, exploration and discussion (7, 8). As such, Buccellati and Kelly-Buccellati table a range of fresh arguments for re-thinking typology beyond and with text at the same time, to enable ‘dynamic reading’ of fragment-whole relationships in an increasingly digital world. Their proposal comes thereby close to what has been termed ‘deep mapping’ in the context of critical cartographies and other spatially-inclined scholarship in the Anglophone world (9, 10). Deep maps seek to transcend the epistemological limitations of 2D-representations of spatiality on traditional maps and introduce different layers of informational depth and heterogeneity, which, similarly to the living digital webpage proposed by the authors, can be continuously extended and revised and which may also greatly promote multidisciplinary and team-based research endeavours. In the same spirit as the authors’ ‘digital discourse’, deep mapping draws attention to the knowledge potential of bringing together the heterogeneous, the etic and the emic, and to pay more attention to ‘multiplanar’ and ‘multilinear’ relationships as well as the associated relations of relations. This proposal to deploy types and typology in general as dynamic arguments is linked to the ambition to contribute to and work on the narrativization of the archaeological record without tacit (and often unconscious) conceptual pre-subscription, countering typologies that remain largely in the abstract and so have contributed to the creeping anonymity of the past.
Bibliography 1. Buccellati, G. and Kelly-Buccellati, M. (2023). The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A website approach to archaeological typology, Zenodo, 7743834, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7743834. 2. Pepper, S C. (1972). World hypotheses: a study in evidence, 7. print (Univ. of California Press). 3. Hayden, B. (1984). Are Emic Types Relevant to Archaeology? Ethnohistory 31, 79–92. https://doi.org/10.2307/482057 4. Tostevin, G. B. (2011). An Introduction to the Special Issue: Reduction Sequence, Chaîne Opératoire, and Other Methods: The Epistemologies of Different Approaches to Lithic Analysis. PaleoAnthropology, 293−296. https://www.doi.org/10.4207/PA.2011.ART59 5. Tostevin, G. B. (2013). Seeing lithics: a middle-range theory for testing for cultural transmission in the pleistocene (Oakville, CT: Oxbow Books). 6. Boissinot, P. (2015). Qu’est-ce qu’un fait archéologique? (Éditions EHESS). https://doi.org/10.4000/lectures.19921 7. Gardin, J.-C. and Roux, V. (2004). The Arkeotek Project: a European Network of Knowledge Bases in the Archaeology of Techniques. Archeologia e Calcolatori 15, 25–40. 8. Husi, P. (2022). La céramique médiévale et moderne du bassin de la Loire moyenne, chrono-typologie et transformation des aires culturelles dans la longue durée (6e—17e s.) (FERACF). 9. Bodenhamer, D. J., Corrigan, J. and Harris, T. M. (2015). Deep Maps and Spatial Narratives (Indiana University Press). 10. Gillings, M., Hacigüzeller, P. and Lock, G. R. (2019). Re-mapping archaeology: critical perspectives, alternative mappings (Routledge).
| The Density of Types and the Dignity of the Fragment. A Website Approach to Archaeological Typology. | Giorgio Buccellati and Marilyn Kelly-Buccellati | <p>Typology hinges on categorization, and the two main axes of categorization are the roster and the lexicon: the first defines elements from an -emic, and the second from an (e)-tic point of view, i. e., as a closed or an open system, respectivel... |  | Antiquity, Theoretical archaeology | Shumon Tobias Hussain | 2023-03-17 09:11:46 | View | |
05 Jan 2024
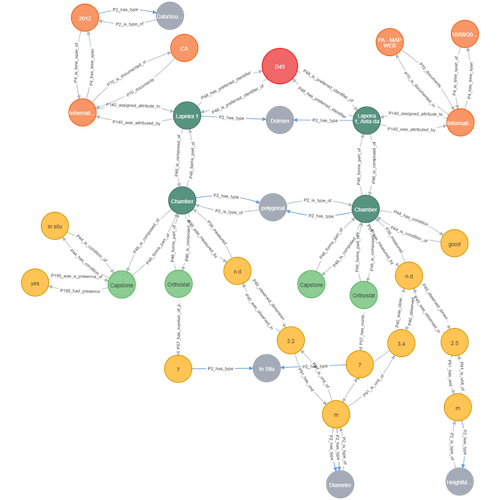
Transforming the CIDOC-CRM model into a megalithic monument property graphAriele Câmara, Ana de Almeida, João Oliveira https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981230Informative description of a project implementing a CIDOC-CRM based native graph database for representing megalithic informationRecommended by Isto Huvila based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe paper “Transforming the CIDOC-CRM model into a megalithic monument property graph” describes an interesting endeavour of developing and implementing a CIDOC-CRM based knowledge graph using a native graph database (Neo4J) to represent megalithic information (Câmara et al. 2023). While there are earlier examples of using native graph databases and CIDOC-CRM in diverse heritage contexts, the present paper is useful addition to the literature as a detailed description of an implementation in the context of megalithic heritage. The paper provides a demonstration of a working implementation, and guidance for future projects. The described project is also documented to an extent that the paper will open up interesting opportunities to compare the approach to previous and forthcoming implementations. The same applies to the knowledge graph and use of CIDOC-CRM in the project. Readers interested in comparing available technologies and those who are developing their own knowledge graphs might have benefited of a more detailed description of the work in relation to the current state-of-the-art and what the use of a native graph database in the built-heritage contexts implies in practice for heritage documentation beyond that it is possible and it has potentially meaningful performance-related advantages. While also the reasons to rely on using plain CIDOC-CRM instead of extensions could have been discussed in more detail, the approach demonstrates how the plain CIDOC-CRM provides a good starting point to satisfy many heritage documentation needs. As a whole, the shortcomings relating to positioning the work to the state-of-the-art and reflecting and discussing design choices do not reduce the value of the paper as a valuable case description for those interested in the use of native graph databases and CIDOC-CRM in heritage documentation in general and the documentation of megalithic heritage in particular. ReferencesCâmara, A., de Almeida, A. and Oliveira, J. (2023). Transforming the CIDOC-CRM model into a megalithic monument property graph, Zenodo, 7981230, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7981230 | Transforming the CIDOC-CRM model into a megalithic monument property graph | Ariele Câmara, Ana de Almeida, João Oliveira | <p>This paper presents a method to store information about megalithic monuments' building components as graph nodes in a knowledge graph (KG). As a case study we analyse the dolmens from the region of Pavia (Portugal). To build the KG, information... |  | Computational archaeology | Isto Huvila | 2023-05-29 13:46:49 | View | |
02 Jan 2024
Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenariosDiamanti, Eleni; Yip, Mauhing; Stahl, Annette; Ødegård, Øyvind https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305098Beyond Deep Blue: Underwater robotics, simulations and archaeologyRecommended by Daniel Carvalho based on reviews by Marco Moderato and 1 anonymous reviewerDiamanti et al. (2024) is a significant contribution to the field of underwater robotics and their use in archaeology, with an innovative approach to some major problems in the deployment of said technologies. It identifies issues when it comes to approaching Underwater Cultural Heritage (UCH) sites and does so through an interest in the combination of data, maneuverability, and the interpretation provided by the instruments that archaeologists operate. The article's motives are clear: it is not enough to find the means to reach these sites, but rather is fundamental to take a step forward in methodology and how we can safeguard certain aspects of data recovery with robust mission planning. To this end, the article does not fail to highlight previous contributions, in an intertwined web of references that demonstrate the marked evolution of the use of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Autonomous Surface Vehicles (ASVs), which are growing exponentially in use (see Kapetanović et al. 2020). It should be emphasized that the notion of ‘aquatic environment’ used here is quite broad and is not limited to oceanic or maritime environments, which allows for a larger perspective on distinct technologies that proliferate in underwater archaeology. There is also a relevant discussion on the typologies of sensors and how these autonomous vehicles obtain their data, where are debated Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and LiDAR systems. Thus, the authors of this article propose the creation of a model that acquires data through simulations, which allows for a better understanding of what a real mission presupposes in the field. Their tripartite method - pre-mission planning; mission plan and post-mission plan - offers a performing algorithm that simplifies and provides reliability to all the parts of the intervention. The use of real cases to create simulation models allows for a substantial approximation to common practice in underwater environments. And yet, the article is at its most innovative status when it combines all the elements it sets out to explore. It could simply focus on the methodological or planning component, on obtaining data, or on theoretical problems. But it goes further, which makes this approach more complete and of interest to the archaeological community. By not taking any part as isolated, the problems and possible solutions arising from the course of the mission are carried over from one parameter to another, where details are worked upon and efficiency goals are set. One of the most significant cases is the tuning of ocean optics in aquatic environments according to the idiosyncracies of real cases (Diamanti et al. 2024: 8), a complex endeavor but absolutely necessary in order to increase the informative potential of the simulation. The exploration of various data capture models is also welcome, for the purposes of comparison and adaptation on a case-by-case basis. The brief theoretical reflection offered at the end of the article dwells in all these points and problematizes the difference between terrestrial and aquatic archaeology. In fact, the distinction does not only exist in the technical component, as although it draws in theoretical elements from archaeology that is carried out on land (see Krieger 2012 for this matter), the problems and interpretations are shaped by different factors and therefore become unique (Diamanti et al 2024: 15). The future, according to the authors, lies in increasing the autonomy of these vehicles so that the human element does not have to make decisions in a systematic way. It is in that note, and in order for that path to become closer to reality, that we strongly recommend this article for publication, in conjunction with the comments of the reviewers. We hope that its integrated approach, which brings together methods, theories and reflections, can become a broader modus operandi within the field of underwater robotics applied to archaeology. References: Diamanti, E., Yip, M., Stahl, A. and Ødegård, Ø. (2024). Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenarios, Zenodo, 8305098, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8305098 Kapetanović, N., Vasilijević, A., Nađ, Đ., Zubčić, K., and Mišković, N. (2020). Marine Robots Mapping the Present and the Past: Unraveling the Secrets of the Deep. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3902. MDPI AG. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/rs12233902 Krieger, W. H. (2012). Theory, Locality, and Methodology in Archaeology: Just Add Water? HOPOS: The Journal of the International Society for the History of Philosophy of Science, 2(2), 243–257. https://doi.org/10.1086/666956
| Advancing data quality of marine archaeological documentation using underwater robotics: from simulation environments to real-world scenarios | Diamanti, Eleni; Yip, Mauhing; Stahl, Annette; Ødegård, Øyvind | <p>This paper presents a novel method for visual-based 3D mapping of underwater cultural heritage sites through marine robotic operations. The proposed methodology addresses the three main stages of an underwater robotic mission, specifically the ... | Computational archaeology, Remote sensing | Daniel Carvalho | 2023-08-31 16:03:10 | View | ||
11 Dec 2023
A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in EuropeFelix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus, Damian Stefański, Hans Vandendriessche, Shumon T. Hussain https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587Questioning Final Palaeolithic and early Mesolithic cultural taxonomy with a data-driven statistical approachRecommended by Anaïs Vignoles based on reviews by Dirk Leder and 2 anonymous reviewersCultural taxonomies are an essential tool for archaeologists working with prehistoric material cultures as they have historically been used to create the basic analytical units for studying cultural evolution through time (de Mortillet, 1883 ; Breuil, 1913). This approach has its limits as the taxonomic units are essentially etic constructions, i.e., they are defined in a cultural context exterior to the one that produced the material culture on which they are based (e.g., Pesesse, 2019). But to approach questions related to cultural evolution, one has to define archaeological units with clear geographic and chronological delineations in order to be compared synchronically and diachronically (e.g., Willey and Philips, 1958). In « A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolitic/Earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe », F. Riede and colleagues propose a novel and interesting approach to question the end of the Palaeolithic and beginning of the Mesolithic’s « named archaeological cultures » (NACs) analytical pertinence (Riede et al., 2023). In this particular context, NACs are indeed very numerous (n = 86) and result from complex and regional research histories. It seems thus pertinent to question the extent to which the said NACs chronological and geographic patterns result from past cultural diversity and evolution, and are not artefacts of research. To do so, the authors adopted a data-driven approach that they describe in detail in the paper. First, they gathered an European data base of lithic tool-kit composition, blade and bladelet technology and armature morphology at 350 key sites considered representative of NACs, dated between 15 and 11 ka (Hussain et al., 2023). These data were then analyzed using geometric morphometrics and a set of statisticaal tests in order to 1) test the coherence of these taxonomic units, and 2) test the chronological change in artefact shape variation. The authors conclude that the data set is partially biased by reasearch practices and histories, as their data-driven approach has only partially replicated traditional NACs for the european Late Palaeolithic/Early Mesolithic. However, their analysis of armature shape evolution has shown a tendency to diversification overtime, a pattern that was already observed in more « traditional » approaches. This study is, in my opinion, an excellent contribution for a significant step in macro-regional approaches to the archaeological record: defining discrete archaeological units that serve as a basis for subsequent analyses aimed at delineating cultural evolutionary processes. The authors propose a carefully designed and statistically grounded procedure in order to achieve these definitions in the most replicable and explicit possible manner. Taking advantage of drawings as a primary source of information is also very original despite several limitations of this approach (such as the necessary selection of most typical artefacts to be represented, the incompleteness of data publication or the difficulty to access all published work across such a large geographic area). The results of the study are convincing enough to allow the authors to discuss the pertinence of European Late Paleo/Early Mesolithic NACs, the potential epistemological and historical factors that could affect this taxonomic framework, as well as to give more weight to the traditional hypothesis of lithic cultural diversification towards the end of the Pleistocene/beginning of the Holocene in Europe. I would also like to underline the authors’ important efforts to ensure transparence and replicability of their study, as well as the accessibility of the data, thanks to extensive supplementary data and a data paper describing their data set in detail. Anaïs L. Vignoles References Breuil, H. (1913). Les subdivisions du paléolithique supérieur et leur signification. In Congrès international d’anthropologie et d’archéologie préhistoriques - compte-rendu de la XIVème session, tome 1:165‑238. Genève: Imprimerie Albert Kündig. Hussain, S. T., Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D. and Vandendriessche, H. (2023). A Pan-European Dataset Revealing Variability in Lithic Technology, Toolkits, and Artefact Shapes ~15-11 Kya. Scientific Data 10 (1): 593. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02500-9. Mortillet, G. (1883). Le Préhistorique, antiquité de l’homme. Reinwald. Paris. Pesesse, D. (2019). Analyser un silex, le façonner à nouveau ? Sur certains usages de la chaîne opératoire au Paléolithique supérieur. Techniques & culture, no 71: 74‑77. https://doi.org/10.4000/tc.11321. Riede, F., Matzig, D. N., Biard, M., Crombé, P., Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, J., Fontana, F., Groß, D., Hess, T., Langlais, M., Mevel, L., Mills, W., Moník, M., Naudinot, N., Posch, C., Rimkus, T., Stefański, D., Vandendriessche, H. and Hussain, S. T. (2023). A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe, Zenodo, 8195587., ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8195587 Willey, G. R. and Phillips, P. (1958). Method and Theory in American Archaeology. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press. | A meta-analysis of Final Palaeolithic/earliest Mesolithic cultural taxonomy and evolution in Europe | Felix Riede, David N. Matzig, Miguel Biard, Philippe Crombé, Javier Fernández-Lopéz de Pablo, Federica Fontana, Daniel Groß, Thomas Hess, Mathieu Langlais, Ludovic Mevel, William Mills, Martin Moník, Nicolas Naudinot, Caroline Posch, Tomas Rimkus,... | <p>Archaeological systematics, together with spatial and chronological information, are commonly used to infer cultural evolutionary dynamics in the past. For the study of the Palaeolithic, and particularly the European Final Palaeolithic and earl... |  | Computational archaeology, Europe, Lithic technology, Mesolithic, Upper Palaeolithic | Anaïs Vignoles | 2023-07-29 16:06:17 | View | |
02 Dec 2023

Research perspectives and their influence for typologiesEnrico Giannichedda https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7322855Complexity and Purpose – A Pragmatic Approach to the Diversity of Archaeological Classificatory Practice and TypologyRecommended by Shumon Tobias Hussain , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak , Felix Riede and Sébastien Plutniak based on reviews by Ulrich Veit, Martin Hinz, Artur Ribeiro and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Ulrich Veit, Martin Hinz, Artur Ribeiro and 1 anonymous reviewer
“Research perspectives and their influence for typologies” by E. Giannichedda (1) is a contribution to the upcoming volume on the role of typology and type-thinking in current archaeological theory and praxis edited by the recommenders. Taking a decidedly Italian perspective on classificatory practice grounded in what the author dubs the “history of material culture”, Giannichedda offers an inventory of six divergent but overall complementary modes of ordering archaeological material: i) chrono-typological and culture-historical, ii) techno-anthropological, iii) social, iv) socio-economic and v) cognitive. These various lenses broadly align with similarly labeled perspectives on the archaeological record more generally. According to the author, they lend themselves to different ways of identifying and using types in archaeological work. Importantly, Giannichedda reminds us that no ordering practice is a neutral act and typologies should not be devised for their own sake but because we have specific epistemic interests. Even though this view is certainly not shared by everyone involved in the broader debate on the purpose and goal of systematics, classification, typology or archaeological taxonomy (2–4), the paper emphatically defends the long-standing idea that ordering practices are not suitable to elucidate the structure and composition of reality but instead devise tools to answer certain questions or help investigate certain dimensions of complex past realities. This position considers typologies as conceptual prosthetics of knowing, a view that broadly resonates with what is referred to as epistemic instrumentalism in the philosophy of science (5, 6). Types and type-work should accordingly reflect well-defined means-end relationships. Based on the recognition of archaeology as part of an integrated “history of material culture” rooted in a blend of continental and Anglophone theories, Giannichedda argues that type-work should pay attention to relevant relations between various artefacts in a given historical context that help further historical understanding. Classificatory practice in archaeology – the ordering of artefactual materials according to properties – must thus proceed with the goal of multifaceted “historical reconstruction in mind”. It should serve this reconstruction, and not the other way around. By drawing on the example of a Medieval nunnery in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, Giannichedda explores how different goals of classification and typo-praxis (linked to i-v; see above) foreground different aspects, features, and relations of archaeological materials and as such allow to pinpoint and examine different constellations of archaeological objects. He argues that archaeological typo-praxis, for this reason, should almost never concern itself with isolated artefacts but should take into account broader historical assemblages of artefacts. This does not necessarily mean to pay equal attention to all available artefacts and materials, however. To the contrary, in many cases, it is necessary to recognize that some artefacts and some features are more important than others as anchors grouping materials and establishing relations with other objects. An example are so-called ‘barometer objects’ (7) or unique pieces which often have exceptional informational value but can easily be overlooked when only shared features are taken into consideration. As Giannichedda reminds us, considering all objects and properties equally is also a normative decision and does not render ordering less subjective. The archaeological analysis of types should therefore always be complemented by an examination of variants, even if some of these variants are idiosyncratic or even unique. A type, then, may be difficult to define universally. In total, “Research perspectives and their influence for typologies” emphasizes the need for “elastic” and “flexible” approaches to archaeological types and typologies in order to effectively respond to the manifold research interests cultivated by archaeologists as well as the many and complex past realities they face. Complexity is taken here to indicate that no single research perspective and associated mode of ordering can adequately capture the dimensionality and richness of these past realities and we can therefore only benefit from multiple co-existing ways of grouping and relating archaeological artefacts. Different logics of grouping may simply reveal different aspects of these realities. As such, Giannichedda’s proposal can be read as a formulation of the now classic pluralism thesis (8–11) – that only a plurality of ways of ordering and interrelating artefacts can unlock the full suite of relationships within historical assemblages archaeologists are interested in.
Bibliography 1. Giannichedda, E. (2023). Research perspectives and their influence for typologies, Zenodo, 7322855, ver. 9 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7322855 2. Dunnell, R. C. (2002). Systematics in Prehistory, Illustrated Edition (The Blackburn Press, 2002). 3. Reynolds, N. and Riede, F. (2019). House of cards: cultural taxonomy and the study of the European Upper Palaeolithic. Antiquity 93, 1350–1358. https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2019.49 4. Lyman, R. L. (2021). On the Importance of Systematics to Archaeological Research: the Covariation of Typological Diversity and Morphological Disparity. J Paleo Arch 4, 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-021-00077-6 5. Van Fraassen, B. C. (2002). The empirical stance (Yale University Press). 6. Stanford, P. K. (2006). Exceeding Our Grasp: Science, History, and the Problem of Unconceived Alternatives (Oxford University Press). https://doi.org/10.1093/0195174089.001.0001 7. Radohs, L. (2023). Urban elite culture: a methodological study of aristocracy and civic elites in sea-trading towns of the southwestern Baltic (12th-14th c.) (Böhlau). 8. Kellert, S. H., Longino, H. E. and Waters, C. K. (2006). Scientific pluralism (University of Minnesota Press). 9. Cat, J. (2012). Essay Review: Scientific Pluralism. Philosophy of Science 79, 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1086/664747 10. Chang, H. (2012). Is Water H2O?: Evidence, Realism and Pluralism (Springer Netherlands). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-3932-1 11. Wylie, A. (2015). “A plurality of pluralisms: Collaborative practice in archaeology” in Objectivity in Science, (Springer), pp. 189–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14349-1_10
| Research perspectives and their influence for typologies | Enrico Giannichedda | <p>This contribution opens with a brief reflection on theoretical archaeology and practical material classification activities. Following this, the various questions that can be asked of artefacts to be classified will be briefly addressed. Questi... |  | Theoretical archaeology | Shumon Tobias Hussain | 2022-11-10 20:14:52 | View | |
23 Nov 2023
Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publicationSophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497Sharing Research Code in ArchaeologyRecommended by James Allison based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Thomas Rose, Joe Roe and 1 anonymous reviewer
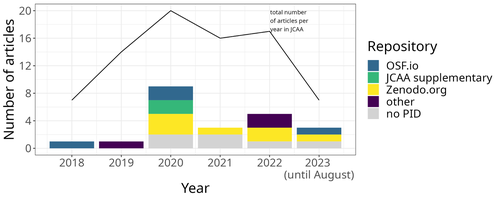
The paper “Percolation Package – From Script Sharing to Package Publication” by Sophie C. Schmidt and Simon Maddison (2023) describes the development of an R package designed to apply Percolation Analysis to archaeological spatial data. In an earlier publication, Maddison and Schmidt (2020) describe Percolation Analysis and provide case studies that demonstrate its usefulness at different spatial scales. In the current paper, the authors use their experience collaborating to develop the R package as part of a broader argument for the importance of code sharing to the research process. The paper begins by describing the development process of the R package, beginning with borrowing code from a geographer, refining it to fit archaeological case studies, and then collaborating to further refine and systematize the code into an R package that is more easily reusable by other researchers. As the review by Joe Roe noted, a strength of the paper is “presenting the development process as it actually happens rather than in an idealized form.” The authors also include a section about the lessons learned from their experience. Moving on from the anecdotal data of their own experience, the authors also explore code sharing practices in archaeology by briefly examining two datasets. One dataset comes from “open-archaeo” (https://open-archaeo.info/), an on-line list of open-source archaeological software maintained by Zack Batist. The other dataset includes articles published between 2018 and 2023 in the Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology. Schmidt and Maddison find that these two datasets provide contrasting views of code sharing in archaeology: many of the resources in the open-archaeo list are housed on Github, lack persistent object identifiers, and many are not easily findable (other than through the open-archaeo list). Research software attached to the published articles, on the other hand, is more easily findable either as a supplement to the published article, or in a repository with a DOI. The examination of code sharing in archaeology through these two datasets is preliminary and incomplete, but it does show that further research into archaeologists’ code-writing and code-sharing practices could be useful. Archaeologists often create software tools to facilitate their research, but how often? How often is research software shared with published articles? How much attention is given to documentation or making the software usable for other researchers? What are best (or good) practices for sharing code to make it findable and usable? Schmidt and Maddison’s paper provides partial answers to these questions, but a more thorough study of code sharing in archaeology would be useful. Differences among journals in how often they publish articles with shared code, or the effects of age, gender, nationality, or context of employment on attitudes toward code sharing seem like obvious factors for a future study to consider. Shared code that is easy to find and easy to use benefits the researchers who adopt code written by others, but code authors also have much to gain by sharing. Properly shared code becomes a citable research product, and the act of code sharing can lead to productive research collaborations, as Schmidt and Maddison describe from their own experience. The strength of this paper is the attention it brings to current code-sharing practices in archaeology. I hope the paper will also help improve code sharing in archaeology by inspiring more archaeologists to share their research code so other researchers can find and use (and cite) it. References Maddison, M.S. and Schmidt, S.C. (2020). Percolation Analysis – Archaeological Applications at Widely Different Spatial Scales. Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology, 3(1), p.269–287. https://doi.org/10.5334/jcaa.54 Schmidt, S. C., and Maddison, M. S. (2023). Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication, Zenodo, 7966497, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7966497 | Percolation Package - From script sharing to package publication | Sophie C Schmidt; Simon Maddison | <p>In this paper we trace the development of an R-package starting with the adaptation of code from a different field, via scripts shared between colleagues, to a published package that is being successfully used by researchers world-wide. Our aim... |  | Computational archaeology | James Allison | 2023-05-24 15:40:15 | View | |
14 Nov 2023
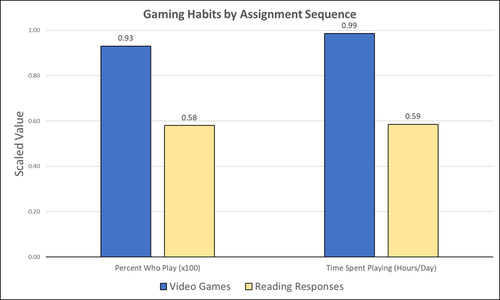
Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics ClassroomStephan, Robert https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286Learning with Archaeogaming? A study based on student feedbackRecommended by Sebastian Hageneuer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jeremiah McCall and 1 anonymous reviewer
This paper (Stephan 2023) is about the use of video games as a pedagogical tool in class. Instead of taking the perspective of a lecturer, the author seeks the student’s perspectives to evaluate the success of an interactive teaching method at the crossroads of history, archaeology, and classics. The paper starts with a literature review, that highlights the intensive use of video games among college students and high schoolers as well as the impact video games can have on learning about the past. The case study this paper is based on is made with the game Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey, which is introduced in the next part of the paper as well as previous works on the same game. The author then explains his method, which entailed the tasks students had to complete for a class in classics. They could either choose to play a video game or more classically read some texts. After the tasks were done, students filled out a 14-question-survey to collect data about prior gaming experience, assignment enjoyment, and other questions specific to the assignments. The results were based on only a fraction of the course participants (n=266) that completed the survey (n=26), which is a low number for doing statistical analysis. Besides some quantitative questions, students had also the possibility to freely give feedback on the assignments. Both survey types (quantitative answers and qualitative feedback) solely relied on the self-assessment of the students and one might wonder how representative a self-assessment is for evaluating learning outcomes. Both problems (size of the survey and actual achievements of learning outcomes) are getting discussed at the end of the paper, that rightly refers to its results as preliminary. I nevertheless think that this survey can help to better understand the role that video games can play in class. As the author rightly claims, this survey needs to be enhanced with a higher number of participants and a better way of determining the learning outcomes objectively. This paper can serve as a start into how we can determine the senseful use of video games in classrooms and what students think about doing so. References
Stephan, R. (2023). Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom, Zenodo, 8221286, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Archaeology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8221286
| Student Feedback on Archaeogaming: Perspectives from a Classics Classroom | Stephan, Robert | <p>This study assesses student feedback from the implementation of Assassin’s Creed: Odyssey as a teaching tool in a lower level, general education Classics course (CLAS 160B1 - Meet the Ancients: Gateway to Greece and Rome). In this course, which... |  | Antiquity, Classic, Mediterranean | Sebastian Hageneuer | Anonymous, Jeremiah McCall | 2023-08-07 16:45:31 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Alain QUEFFELEC
Nelson ALMEIDA
Johan ARIF
Marta ARZARELLO
Ruth BLASCO
Matthew COLLINS
Otis CRANDELL
Luc DOYON
Alice LEPLONGEON
Florent RIVALS
Aitor RUIZ-REDONDO










